|
Generalization (learning)
Generalization is the concept that humans, other animals, and artificial neural networks use past learning in present situations of learning if the conditions in the situations are regarded as similar. The learner uses generalized patterns, principles, and other similarities between past experiences and novel experiences to more efficiently navigate the world.Banich, M. T., Dukes, P., & Caccamise, D. (2010). Generalization of knowledge: Multidisciplinary perspectives. Psychology Press. For example, if a person has learned in the past that every time they eat an apple, their throat becomes itchy and swollen, they might assume they are allergic to all fruit. When this person is offered a banana to eat, they reject it upon assuming they are also allergic to it through generalizing that all fruits cause the same reaction. Although this generalization about being allergic to all fruit based on experiences with one fruit could be correct in some cases, it may not be correct in all. Both po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Networks
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning (also respondent conditioning and Pavlovian conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent Stimulus (physiology), stimulus (e.g. food, a puff of air on the eye, a potential rival) is paired with a neutral stimulus (e.g. the sound of a Triangle (musical instrument), musical triangle). The term ''classical conditioning'' refers to the process of an automatic, conditioned response that is paired with a specific stimulus. It is essentially equivalent to a signal. The Russian physiology, physiologist Ivan Pavlov studied classical conditioning with detailed experiments with dogs, and published the experimental results in 1897. In the study of digestion, Pavlov observed that the experimental dogs salivated when fed red meat. Pavlovian conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified, either by reinforcement or by Punishment (psychology), punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are components of the hippocampal formation located in the limbic system. The hippocampus plays important roles in the Memory consolidation, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables Navigation#Navigation in spatial cognition, navigation. In humans, and other primates the hippocampus is located in the archicortex, one of the three regions of allocortex, in each cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere with direct neural projections to, and reciprocal indirect projections from the neocortex. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
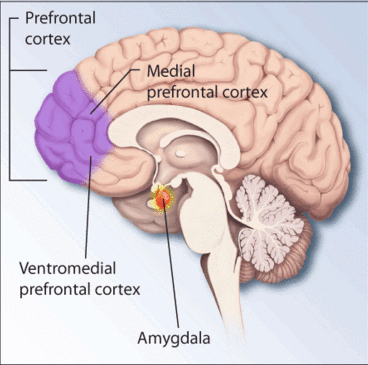
Amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In Primate, primates, it is located lateral and medial, medially within the temporal lobes. It consists of many nuclei, each made up of further subnuclei. The subdivision most commonly made is into the Basolateral amygdala, basolateral, Central nucleus of the amygdala, central, cortical, and medial nuclei together with the intercalated cells of the amygdala, intercalated cell clusters. The amygdala has a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, decision-making, and emotions, emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression). The amygdala was first identified and named by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure Thirteen Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei have been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Albert Experiment
The Little Albert experiment was an unethical study that mid-20th century psychologists interpret as evidence of classical conditioning in humans. The study is also claimed to be an example of stimulus generalization although reading the research report demonstrates that fear did not generalize by color or tactile qualities. It was carried out by John B. Watson and his graduate student, Rosalie Rayner, at Johns Hopkins University. The results were first published in the February 1920 issue of the '' Journal of Experimental Psychology''. After observing children in the field, Watson hypothesized that the fearful response of children to loud noises is an innate unconditioned response. He wanted to test the notion that by following the principles of the procedure now known as "classical conditioning", he could use this unconditioned response to condition a child to fear a distinctive stimulus that normally would not be feared by a child (in this case, furry objects). However, he a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster, traffic collision, or other threats on a person's life or well-being. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress (medicine), distress to Psychological trauma, trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event and can include triggers such as misophonia. Young children are less likely to show distress, but instead may express their memories through play (activity), play. Most people who experience traumatic events do not develop PTSD. People who experience interpersonal violence such as rape, other sexual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physical and cognitive symptoms, such as restlessness, irritability, easy fatigue, difficulty concentrating, increased heart rate, chest pain, abdominal pain, and a variety of other symptoms that may vary based on the individual. In casual discourse, the words ''anxiety'' and ''fear'' are often used interchangeably. In clinical usage, they have distinct meanings; anxiety is clinically defined as an unpleasant emotional state for which the cause is either not readily identified or perceived to be uncontrollable or unavoidable, whereas fear is clinically defined as an emotional and physiological response to a recognized external threat. The umbrella term 'anxiety disorder' refers to a number of specific disorders that include fears (phobias) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maladaptation
In evolution, a maladaptation ( /ˌmælædæpˈteɪʃən/) is a trait that is (or has become) more harmful than helpful, in contrast with an adaptation, which is more helpful than harmful. All organisms, from bacteria to humans, display maladaptive and adaptive traits. Like adaptation, maladaptation may be viewed as occurring over geological time, or within the lifetime of one individual or a group. Maladaptation can arise when adaptations to environmental challenges have unintended harmful effects by either decreasing the current fitness of the organism or creating new risks which may decrease survivability. This could be caused by changes in trait distribution from genetic loading, exogenous environmental changes in the fitness landscape, or feedback in eco-plasticity, altering the fitness landscape. It can also signify an adaptation that, whilst reasonable at the time, has become less and less suitable and more of a problem or hindrance in its own right, as time goes on. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procedural Memory
Procedural memory is a type of implicit memory ( unconscious, long-term memory) which aids the performance of particular types of tasks without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Procedural memory guides the processes we perform, and most frequently resides below the level of conscious awareness. When needed, procedural memories are automatically retrieved and utilized for execution of the integrated procedures involved in both cognitive and motor skills, from tying shoes, to reading, to flying an airplane. Procedural memories are accessed and used without the need for conscious control or attention. Procedural memory is created through ''procedural learning'', or repeating a complex activity over and over again until all of the relevant neural systems work together to automatically produce the activity. Implicit procedural learning is essential for the development of any motor skill or cognitive activity. History The difference between procedural and declarat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrimination Learning
Discrimination learning is defined in psychology as the ability to respond differently to different stimuli. This type of learning is used in studies regarding operant and classical conditioning. Operant conditioning involves the modification of a behavior by means of reinforcement or punishment. In this way, a discriminative stimulus will act as an indicator to when a behavior will persist and when it will not. Classical conditioning involves learning through association when two stimuli are paired together repeatedly. This conditioning demonstrates discrimination through specific micro-instances of reinforcement and non-reinforcement. This phenomenon is considered to be more advanced than learning styles such as generalization and yet simultaneously acts as a basic unit to learning as a whole. The complex and fundamental nature of discrimination learning allows for psychologists and researchers to perform more in-depth research that supports psychological advancements. Research on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-term Memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recited. The duration of short-term memory (absent rehearsal or active maintenance) is estimated to be on the order of seconds. The commonly cited capacity of 7 items, found in Miller's Law, has been superseded by 4±1 items. In contrast, long-term memory holds information indefinitely. Short-term memory is not the same as working memory, which refers to structures and processes used for temporarily storing and manipulating information. Stores The idea of separate memories for short-term and long-term storage originated in the 19th century. A model of memory developed in the 1960s assumed that all memories are formed in one store and transfer to other stores after a small period of time. This model is referred to as the "modal model", mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |