|
Four-carbon Molecule
Four-carbon molecules are based on a skeleton made from four carbon atoms. They may be in a chain, branched chains, cycles or even bicyclic compounds Hydrocarbons that include four atoms are: *butane C4H10 *isobutane C4H10 *but-1-ene C4H8 * but-2-ene C4H8 * but-1-yne C4H6 * but-2-yne C4H6 *isobutylene C4H8 *butadiene C4H6 * 1,2-butadiene C4H6 * vinylacetylene C4H4 *diacetylene C4H2 * butatriene C4H4 *cyclobutane C4H8 *cyclobutene C4H6 * cyclobutyne C4H4 *cyclobutadiene C4H4 * methylenecyclopropene C4H4 * bicyclobutane C4H6 * 1-bicyclobutene C4H4 * Δ1,3-bicyclobutene C4H4 * propalene C4H2 * methylcyclopropane C4H8 * 1-methylcyclopropene C4H6 * 3-methylcyclopropene C4H6 * methylenecyclopropane C4H6 * 3-methylcyclopropyne C4H4 * methylenecyclopropyne C4H2 *tetrahedrane Tetrahedrane is a hypothetical platonic hydrocarbon with chemical formula and a tetrahedral structure. The molecule would be subject to considerable angle strain and has not been synthesized as of 2021. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, C and C being stable, while C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of all known life. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen. The atoms of carbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclobutyne
Cyclobutyne (C4H4) is a hydrocarbon molecule containing a triple bond within a four carbon atom ring. This cycloalkyne is very unstable due to its high ring strain and has not been isolated in the pure state. However, osmium coordination complexes containing cyclobutyne have been synthesized. See also *Cyclobutene Cyclobutene is a cycloalkene. It is of interest in research but currently has no practical applications. It is a colorless easily condensed gas. A modern synthesis involves the 2-step dehydration of cyclobutanol. The compound was first prepared ... References Alkynes Four-membered rings {{hydrocarbon-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
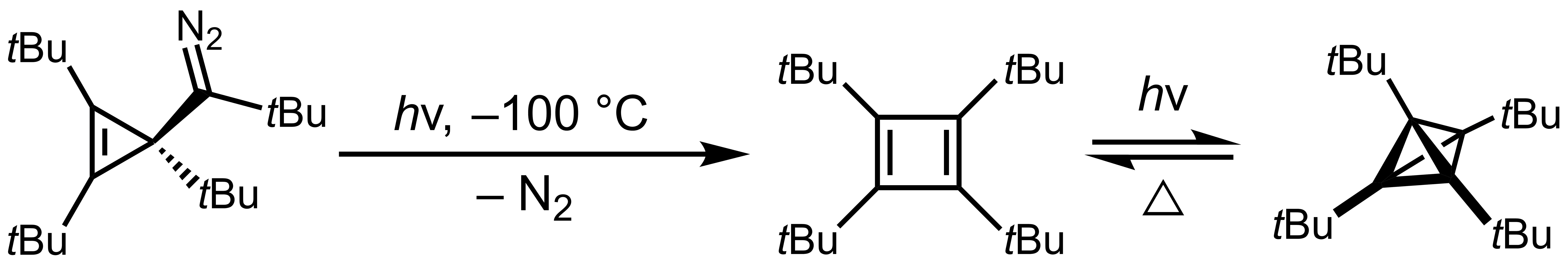
Tetrahedrane
Tetrahedrane is a hypothetical platonic hydrocarbon with chemical formula and a tetrahedral structure. The molecule would be subject to considerable angle strain and has not been synthesized as of 2021. However, a number of derivatives have been prepared. In a more general sense, the term ''tetrahedranes'' is used to describe a class of molecules and ions with related structure, e.g. white phosphorus. Organic tetrahedranes In 1978, Günther Maier prepared tetra- ''tert''-butyl-tetrahedrane. These bulky substituents envelop the tetrahedrane core. Maier suggested that bonds in the core are prevented from breaking because this would force the substituents closer together (corset effect) resulting in Van der Waals strain. Tetrahedrane is one of the possible platonic hydrocarbons and has the IUPAC name tricyclo .1.0.02,4utane. Unsubstituted tetrahedrane () remains elusive, although it is predicted to be kinetically stable. One strategy that has been explored (but thus far failed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylenecyclopropane
Methylenecyclopropane is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)2CCH2. It is a colourless easily condensed gas that is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. Synthesis Methylenecyclopropane can be synthesised via an intramolecular cyclisation reaction from methallyl chloride by treatment with a strong base such as sodium amide. : Reactions Being a strained and unsaturated molecule methylenecyclopropane undergoes many reactions, especially in the presence of metal catalysts. For example, methylenecyclopropanes can be converted to cyclobutenes in the presence of a Platinum catalyst.''PtCl2-Catalyzed Rearrangement of Methylenecyclopropanes'' Alois Fürstner and Christophe Aïssa J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2006; 128(19) pp 6306 -6307Abstract/ref> This can be considered similar to the ring expansion seen in vinylcyclopropane rearrangements : Substituted methylenecyclopropanes can also be involved in trimethylenemethane cycloaddition reactions. See also * Methylenecyclopropene * 1- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylcyclopropane
Methylcyclopropane is an organic compound with the structural formula C3H5CH3. This colorless gas is the monomethyl derivative of cyclopropane Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself i .... Reactions Methylcyclopropane, like many other cyclopropanes, undergoes ring-opening reactions. Bond cleavage in certain reactions is also reported in conjunction with the use of methylenecyclopropane groups as protective groups for amines. References {{Hydrocarbons Cyclopropyl compounds Hydrocarbons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propalene
Propalene or bicyclo .1.0uta-1,3-diene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclopropene rings. Computational studies indicate that the molecule is planar, with the carbon framework forming a parallelogram that has distinctly alternating short and long carbon–carbon bonds. See also *Butadiene *Cyclobutadiene * Bicyclobutane *Butalene *Pentalene *Heptalene *Octalene Octalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclooctatetraene rings. Anions Octalene can be readily reduced by lithium to a dianion and, unusually for such a small molecule, a tetraanion .Müllen, K., Oth, J. F. M., Engels, H.-W ... References Polycyclic nonaromatic hydrocarbons Bicyclic compounds Cyclopropenes {{Hydrocarbon-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |