|
Frictional Unemployment
Frictional unemployment is a form of unemployment reflecting the gap between someone voluntarily leaving a job and finding another. As such, it is sometimes called search unemployment, though it also includes gaps in employment when transferring from one job to another. Frictional unemployment is one of the three broad categories of unemployment, the others being structural unemployment and cyclical unemployment. Causes of frictional unemployment include better job opportunities, services, salary and wages, dissatisfaction with the previous job, and strikes by trade unions and other forms of non-unionized work actions. Analysis Frictional unemployment exists because both jobs and workers are heterogeneous, and a mismatch can result between the characteristics of supply and demand. Such a mismatch can be related to skills, payment, worktime, location, attitude, taste, and a multitude of other factors. New entrants (such as graduating students) and re-entrants (such as former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * new technologies and inventions * policies of the government * regulation and market * war, civil disorder, and natural disasters Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, can in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Unemployment
Structural unemployment is a form of involuntary unemployment caused by a mismatch between the skills that workers in the economy can offer, and the skills demanded of workers by employers (also known as the skills gap). Structural unemployment is often brought about by technological changes that make the job skills of many workers obsolete. Structural unemployment is one of three categories of unemployment distinguished by economists, the others being frictional unemployment and cyclical unemployment. Because it requires either migration or re-training, structural unemployment can be long-term and slow to fix. Causes and examples From an individual perspective, structural unemployment can be due to: * Inability to afford or decision not to pursue further education or job training. * Choice of a field of study which did not produce marketable job skills. * Inability to afford relocation. * Inability to relocate due to inability to sell a house (for example due to the colla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * new technologies and inventions * policies of the government * regulation and market * war, civil disorder, and natural disasters Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, can in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Beveridge 2004 Through Fall 2010
US or Us most often refers to: * ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from '' Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's Talk About Love'', 1997 * "Us", by Gucci Mane from '' Delusions of Grandeur'', 2019 * "Us", by Spoon from '' Hot Thoughts'', 2017 Other media * US Festival, two 1980s California music festivals organized by Steve Wozniak * ''Us'' (1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Agents
In economic theory and econometrics, the term heterogeneity refers to differences across the units being studied. For example, a macroeconomic model in which consumers are assumed to differ from one another is said to have heterogeneous agents. Unobserved heterogeneity in econometrics In econometrics, statistical inferences may be erroneous if, in addition to the observed variables under study, there exist other relevant variables that are unobserved, but correlated with the observed variables; dependent and independent variables .M. Arellano (2003), Panel Data Econometrics', Chapter 2, 'Unobserved heterogeneity', pp. 7-31. Oxford University Press. Methods for obtaining valid statistical inferences in the presence of unobserved heterogeneity include the instrumental variables method; multilevel models, including fixed effects and random effects models; and the Heckman correction for selection bias. Economic models with heterogeneous agents {{Further, Agent-based computational ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Employment
Full employment is an economic situation in which there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Full employment does not entail the disappearance of all unemployment, as other kinds of unemployment, namely structural and frictional, may remain. Full employment does not entail 100% employment-to-population ratio. For instance, workers who are "between jobs" for short periods of time as they search for better employment are not counted against full employment, as such unemployment is frictional rather than cyclical. An economy with full employment might also have unemployment or underemployment where part-time workers cannot find jobs appropriate to their skill level, as such unemployment is considered structural rather than cyclical. Full employment marks the point past which expansionary fiscal and/or monetary policy cannot reduce unemployment any further without causing inflation. Some economists define full employment somewhat differently, as the unemployment rate at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unemployment Rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * new technologies and inventions * policies of the government * regulation and market * war, civil disorder, and natural disasters Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Market
Labour economics seeks to understand the functioning and dynamics of the Market (economics), markets for wage labour. Labour (human activity), Labour is a commodity that is supplied by labourers, usually in exchange for a wage paid by demanding firms. Because these labourers exist as parts of a social, institutional, or political system, labour economics must also account for social, cultural and political variables. Labour markets or job markets function through the interaction of workers and employers. Labour economics looks at the suppliers of labour services (workers) and the demanders of labour services (employers), and attempts to understand the resulting pattern of wages, employment, and income. These patterns exist because each individual in the market is presumed to make rational choices based on the information that they know regarding wage, desire to provide labour, and desire for leisure. Labour markets are normally geographically bounded, but the rise of the internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beveridge Curve
A Beveridge curve, or UV curve, is a graphical representation of the relationship between unemployment and the vacancy (economics), job vacancy rate, the number of unfilled jobs expressed as a proportion of the workforce, labour force. It typically has vacancies on the vertical axis and unemployment on the horizontal. The curve, named after William Beveridge, is hyperbolic-shaped and slopes downward, as a higher rate of unemployment normally occurs with a lower rate of vacancies. If it moves outward over time, a given level of vacancies would be associated with higher and higher levels of unemployment, which would imply decreasing efficiency in the labour market. Inefficient labour markets are caused by mismatches between available jobs and the unemployed and an immobile labour force. The position on the curve can indicate the current state of the economy in the business cycle. For example, recessionary periods are indicated by high unemployment and low vacancies, corresponding to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
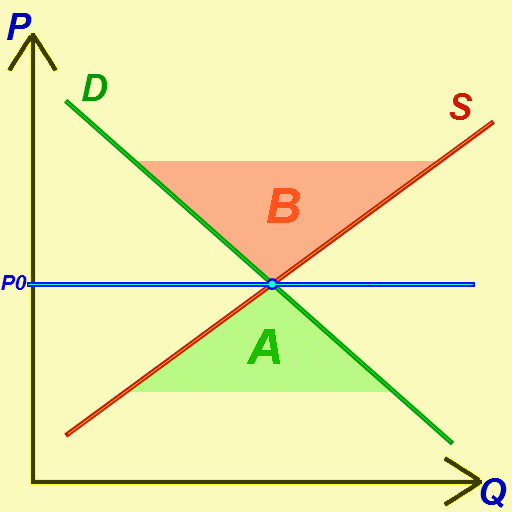
Market Clearing
In economics, market clearing is the process by which, in an economic market, the supply of whatever is traded is equated to the demand so that there is no excess supply or demand, ensuring that there is neither a surplus nor a shortage. The new classical economics assumes that in any given market, assuming that all buyers and sellers have access to information and that there is no "friction" impeding price changes, prices ''constantly'' adjust up or down to ensure market clearing. Mechanism and examples A market-clearing price is the price of a good or service at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, also called the equilibrium price. The theory claims that markets tend to move toward this price. Supply is fixed for a one-time sale of goods, so the market-clearing price is simply the maximum price at which all items can be sold. In a market where goods are produced and sold on an ongoing basis, the theory predicts that the market will move toward a price wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underemployment
Underemployment is the underuse of a worker because their job does not use their skills, offers them too few hours, or leaves the worker idle. It is contrasted with unemployment, where a person lacks a job at all despite wanting one. Examples of workers who may be considered underemployed include those who hold a part-time job but wish to work more hours, part-time workers who wish to work full-time, and overqualified workers who have education, experience, or skills beyond their role's requirements. Underemployment has been studied from a variety of perspectives, including economics, management, psychology, and sociology. In economics, underemployment has three different distinct meanings and applications. Policy-makers may under-research these meanings when assessing the economy as they focus on unemployment instead: # " Overqualification" or "overeducation", the employment of workers with high education, skill levels, or experience in jobs that do not require such abilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |