|
Foil Bearing
A foil bearing, also known as a foil-air bearing, is a type of air bearing. A shaft is supported by a compliant, spring-loaded foil journal lining. Once the shaft is spinning fast enough, the working fluid (usually air) pushes the foil away from the shaft so that no contact occurs. The shaft and foil are separated by the air's high pressure, which is generated by the rotation that pulls gas into the bearing via viscosity effects. The high speed of the shaft with respect to the foil is required to initiate the air gap, and once this has been achieved, no wear occurs. Unlike aerostatic or hydrostatic bearings, foil bearings require no external pressurisation system for the working fluid, so the hydrodynamic bearing is self-starting. Development Foil bearings were first developed in the late 1950s by AiResearch Mfg. Co. of the Garrett Corporation using independent R&D funds to serve military and space applications. They were first tested for commercial use in United Airlines B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DC-10
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas. The DC-10 was intended to succeed the DC-8 for long-range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; it was introduced on August 5, 1971, by American Airlines. The trijet has two turbofans on underwing pylons and a third one at the base of the vertical stabilizer. The twin-aisle layout has a typical seating for 270 in two classes. The initial DC-10-10 had a range for transcontinental flights. The DC-10-15 had more powerful engines for hot and high airports. The DC-10-30 and −40 models (with a third main landing gear leg to support higher weights) each had intercontinental ranges of up to . The KC-10 Extender (based on the DC-10-30) is a U.S. Air Force tanker. A design flaw in the original cargo doors caused a poor safety record in early operations. Following the American Airlines Flight 191 crash (the deadliest aviation accident in US history), the US Feder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Speed
In solid mechanics, in the field of rotordynamics, the critical speed is the theoretical angular velocity that excites the natural frequency of a rotating object, such as a shaft, propeller, leadscrew, or gear. As the speed of rotation approaches the object's natural frequency, the object begins to resonate, which dramatically increases system vibration. The resulting resonance occurs regardless of orientation. When the rotational speed is equal to the numerical value of the natural vibration, then that speed is referred to as critical speed. Critical speed of shafts All rotating shafts, even in the absence of external load, will deflect during rotation. The unbalanced mass of the rotating object causes deflection that will create resonant vibration at certain speeds, known as the critical speeds. The magnitude of deflection depends upon the following: *Stiffness of the shaft and its support *Total mass of shaft and attached parts *Unbalance of the mass with respect to the axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the maximum operating temperature (or peak operating temperature). Outside this range of safe operating temperatures the device may fail. It is one component of reliability engineering. Similarly, biological systems have a viable temperature range, which might be referred to as an "operating temperature". Ranges Most devices are manufactured in several temperature grades. Broadly accepted grades are: *Commercial: 0 ° to 70 °C *Industrial: −40 ° to 85 °C *Military: −55 ° to 125 °C Nevertheless, each manufacturer defines its own temperature grades so designers must pay close attention to actual datasheet spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Drag
Parasitic drag, also known as profile drag, is a type of aerodynamic drag that acts on any object when the object is moving through a fluid. Parasitic drag is a combination of form drag and skin friction drag. It affects all objects regardless of whether they are capable of generating lift. Total drag on an aircraft is made up of parasitic drag and lift-induced drag. Parasitic drag comprises all types of drag except lift-induced drag. Form drag Form drag arises because of the shape of the object. The general size and shape of the body are the most important factors in form drag; bodies with a larger presented cross-section will have a higher drag than thinner bodies; sleek ("streamlined") objects have lower form drag. Form drag follows the drag equation, meaning that it increases with the square of the velocity, and thus becomes more important for high-speed aircraft. Form drag depends on the longitudinal section of the body. A prudent choice of body profile is essential for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' (" stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
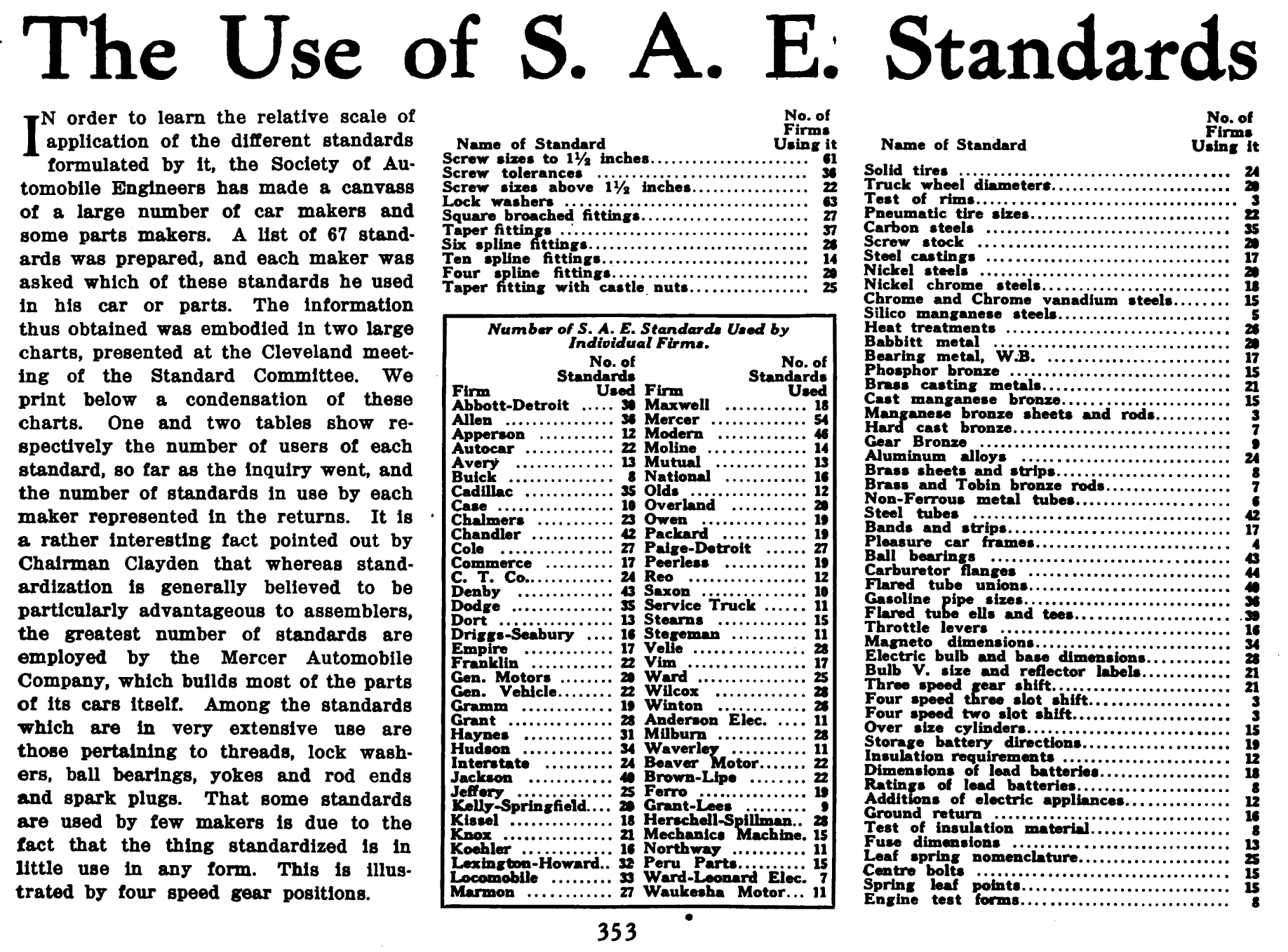
Society Of Automobile Engineers
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE International's world headquarters is in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 20 miles north of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Principal emphasis is placed on global transport industries such as aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicles. The organization adopted the name SAE International to reflect the broader emphasis on mobility. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. For historical legacy reasons, the label "SAE" is commonly used on tools and hardware in North America to indicate United States cus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbomachinery
Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.Logan, Earl. "Handbook of turbomachinery". 1995. Marcel Deckker.Vandad Talimi (Original author unknown). "Mechanical Equipment and Systems". 2013. Memorial University of Newfoundland. http://www.engr.mun.ca/~yuri/Courses/MechanicalSystems/Turbomachinery.pdf These two types of machines are governed by the same basic relationships including Newton's second Law of Motion and Euler's pump and turbine equation for compressible fluids. Centrifugal pumps are also turbomachines that transfer energy from a rotor to a fluid, usually a liquid, while turbines and compressors usually work with a gas. History The first turbomachines could be identified as water wheels, which appeared between the 3rd and 1st centuries BCE in the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Automotive Engineers
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE International's world headquarters is in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 20 miles north of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Principal emphasis is placed on global transport industries such as aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicles. The organization adopted the name SAE International to reflect the broader emphasis on mobility. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. For historical legacy reasons, the label "SAE" is commonly used on tools and hardware in North America to indicate United States cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cryogenic” by accepting a threshold of 120 K (or –153 °C) to distinguish these terms from the conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120K while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120K. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology considers the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below -153 Celsius (120K; -243.4 Fahrenheit) Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
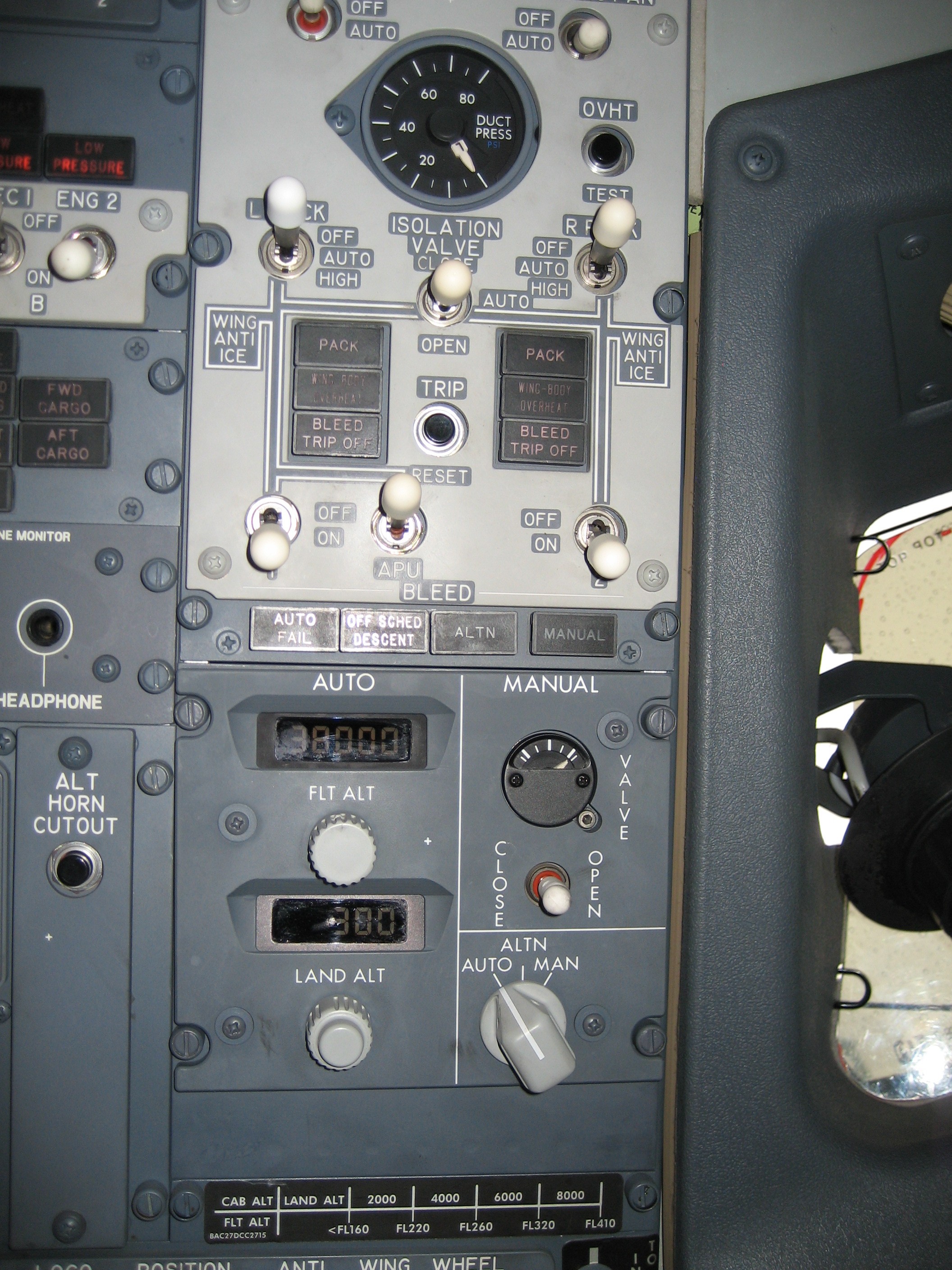
Environmental Control System
In aeronautics, an environmental control system (ECS) of an aircraft is an essential component which provides air supply, thermal control and cabin pressurization for the crew and passengers. Additional functions include the cooling of avionics, smoke detection, and fire suppression. Overview The systems described below are specific to current production Boeing airliners, although the details are essentially identical for passenger jets from Airbus and other companies. An exception was Concorde which had a supplementary air supply system fitted due to the higher altitudes at which it flew, and also the slightly higher cabin pressure it employed. Air supply On jetliners, air is supplied to the ECS by being bled from a compressor stage of each gas turbine engine, upstream of the combustor. The temperature and pressure of this bleed air varies according to which compressor stage is used, and the power setting of the engine. A manifold pressure regulating shut-off valv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |