|
Feature (linguistics)
In linguistics, a feature is any characteristic used to classify a phoneme or word. These are often binary or unary conditions which act as constraints in various forms of linguistic analysis. In phonology In phonology, segments are categorized into natural classes on the basis of their distinctive features. Each feature is a quality or characteristic of the natural class, such as voice or manner. A unique combination of features defines a phoneme. Examples of phonemic or distinctive features are: [+/- voice ], [+/- Advanced tongue root, ATR ] (binary features) and [ coronal consonant, CORONAL ] (a unary feature; also a place of articulation, place feature). Surface representations can be expressed as the result of rules acting on the features of the underlying representation. These rules are formulated in terms of transformations on features. In morphology and syntax In morphology and syntax, words are often organized into lexical categories or word classes, such as "n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the science, scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the Cognition, cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
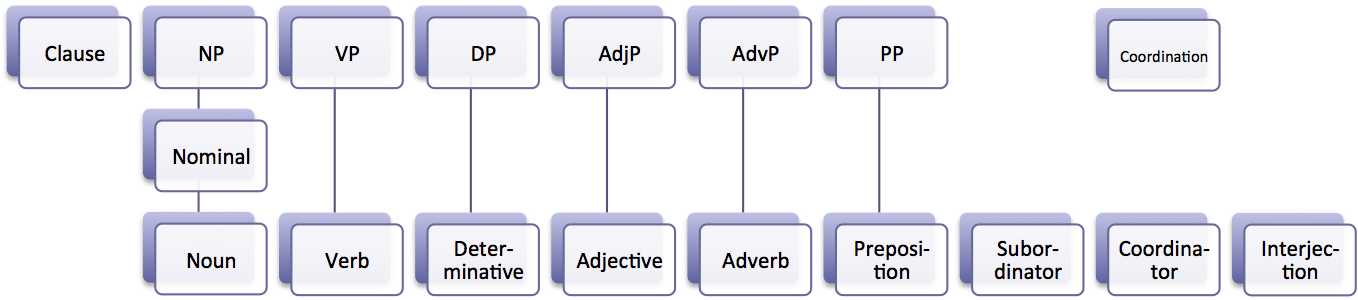
Lexical Category
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Feature
A semantic feature is a component of the concept associated with a lexical item ('female' + 'performer' = 'actress'). More generally, it can also be a component of the concept associated with any grammatical unit, whether composed or not ('female' + 'performer' = 'the female performer' or 'the actress'). An individual semantic feature constitutes one component of a word's intention, which is the inherent sense or concept evoked. Linguistic meaning of a word is proposed to arise from contrasts and significant differences with other words. Semantic features enable linguistics to explain how words that share certain features may be members of the same semantic domain. Correspondingly, the contrast in meanings of words is explained by diverging semantic features. For example, ''father'' and ''son'' share the common components of "human", "kinship", "male" and are thus part of a semantic domain of male family relations. They differ in terms of "generation" and "adulthood", which is what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Class
A semantic class contains words that share a semantic feature. For example within nouns there are two sub classes, concrete nouns and abstract nouns. The concrete nouns include people, plants, animals, materials and objects while the abstract nouns refer to concepts such as qualities, actions, and processes. According to the nature of the noun, they are categorized into different semantic classes. Semantic classes may intersect. The intersection of ''female'' and ''young'' can be ''girl''. See also * Semantic property * Categorization Categorization is the ability and activity of recognizing shared features or similarities between the elements of the experience of the world (such as objects, events, or ideas), organizing and classifying experience by associating them to a ... * Semantic field References * Semantics {{semantics-stub es:Campo semántico fr:Classe sémantique kk:Семантикалық өріс ru:Семантическое поле ta:ச� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and computer science. History In English, the study of meaning in language has been known by many names that involve the Ancient Greek word (''sema'', "sign, mark, token"). In 1690, a Greek rendering of the term ''semiotics'', the interpretation of signs and symbols, finds an early allusion in John Locke's ''An Essay Concerning Human Understanding'': The third Branch may be called [''simeiotikí'', "semiotics"], or the Doctrine of Signs, the most usual whereof being words, it is aptly enough termed also , Logick. In 1831, the term is suggested for the third branch of division of knowledge akin to Locke; the "signs of our knowledge". In 1857, the term '' semasiology'' (borrowed from German ''Semasiologie'') is attested in Josiah W. Gibb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Class
In linguistics, a noun class is a particular category of nouns. A noun may belong to a given class because of the characteristic features of its referent, such as gender, animacy, shape, but such designations are often clearly conventional. Some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", but others consider these different concepts. Noun classes should not be confused with noun classifiers. Notion There are three main ways by which natural languages categorize nouns into noun classes: * according to similarities in their meaning (semantic criterion); * by grouping them with other nouns that have similar form (morphology); * through an arbitrary convention. Usually, a combination of the three types of criteria is used, though one is more prevalent. Noun classes form a system of grammatical agreement. A noun in a given class may require: * agreement affixes on adjectives, pronouns, numerals, etc. in the same noun phrase, * agreement affixes on the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Conjugation
In linguistics, conjugation () is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb ''break'' can be conjugated to form the words ''break'', ''breaks'', ''broke'', ''broken'' and ''breaking''. While English has a relatively simple conjugation, other languages such as French and Arabic are more complex, with each verb having dozens of conjugated forms. Some languages such as Georgian and Basque have highly complex conjugation systems with hundreds of possible conjugations for every verb. Verbs may inflect for grammatical categories such as person, number, gender, case, tense, aspect, mood, voice, possession, definiteness, politeness, causativity, clusivity, interrogatives, transitivity, valency, polarity, telicity, volition, mirativity, evidentiality, animacy, associativity, pluractionality, and reciprocity. Verbs may also be affected by agreement, polypersona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Person
In linguistics, grammatical person is the grammatical distinction between deictic references to participant(s) in an event; typically the distinction is between the speaker ( first person), the addressee ( second person), and others ( third person). A language's set of ''personal'' pronouns are defined by grammatical person, but other pronouns would not. ''First person'' includes the speaker (English: ''I'', ''we'', ''me'', and ''us''), ''second person'' is the person or people spoken to (English: ''you''), and ''third person'' includes all that are not listed above (English: ''he'', ''she'', ''it'', ''they'', ''him'', ''her'', ''them''). It also frequently affects verbs, and sometimes nouns or possessive relationships. Related classifications Number In Indo-European languages, first-, second-, and third-person pronouns are typically also marked for singular and plural forms, and sometimes dual form as well (grammatical number). Inclusive/exclusive distinction Some ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tense–aspect–mood
Tense–aspect–mood (commonly abbreviated ) or tense–modality–aspect (abbreviated as ) is a group of grammatical categories that are important to understanding spoken or written content, and which are marked in different ways by different languages. TAM covers the expression of three major components of words which lead to or assist in the correct understanding of the speaker's meaning: * Tense—the position of the state or action in time, that is, whether it is in the past, present or future. * Aspect—the extension of the state or action in time, that is, whether it is unitary (perfective), continuous or repeated (imperfective). * Mood or Modality—the reality of the state or action, that is, whether it is actual (realis), a possibility or a necessity (irrealis). For example, in English the word "walk" would be used in different ways for the different combinations of TAM: * Tense: He walked (past), He walks (present), He will walk (future). * Aspect: He walked (uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''; the values present in a given language (of which there are usually two or three) are called the ''genders'' of that language. Whereas some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", others use different definitions for each; many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to sex. Gender systems are used in approximately one half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behaviour of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually have two to four different genders, but some are attested with up to 20. Common gender ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement (linguistics), agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and other languages present number categories of singular or plural, both of which are cited by using the hash sign (#) or by the numero signs "No." and "Nos." respectively. Some languages also have a Dual (grammatical number), dual, #Trial, trial and #Paucal, paucal number or other arrangements. The count distinctions typically, but not always, correspond to the actual count of the referents of the marker (linguistics), marked noun or pronoun. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see "Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |