|
Gamma Diversity
In ecology, gamma diversity (γ-diversity) is the total species diversity in a landscape. The term was introduced by R. H. WhittakerWhittaker, R. H. (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 279–338. together with the terms alpha diversity (α-diversity) and beta diversity (β-diversity). Whittaker's idea was that the total species diversity in a landscape (γ) is determined by two different things, the mean species diversity in sites at a more local scale (α) and the differentiation among those sites (β). According to this reasoning, alpha diversity and beta diversity constitute independent components of gamma diversity: γ = α × β : Scale considerations The area or landscape of interest may be of very different sizes in different situations, and no consensus has been reached on what spatial scales are appropriate to quantify gamma diversity. It has therefore been proposed that the definition of gamma diversity does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Abundance
In ecology, local abundance is the relative representation of a species in a particular ecosystem. It is usually measured as the number of individuals found per sample. The ratio of abundance of one species to one or multiple other species living in an ecosystem is referred to as relative species abundances. Both indicators are relevant for computing biodiversity. A variety of sampling methods are used to measure abundance. For larger animals, these may include spotlight counts, track counts and roadkill counts, as well as presence at monitoring stations. In many plant communities the abundances of plant species are measured by plant cover, i.e. the relative area covered by different plant species in a small plot. Abundance is in simplest terms usually measured by identifying and counting every individual of every species in a given sector. It is common for the distribution of species to be skewed so that a few species take up the bulk of individuals collected. Relative spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement Of Biodiversity
A variety of objective means exist to empirically measure biodiversity. Each measure relates to a particular use of the data, and is likely to be associated with the variety of genes. Biodiversity is commonly measured in terms of taxonomic richness of a geographic area over a time interval. In order to calculate biodiversity, species evenness, species richness, and species diversity are to be obtained first. ''Species evenness'' is the relative number of individuals of each species in a given area. ''Species richness'' is the number of species present in a given area. ''Species diversity'' is the relationship between species evenness and species richness. There are many ways to measure biodiversity within a given ecosystem. However, the two most popular are Shannon-Weaver diversity index, commonly referred to as Shannon diversity index, and the other is Simpsons diversity index. Although many scientists prefer to use Shannon's diversity index simply because it takes into account sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Biodiversity
Global biodiversity is the measure of biodiversity on planet Earth and is defined as the total variability of life forms. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 2 million to 1 trillion, but most estimates are around 11 million species or fewer. About 1.74 million species were databased as of 2018, and over 80 percent have not yet been described. The total amount of DNA base pairs on Earth, as a possible approximation of global biodiversity, is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon). In other related studies, around 1.9 million extant species are believed to have been described currently, but some scientists believe 20% are synonyms, reducing the total valid described species to 1.5 million. In 2013, a study published in Science estimated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
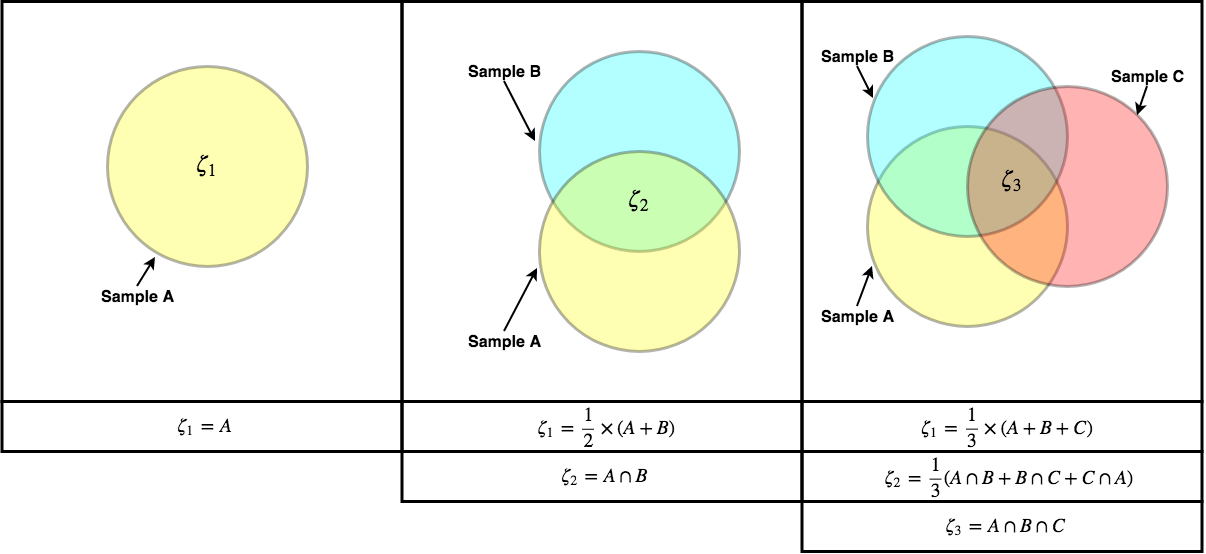
Zeta Diversity
In ecology, zeta diversity (ζ-diversity), first described in 2014, measures the degree of overlap in the type of taxa present between a set of observed communities. It was developed to provide a more generalized framework for describing various measures of diversity, and can also be used to test various hypotheses pertaining to biogeography. Zeta diversity as an extension of other measures of diversity α-diversity The most basic measure of community diversity, alpha diversity (α-diversity), can be described as the average number of distinct taxonomic groups (e.g. unique genera or operational taxonomic unit) present, independent of their abundances, on a per sample basis. In the ζ-diversity framework this can be described as ζ1, the number of unique taxa present in one sample. β-diversity Beta diversity In ecology, beta diversity (β-diversity or true beta diversity) is the ratio between regional and local species diversity. The term was introduced by Robert Whittaker ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Diversity
In ecology, beta diversity (β-diversity or true beta diversity) is the ratio between regional and local species diversity. The term was introduced by Robert Whittaker (ecologist), R. H. Whittaker together with the terms alpha diversity (α-diversity) and gamma diversity (γ-diversity). The idea was that the total species diversity in a landscape (γ) is determined by two different things: the mean species diversity at the local level (α) and the differentiation among local sites (β). Other formulations for beta diversity include "absolute species turnover", "Whittaker's species turnover" and "proportional species turnover". Whittaker proposed several ways of quantifying differentiation, and subsequent generations of ecologists have invented more. As a result, there are now many defined types of beta diversity. Some use ''beta diversity'' to refer to any of several indices related to compositional heterogeneity. Confusion is avoided by using distinct names for other formulations.T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Diversity
In ecology, alpha diversity (α-diversity) is the mean species diversity in a site at a local scale. The term was introduced by R. H. WhittakerWhittaker, R. H. (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 279–338. Whittaker, R. H. (1972). Evolution and Measurement of Species Diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251. together with the terms beta diversity (β-diversity) and gamma diversity (γ-diversity). Whittaker's idea was that the total species diversity in a landscape (gamma diversity) is determined by two different things, the mean species diversity in sites at a more local scale (alpha diversity) and the differentiation among those sites (beta diversity). Scale considerations Both the area or landscape of interest and the sites within it may be of very different sizes in different situations, and no consensus has been reached on what spatial scales are appropriate to quantify alpha diversity. It has therefore been proposed that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Whittaker (ecologist)
Robert Harding Whittaker (December 27, 1920 – October 20, 1980) was an American plant ecologist, active from the 1950s to the 1970s. He was the first to propose the five kingdom taxonomic classification of the world's biota into the Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, and Monera in 1969.Hagen, Joel B. (2012)Five kingdoms, more or less: Robert Whittaker and the broad classification of organisms. ''BioScience'', 62 (1): 67-74. He also proposed the Whittaker Biome Classification, which categorized biome types upon two abiotic factors: temperature and precipitation. He proposed the concepts of Alpha diversity, Beta diversity, and Gamma diversity.Whittaker, R. H. (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 279–338. Whittaker, R. H. (1972). Evolution and Measurement of Species Diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251. Whittaker was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1974, received the Ecological Society of America's Eminent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Richness
Species richness is the number of different species represented in an community (ecology), ecological community, landscape or region. Species richness is simply a count of species, and it does not take into account the Abundance (ecology), abundances of the species or their Relative species abundance, relative abundance distributions. Species richness is sometimes considered synonymous with species diversity, but the formal metric species diversity takes into account both species richness and species evenness. Sampling considerations Depending on the purposes of quantifying species richness, the individuals can be Forest inventory#Simple random sampling, selected in different ways. They can be, for example, trees found in an forest inventory, inventory plot, birds observed from a monitoring point, or beetles collected in a pitfall trap. Once the set of individuals has been defined, its species richness can be exactly quantified, provided the species-level Taxonomy (biology), taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |