|
Galaxy Filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of galactic superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can commonly reach 50 to 80 megaparsecs ()—with the largest found to date being the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall at around in length—and form the boundaries between voids. Due to the accelerating expansion of the universe, the individual clusters of gravitationally bound galaxies that make up galaxy filaments are moving away from each other at an accelerated rate; in the far future they will dissolve. Galaxy filaments form the cosmic web and define the overall structure of the observable universe. Discovery Discovery of structures larger than superclusters began in the late 1980s. In 1987, astronomer R. Brent Tully of the University of Hawaii's Institute of Astronomy identified what he called the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex. The CfA2 Great Wall was discovered in 1989, followed by the Sloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma Supercluster
The Coma Supercluster (SCl 117) is a nearby supercluster of galaxies that includes the Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) and the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367). Located 300 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Coma Berenices, it is in the center of the Great Wall and a part of the Coma Filament. It is roughly spherical, about 98 mega light-years in diameter, and contains more than 3,000 galaxies. Although the extent of the Coma Cluster has been understood since around 1900, it took several decades for the existence of the supercluster to be discovered; this was due to the very large physical separation (around 21 Mpc) and angular separation (around 20°) between the Coma and Leo Clusters. In 1977, further analysis of the redshifts of hundreds of galaxies within the supercluster confirmed that these were all part of a larger group of clusters. Despite this, it was still one of the first superclusters to be discovered, and helped astronomers understand the large scale structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sculptor Wall
The Sculptor Wall is a superstructure of galaxies ( "wall of galaxies") relatively near to the Milky Way Galaxy (redshift In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and increase in frequency and e ... of approximately z=0.03), also known as the Sculptor superclusters. (slices 8 and 10 under SGH) The superstructure is also called the Southern Great Wall, the Great Southern Wall, or just the Southern Wall, in reference to the Northern Great Wall. The structure is 8000 km/s long (where km/s indicates the rate of expansion between two objects at the extents of a superstructure), 5000 km/s wide, 1000 km/s deep, in ''redshift space'' dimensions. Because these structures are so large, it is convenient to estimate their size by measuring their redshift; using a value of 67.8 for Hubble's constant, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma Cluster
The Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) is a large cluster of galaxies that contains over 1,000 identified galaxies. Along with the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367), it is one of the two major clusters comprising the Coma Supercluster. It is located in and takes its name from the constellation Coma Berenices. The cluster's mean distance from Earth is 99 Mpc (321 million light years). Its ten brightest spiral galaxies have apparent magnitudes of 12–14 that are observable with amateur telescopes larger than 20 cm. The central region is dominated by two supergiant elliptical galaxies: NGC 4874 and NGC 4889. The cluster is within a few degrees of the north galactic pole on the sky. Most of the galaxies that inhabit the central portion of the Coma Cluster are ellipticals. Both dwarf and giant ellipticals are found in abundance in the Coma Cluster. Cluster members As is usual for clusters of this richness, the galaxies are overwhelmingly elliptical and S0 galaxies, with only a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tip Of The Red-giant Branch
Tip of the red-giant branch (TRGB) is a primary distance indicator used in astronomy. It uses the luminosity of the brightest red-giant-branch stars in a galaxy as a standard candle to gauge the distance to that galaxy. It has been used in conjunction with observations from the Hubble Space Telescope to determine the relative motions of the Local Cluster of galaxies within the Local Supercluster. Ground-based, 8-meter-class telescopes like the VLT are also able to measure the TRGB distance within reasonable observation times in the local universe. Method The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (HR diagram) is a plot of stellar luminosity versus surface temperature for a population of stars. During the core hydrogen burning phase of a Sun-like star's lifetime, it will appear on the HR diagram at a position along a diagonal band called the main sequence. When the hydrogen at the core is exhausted, energy will continue to be generated by hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
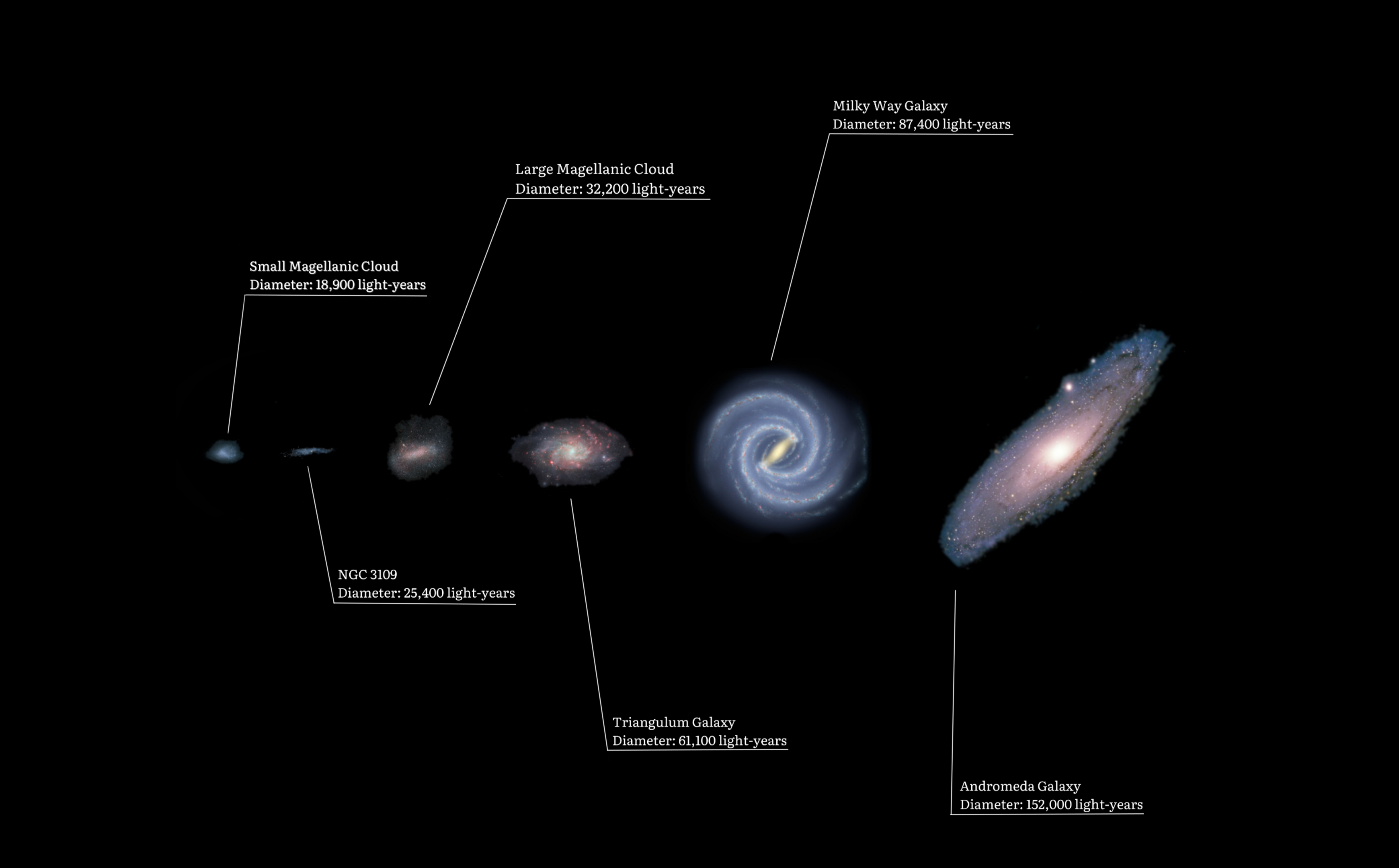
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a " dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda and the Milky Way galaxies, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noah Brosch
Noah Brosch (Hebrew: נח ברוש; born 1948) is an Israeli astronomer, astrophysicist and space researcher. Biography Noah Brosch was born in Bucharest (Romania) in 1948 and immigrated with his family to Israel in 1963. Brosch studied at Tel Aviv University (BSc 1975 and MSc 1977) and at the Leiden University (PhD 1983). He is a tenured Principal Research Associate (degree equivalent to Research Associate Professor) at Tel Aviv University and served as Director of the Wise Observatory from 2000 to 2006 and again from 2007 to 2010. He is a member of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and from 2009 to 2012 served as the Vice-President of its Division XI (Space and High-Energies Astrophysics) of the IAU. Noah Brosch has been active in the field of space ultraviolet (UV) astronomy, as one of the founding members of the Network for Ultraviolet Astrophysics (NUVA), a pan-European network set-up to identify the needs of the astronomical community in the UV spectral domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx–Ursa Major Supercluster
Lynx–Ursa Major Supercluster is a supercluster A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in tu ... in the Lynx–Ursa Major Region. It was discovered by Giovanelli and Haynes in 1982. The supercluster is connected to Lynx–Ursa Major Filament. References Galaxy superclusters {{supercluster-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx–Ursa Major Filament
Lynx–Ursa Major Filament (LUM Filament) is a galaxy filament. The filament is connected to and separate from the Lynx–Ursa Major Supercluster Lynx–Ursa Major Supercluster is a supercluster A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (w .... References Galaxy filaments Large-scale structure of the cosmos {{physical-cosmology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major Filament
Ursa Major Filament is a galaxy filament. The filament is connected to the CfA Homunculus, a portion of the filament forms a portion of the "leg" of the Homunculus.''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'', Volume 121, Issue 2, pp. 445-472. "Photometric Properties of Kiso Ultraviolet-Excess Galaxies in the Lynx-Ursa Major Region" ''04/1999'' See also * Abell catalogue * Large-scale structure of the universe * Supercluster A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in tu ... References Galaxy filaments Large-scale structure of the cosmos {{physical-cosmology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |