|
Fin (aeronautics)
An aircraft stabilizer is an aerodynamic surface, typically including one or more movable control surfaces, that provides longitudinal (pitch) and/or directional (yaw) stability and control. A stabilizer can feature a fixed or adjustable structure on which any movable control surfaces are hinged, or it can itself be a fully movable surface such as a stabilator. Depending on the context, "stabilizer" may sometimes describe only the front part of the overall surface. In the conventional aircraft configuration, separate vertical (fin) and horizontal (tailplane) stabilizers form an empennage positioned at the tail of the aircraft. Other arrangements of the empennage, such as the V-tail configuration, feature stabilizers which contribute to a combination of longitudinal and directional stabilization and control. Longitudinal stability and control may be obtained with other wing configurations, including canard, tandem wing and tailless aircraft. Some types of aircraft are stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Of A Conventional Aircraft
The tail is the elongated section at the rear end of a bilaterian animal's body; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage extending backwards from the midline of the torso. In vertebrate animals that evolved to lose their tails (e.g. frogs and hominid primates), the coccyx is the homologous vestigial of the tail. While tails are primarily considered a feature of vertebrates, some invertebrates such as scorpions and springtails, as well as snails and slugs, have tail-like appendages that are also referred to as tails. Tail-shaped objects are sometimes referred to as "caudate" (e.g. caudate lobe, caudate nucleus), and the body part associated with or proximal to the tail are given the adjective " caudal" (which is considered a more precise anatomical terminology). Function Animal tails are used in a variety of ways. They provide a source of thrust for aquatic locomotion for fish, cetaceans and crocodilians and other forms of marine life. Terrestrial species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transonic
Transonic (or transsonic) flow is air flowing around an object at a speed that generates regions of both subsonic and Supersonic speed, supersonic airflow around that object. The exact range of speeds depends on the object's critical Mach number, but transonic flow is seen at flight speeds close to the speed of sound (343 m/s at sea level), typically between Mach number, Mach 0.8 and 1.2. The issue of transonic speed (or transonic region) first appeared during World War II. Pilots found as they approached the sound barrier the airflow caused aircraft to become unsteady. Experts found that shock waves can cause large-scale Flow separation, separation downstream, increasing drag, adding asymmetry and unsteadiness to the flow around the vehicle. Research has been done into weakening shock waves in transonic flight through the use of Anti-shock body, anti-shock bodies and supercritical airfoils. Most modern jet engine, jet powered aircraft are engineered to operate at transon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piper PA-24 Comanche
The Piper PA-24 Comanche is an American single-engine, low-wing, all-metal monoplane of semimonocoque construction with tricycle Landing gear, retractable landing gear and four or six seats. The Comanche was designed and built by Piper Aircraft and first flew on May 24, 1956. Together with the PA-30 and PA-39 Piper Twin Comanche, Twin Comanches, it made up the core of Piper's lineup until 1972, when the production lines for both aircraft were destroyed in the Lock Haven, Pennsylvania#Floods, 1972 Lock Haven flood. Design and development Two prototypes were built in 1956, with the first being completed by June 20, 1956. The first production aircraft, powered by a Lycoming O-360, Lycoming O-360-A1A engine, first flew on October 21, 1957. In 1958, it was joined by a higher-powered PA-24-250 with a Lycoming O-540, Lycoming O-540-A1A5 engine; this model was originally to be known as the PA-26, but Piper decided to keep the PA-24 designation. In 1964, the PA-24-400 was introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim Tab
Trim tabs are small surfaces connected to the trailing edge of a larger Flight control surfaces, control surface on a boat or aircraft, used to control the trim of the controls, i.e. to counteract hydro- or aerodynamic forces and stabilise the boat or aircraft in a particular desired Orientation (geometry), attitude without the need for the operator to constantly apply a control force. This is done by adjusting the angle of the tab relative to the larger surface. Changing the setting of a trim tab adjusts the neutral or resting position of a control surface (such as an Elevator (aircraft), elevator or rudder). As the desired position of a control surface changes (corresponding mainly to different speeds), an adjustable trim tab will allow the operator to reduce the manual force required to maintain that position—to zero, if desired. Thus the trim tab acts as a servo tab. Because the Center of pressure (fluid mechanics), center of pressure of the trim tab is farther away from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Tunnel
A wind tunnel is "an apparatus for producing a controlled stream of air for conducting aerodynamic experiments". The experiment is conducted in the test section of the wind tunnel and a complete tunnel configuration includes air ducting to and from the test section and a device for keeping the air in motion, such as a fan. Wind tunnel uses include assessing the effects of air on an aircraft in flight or a ground vehicle moving on land, and measuring the effect of wind on Building, buildings and bridges. Wind tunnel test sections range in size from less than a foot across, to over , and with air speeds from a light breeze to hypersonic. The earliest wind tunnels were invented towards the end of the 19th century, in the early days of aeronautical research, as part of the effort to develop heavier-than-air flying machines. The wind tunnel reversed the usual situation. Instead of the air standing still and an aircraft moving, an object would be held still and the air moved around it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifting-line Theory
The Lanchester–Prandtl lifting-line theoryAnderson, John D. (2001), ''Fundamentals of Aerodynamics'', p. 360. McGraw-Hill, Boston. . is a mathematical model in aerodynamics that predicts lift distribution over a three-dimensional wing from the wing's geometry. The theory was expressed independently by Frederick W. Lanchester in 1907, and by Ludwig Prandtl in 1918–1919 after working with Albert Betz and Max Munk. In this model, the vortex bound to the wing develops along the whole wingspan because it is shed as a vortex-sheet from the trailing edge, rather than just as a single vortex from the wing-tips. Introduction It is difficult to predict analytically the overall amount of lift that a wing of given geometry will generate. When analyzing a three-dimensional finite wing, a traditional approach slices the wing into cross-sections and analyzes each cross-section independently as a wing in a two-dimensional world. Each of these slices is called an airfoil, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
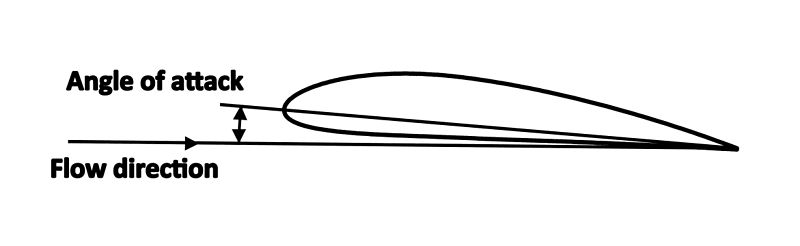
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a Airfoil#Airfoil terminology, reference line on a body (often the chord (aircraft), chord line of an airfoil) and the vector (geometry), vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the Wing root, root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downwash
In aeronautics, downwash is the change in direction of air deflected by the aerodynamic action of an airfoil, wing, or helicopter rotor blade in motion, as part of the process of producing lift.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 172. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. In helicopter aerodynamics discussions, it may be referred to as induced flow. Lift on an airfoil is an example of the application of Newton's third law of motion – the force required to deflect the air in the downwards direction is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the lift force on the airfoil. Lift on an airfoil is also an example of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem. The Kutta condition explains the existence of downwash at the trailing edge of the wing."The main fact of all heavier-than-air flight is this: ''the wing keeps the airplane up by pushing the air down.''" In: See also * Brownout (aeronautics) * Jet blast *Slipstream *Wake turbulence *Wingtip vortices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilator
A stabilator is a fully movable aircraft horizontal stabilizer (aircraft), stabilizer. It serves the usual functions of longitudinal stability, control and stick force requirements otherwise performed by the separate parts of a conventional horizontal stabilizer (which is fixed) and elevator (aeronautics), elevator (which is adjustable). Apart from reduced drag, particularly at high Mach numbers, it is a useful device for changing the aircraft balance within wide limits, and for reducing stick forces. Stabilator is a portmanteau of ''stabilizer'' and ''elevator''. It is also known as an all-moving tailplane (British English), all-movable tail(plane), all-moving stabilizer, all-flying tail (American English), all-flying horizontal tail, full-flying stabilizer, and slab tailplane. General aviation Because it involves a moving balanced surface, a stabilator can allow the pilot to generate a given pitching moment with a lower control force. Due to the high forces involved in tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevator (aircraft)
Elevators are flight control surfaces, usually at the rear of an aircraft, which control the aircraft's pitch, and therefore the angle of attack and the lift of the wing. The elevators are usually hinged to the tailplane or horizontal stabilizer. They may be the only pitch control surface present, and are sometimes located at the front of the aircraft (early airplanes and canards) or integrated into a rear "all-moving tailplane", also called a slab elevator or stabilator. Elevator control effectiveness The elevator is a usable up and down system that controls the plane, horizontal stabilizer usually creates a ''downward'' force which balances the nose down moment created by the wing lift force, which typically applies at a point (the wing center of lift) situated aft of the airplane's center of gravity. The effects of drag and changing the engine thrust may also result in pitch moments that need to be compensated with the horizontal stabilizer. Both the horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (aviation)
An aircraft in flight is free to rotate in three dimensions: '' yaw'', nose left or right about an axis running up and down; ''pitch'', nose up or down about an axis running from wing to wing; and ''roll'', rotation about an axis running from nose to tail. The axes are alternatively designated as ''vertical'', ''lateral'' (or ''transverse''), and ''longitudinal'' respectively. These axes move with the vehicle and rotate relative to the Earth along with the craft. These definitions were analogously applied to spacecraft when the first crewed spacecraft were designed in the late 1950s. These rotations are produced by torques (or moments) about the principal axes. On an aircraft, these are intentionally produced by means of moving control surfaces, which vary the distribution of the net aerodynamic force about the vehicle's center of gravity. Elevators (moving flaps on the horizontal tail) produce pitch, a rudder on the vertical tail produces yaw, and ailerons (flaps on the wings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |