 |
First Metacarpal Bone
The first metacarpal bone or the metacarpal bone of the thumb is the first bone proximal to the thumb. It is connected to the trapezium of the carpus at the first carpometacarpal joint and to the proximal thumb phalanx at the first metacarpophalangeal joint. Characteristics The first metacarpal bone is short and thick with a shaft thicker and broader than those of the other metacarpal bones. Its narrow shaft connects its widened base and rounded head; the former consisting of a thick cortical bone surrounding the open medullary canal; the latter two consisting of cancellous bone surrounded by a thin cortical shell. Head The head is less rounded and less spherical than those of the other metacarpals, making it better suited for a hinge-like articulation. The distal articular surface is quadrilateral, wide, and flat; thicker and broader transversely and extends much further palmarly than dorsally. On the palmar aspect of the articular surface there is a pair of emin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
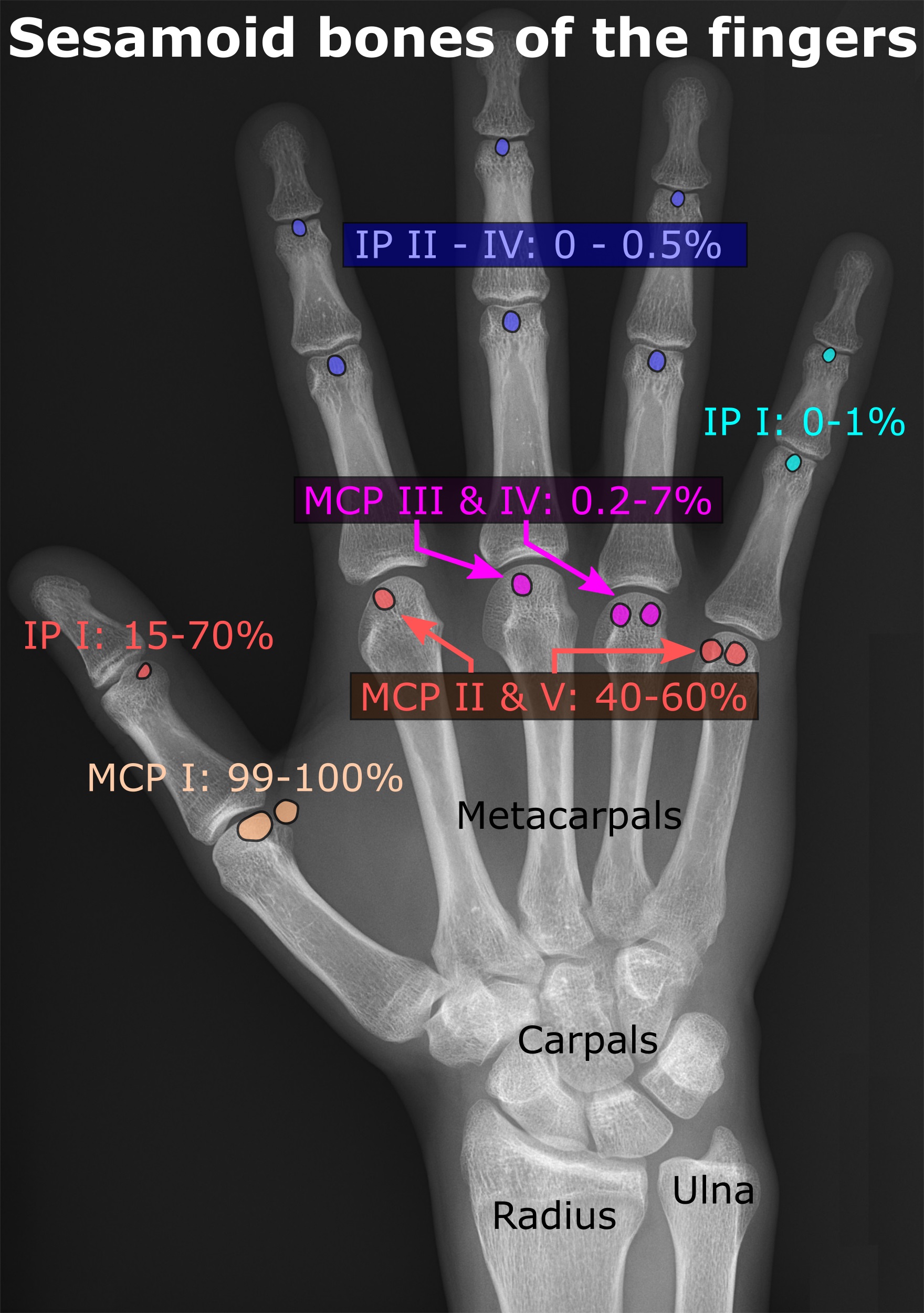 |
Sesamoid Bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a anatomical variation, normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit Muscle#Function, muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the human body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the Anatomical terms of location#Arms, distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone and fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Rolando's Fracture
The Rolando fracture is a type of broken finger involving the base of the thumb. It is an intra-articular fracture. It was first described in 1910 by Silvio Rolando.Rolando S. Fracture de la base du premier metacarpien et principalement sur une variete` non encore e`crite. Presse Med 1910;33:303–4 n French It is typically T- or Y-shaped. Treatment There are several proposed methods of treatment. The quality of reduction does not correlate with late symptoms and osteoarthritic changes. Despite this fact, the joint surface should be restored as close to its anatomical position as possible. Some advocate fixation with Kirschner wires, or plate and screw constructions. Another accepted treatment is an external fixator accompanied by the tension band wiring technique. Tension band wiring is a technique in which the bone fragments are transfixed by Kirschner wires, which are then also used as an anchor for a loop of flexible wire. As the loop is tightened the bone fragments ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Bennett's Fracture
Bennett's fracture or Bennett fracture is a type of partial broken finger involving the base of the thumb, and extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. Treatment typically requires surgery. This intra-articular fracture is the most common type of fracture of the thumb, and is nearly always accompanied by some degree of subluxation or frank dislocation of the carpometacarpal joint. Symptoms and signs Symptoms of Bennett fracture are instability of the CMC joint of the thumb, accompanied by pain and weakness of the pinch grasp. Characteristic signs include pain, swelling, and ecchymosis around the base of the thumb and thenar eminence, and especially over the CMC joint of the thumb. Physical examination demonstrates instability of the CMC joint of the thumb. The patient will often manifest a weakened ability to grasp objects or perform such tasks as tying shoes and tearing a piece of paper. Other complaints include intense pain experienced upon catching the thumb on an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Trapezium (bone)
The trapezium bone (greater multangular bone) is a carpal bone in the hand. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The trapezium is distinguished by a deep groove on its anterior surface. It is situated at the radial side of the carpus, between the scaphoid and the first metacarpal bone (the metacarpal bone of the thumb). It is homologous with the first distal carpal of reptiles and amphibians. Surfaces The trapezium is an irregular-shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The trapezium is found within the distal row of carpal bones, and is directly adjacent to the metacarpal bone of the thumb. On its ulnar surface are found the trapezoid and scaphoid bones. The '' superior surface'' is directed upward and medialward; medially it is smooth, and articulates with the scaphoid; laterally it is rough and continuous with the lateral surface. The '' inferior surface'' is oval, concave from side to side, convex from before backward, so as to form a saddle- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
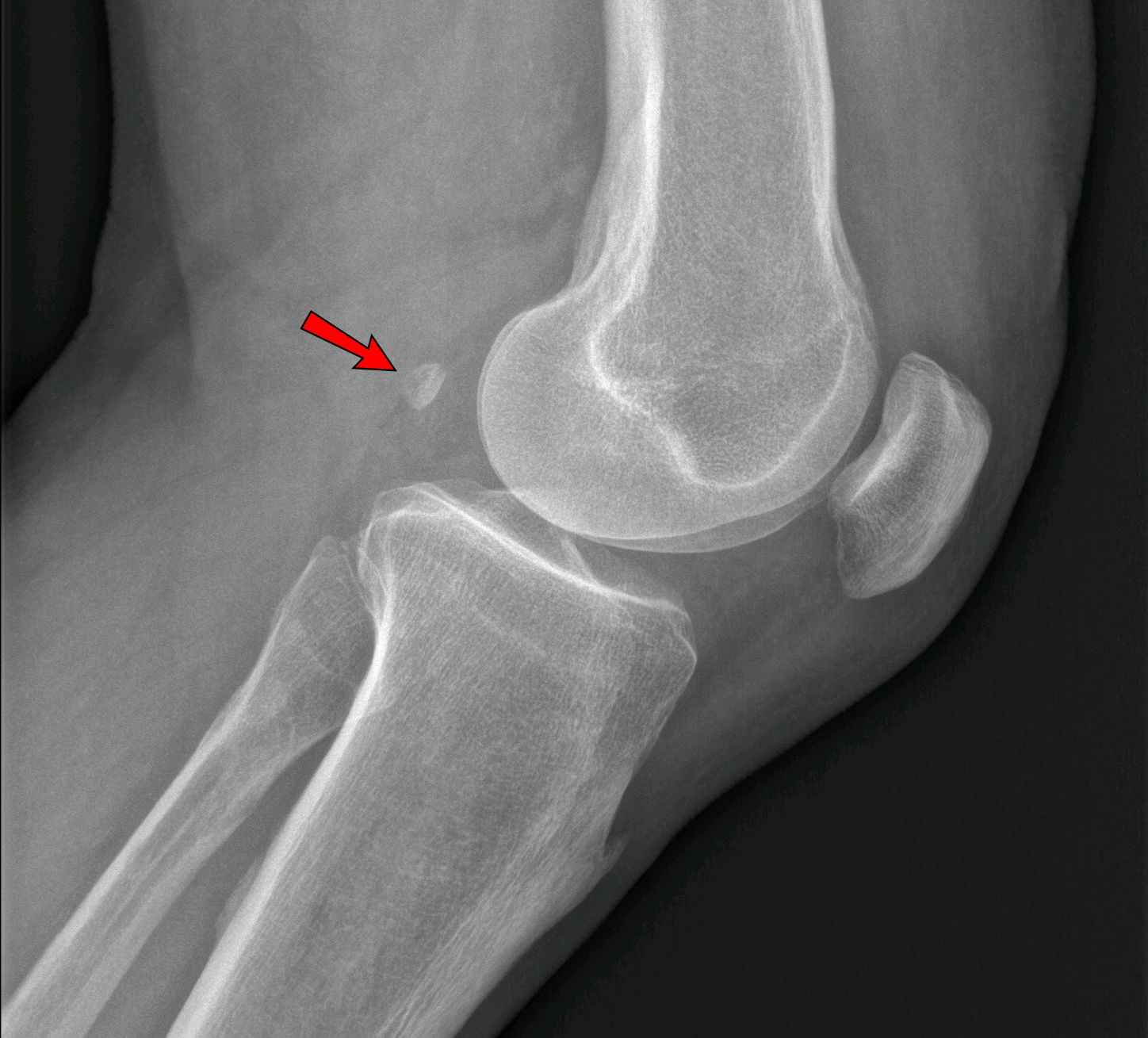 |
Accessory Bone
An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a anatomical variation, variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosis, misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography. Wrist and hand Os ulnostyloideum The ''os ulnostyloideum'' is an ulnar styloid process that is not fused to the rest of the ulna bone.R. O'Rahilly. ''A survey of carpal and tarsal anomalies.'' J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953; 35: 626–642 On X-rays, an ''os ulnostyloideum'' is sometimes mistaken for an avulsion fracture of the styloid process. However, the distinction between these is extremely difficult.T.E. Keats, M.W. Anderson. ''Atlas of normal roentgen variants that may simulate disease''. 7th edition, Mosby Inc. 2001 It is alleged that the os ulnostyloideum has a close relationship with or is synonymous with the os triquetrum secundarium. Os centrale The ''os carpi centrale'' (also briefly ''os centrale'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Gray234 - First Metacarpal Bone
Grey (more frequent in British English) or gray (more frequent in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning that it has no chroma. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash, and of lead. The first recorded use of ''grey'' as a color name in the English language was in 700 CE.Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 196 ''Grey'' is the dominant spelling in European and Commonwealth English, while ''gray'' is more common in American English; however, both spellings are valid in both varieties of English. In Europe and North America, surveys show that gray is the color most commonly associated with neutrality, conformity, boredom, uncertainty, old age, indifference, and modesty. Only one percent of respondents chose it as their favorite color. Etymology ''Grey'' comes from the Middle English or , from the Old English , and is related to the Dutch and Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox. Structure The abductor pollicis longus lies immediately below the supinator and is sometimes united with it. It arises from the lateral part of the dorsal surface of the body of the ulna, below the insertion of the anconeus, from the interosseous membrane, and from the middle third of the dorsal surface of the body of the radius.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see infobox Passing obliquely downward and lateralward, it ends in a tendon, which runs through a groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius, accompanied by the tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis. The insertion is divided into a distal, superficial part and a proximal, deep part. The superficial part is inserted with one or more tendons into the radial side of the base of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dorsal Interossei Of The Hand
In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from the hand's midline (ray of middle finger) and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow ... joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers. Structure There are four dorsal interossei in each hand. They are specified as 'dorsal' to contrast them with the palmar interossei, which are located on the anterior side of the metacarpals. The dorsal interosseous muscles are bipennate, with each muscle arising by two heads from the adjacent sides of the metacarpal bones, but more extensively from the metacarpal bone of the finger into whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Opponens Pollicis Muscle
The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis. Structure The opponens pollicis muscle is one of the three thenar muscles. It originates from the flexor retinaculum of the hand and the tubercle of the trapezium. It passes downward and laterally, and is inserted into the whole length of the metacarpal bone of the thumb on its radial side. Innervation Like the other thenar muscles, the opponens pollicis is innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve. In 20% of the population, opponens pollicis is innervated by the ulnar nerve. Blood supply The opponens pollicis receives its blood supply from the superficial palmar arch. Function ''Opposition of the thumb'' is a combination of actions that allows the tip of the thumb to touch the tips of other fingers. The part of apposition that this m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialised connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralisation of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Metacarpal Bone
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |