|
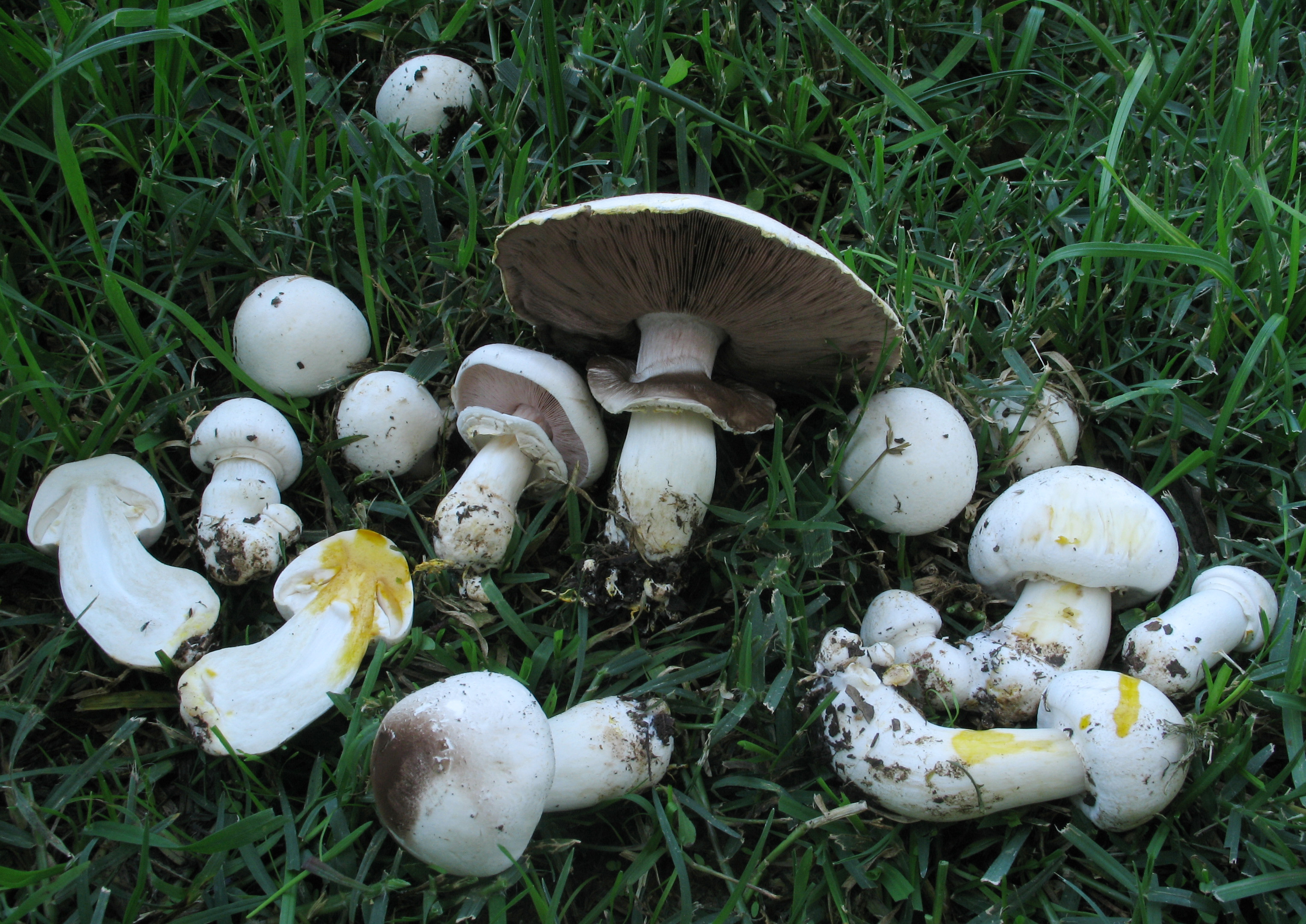
Field Mushroom
''Agaricus campestris'' is a widely eaten gilled mushroom closely related to the cultivated button mushroom ''Agaricus bisporus''. It is commonly known as the field mushroom or, in North America, meadow mushroom. Taxonomy This species was originally noted and named in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus as ''Agaricus campestris''. It was placed in the genus ''Psalliota'' by Lucien Quelet in 1872. Some variants have been isolated over the years, a few of which now have species status, for example, '' Agaricus bernardii'' Quel. (1878), ''Agaricus bisporus'' (J.E. Lange) Imbach (1946), '' Agaricus bitorquis'' (Quel.) Sacc. (1887), '' Agaricus cappellianus'' Hlavacek (1987), and '' Agaricus silvicola'' (Vittad.) Peck (1872). Some were so similar they did not warrant even varietal status, while others have retained it. ''Agaricus campestris'' var. ''equestris'' (F.H.Moller) Pilat (1951) is still valid. ''A. campestris'' var. ''isabellinus'' (F.H.Moller) Pilat (1951), and ''A. campestris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868, and has been officially headquartered at the university's flagship campus in Berkeley, California, since its inception. As the non-profit publishing arm of the University of California system, the UC Press is fully subsidized by the university and the State of California. A third of its authors are faculty members of the university. The press publishes over 250 new books and almost four dozen multi-issue journals annually, in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, and maintains approximately 4,000 book titles in print. It is also the digital publisher of Collabra and Luminos open access (OA) initiatives. The University of California Press publishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Arvensis
''Agaricus arvensis'', commonly known as the horse mushroom, is a mushroom of the genus ''Agaricus''. Taxonomy It was described as ''Agaricus arvensis'' by Jacob Christian Schaeffer in 1762, and given numerous binomial descriptions since. Its specific name arvensis means 'of the field'. Description The cap is , whitish, smooth, and dry; it stains yellow, particularly when young. The gills are pale pink to white at first, later passing through grey and brown to become dull chocolate. There is a large spreading ring, white above but sometimes with yellowish scales underneath. Viewed from below, on a closed-cap specimen, the twin-layered ring has a well-developed 'cogwheel' pattern around the stipe. This is the lower part of the double ring. The stalk is long and 1–3 cm wide. The spores are brown and smooth. The odor is described as like anise. It belongs to a group of ''Agaricus'' which tend to stain yellow on bruising. Similar species When young, this fungus is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Hondensis
''Agaricus hondensis'', commonly known as the felt-ringed agaricus, is a species of fungus in the family Agaricaceae. The species was officially described in 1912 by mycologist William Alphonso Murrill, along with three other ''Agaricus'' species that have since been placed in synonymy with ''A. hondensis''. Found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, ''A. hondensis'' fruits in the fall under conifers or in mixed forests. The fungus produces fruit bodies (mushrooms) with white to gray-brown caps up to in diameter covered with pale pinkish-brown scales that darken in age. The tightly-packed gills on the cap underside are initially white before becoming pinkish, lilac-gray, and finally brownish as the spores mature. The stout stipe is bulbous and has a thick, white, felt-like ring. The mushroom is poisonous, and causes severe gastrointestinal upset if consumed. It has an unpleasant odor similar to phenol or creosote, and develops a soapy-metallic taste w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Californicus
''Agaricus californicus'', commonly known as the California agaricus, is a poisonous mushroom in the section ''Xanthodermati'' of the genus ''Agaricus''. It is mildly poisonous, causing gastrointestinal upset in many individuals. The etiology of these symptoms is unclear and some individuals can eat it without experiencing symptoms, but since there is no way to tell who can eat the mushroom safely it is generally recommended against. Description The caps are wide, white, sometimes with a grayish-tan center, dry, and either unchanged or yellowing slightly when bruised. The stalk is long and 1–2 wide, perhaps larger at the base. The spores are brown and smooth. Differentiating ''A. californicus'' ''Agaricus californicus'' is similar in general appearance to many other ''Agaricus'' species, especially to ''A. arvensis'', ''A. bisporus'', ''A. campestris'', ''A. cupreobrunneus'', and which are commonly collected for the table. Since ''A. californicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Hygroscopica
''Amanita hygroscopia'' ( /æməˈnaɪtə /ha͡ɪɡɹəskˈo͡ʊpi͡ə), also known as the pink-gilled destroying angel is a deadly poisonous fungus, one of many in the genus ''Amanita''. It was first described by William Chambers Coker in 1917. Resembling several edible species, most notably ''Agaricus campestris,'' poisonings are not uncommon from ''A. hygroscopica.'' Amatoxins, the class of toxins found in these mushrooms, are thermostable: they resist changes due to heat, so their toxic effects are not reduced by cooking. Description The cap is 25 mm wide and hemispheric. The gills are adnate, crowded, medium broad, entire, white, unchanging. The stem is about 30 × 5 - 8 mm, narrowing upward, smooth, glabrous, white, unchanging when bruised. The ring is fixed 10 mm from the top of the stem, very short, skirt-like, grooved by the gills above, white, persistent. The bulb is ovoid, white, 20 × 15 mm. The volva is neither appressed nor widely spreading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Virosa
''Amanita virosa'', commonly known in Europe as the destroying angel or the European destroying angel amanita, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus ''Amanita''. Occurring in Europe, ''A. virosa'' associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees. The large fruiting bodies (''i.e.'', the mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the caps, stipes and gills are all white in colour. Immature specimens of ''A. virosa'' resemble several edible species commonly consumed by humans, increasing the risk of accidental poisoning. Small specimens may resemble the common Portobello mushroom to non-experts, but just one cap of ''A. virosa'' is enough to kill an adult human. The symptoms of poisoning generally come several hours afterwards, a fact which makes this fungus even more problematic. Along with its geographical namesakes, ''A. virosa'' is one of the most poisonous of all known poisonous mushrooms; its principal toxic constituent α-Amanitin dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheilocystidia
A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are often unique to a particular species or genus, they are a useful micromorphological characteristic in the identification of basidiomycetes. In general, the adaptive significance of cystidia is not well understood. Classification of cystidia By position Cystidia may occur on the edge of a lamella (or analogous hymenophoral structure) (cheilocystidia), on the face of a lamella (pleurocystidia), on the surface of the cap (dermatocystidia or pileocystidia), on the margin of the cap (circumcystidia) or on the stipe (caulocystidia). Especially the pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia are important for identification within many genera. Sometimes the cheilocystidia give the gill edge a distinct colour which is visible to the naked eye or wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiospore
A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by Basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop on appendages from each basidium, of which two are of one strain and the other two of its opposite strain. In gills under a cap of one common species, there exist millions of basidia. Some gilled mushrooms in the order Agaricales have the ability to release billions of spores. The puffball fungus ''Calvatia gigantea'' has been calculated to produce about five trillion basidiospores. Most basidiospores are forcibly discharged, and are thus considered ballistospores. These spores serve as the main air dispersal units for the fungi. The spores are released during periods of high humidity and generally have a night-time or pre-dawn peak concentration in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Xanthodermus
''Agaricus xanthodermus'', commonly known as the yellow-staining mushroom or simply the yellow-stainer, is a mushroom of the genus ''Agaricus'', which displays a strong yellow colouration at the base of the stem when cut. It is poisonous for most people, causing gastrointestinal upset, but can be eaten by some without apparent negative effect. Taxonomy This species was first officially defined under the name ''Agaricus xanthodermus'' in 1876 by Léon Gaston Genevier, in a letter published in the bulletin of the French Botanical Society. Genevier described the ''Agaricus'' mushrooms commonly eaten (perhaps sometimes inadvisedly) in the region of Nantes, and attempted to clarify the distinctions between them. He proposed a detailed reclassification into 5 species, including this new one. Apparently up until that time, these yellow-staining mushrooms were considered to be just varieties of other species which are edible: '' A. arvensis'', A. edulis', and '' A. silvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trama (mycology)
In mycology, the term trama is used in two ways. In the broad sense, it is the inner, fleshy portion of a mushroom's basidiocarp, or fruit body. It is distinct from the outer layer of tissue, known as the pileipellis or cuticle, and from the spore-bearing tissue layer known as the hymenium. In essence, the trama is the tissue that is commonly referred to as the "flesh" of mushrooms and similar fungi.Largent D, Johnson D, Watling R. 1977. ''How to Identify Mushrooms to Genus III: Microscopic Features''. Arcata, CA: Mad River Press. . pp. 60–70. The second use is more specific, and refers to the "hymenophoral trama" that supports the hymenium. It is similarly interior, connective tissue, but it is more specifically the central layer of hyphae running from the underside of the mushroom cap to the lamella or gill, upon which the hymenium rests. Various types have been classified by their structure, including trametoid, cantharelloid, boletoid, and agaricoid, with agaricoid the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |