|
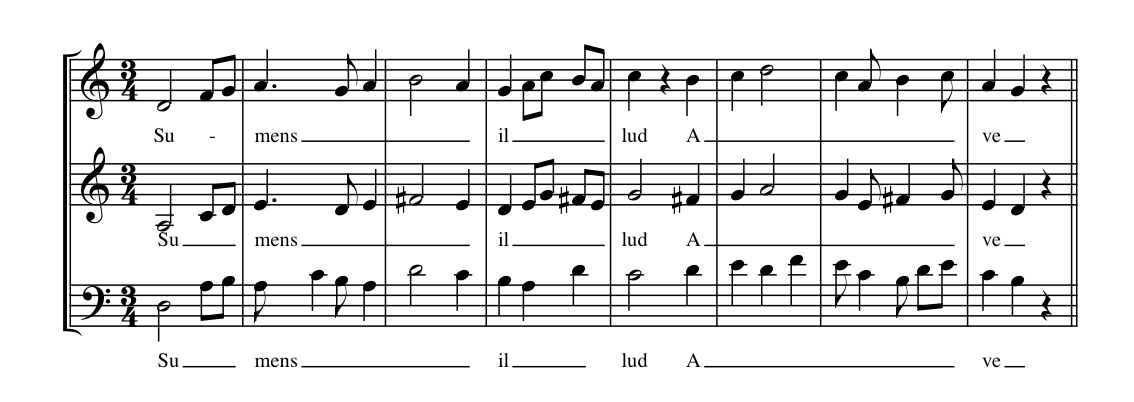
Fauxbourdon
Fauxbourdon (also fauxbordon, and also commonly two words: faux bourdon or faulx bourdon, and in Italian falso bordone) – Music of France, French for ''false drone'' – is a technique of musical harmony, harmonisation used in the late Medieval music, Middle Ages and early Renaissance music, Renaissance, particularly by composers of the Burgundian School. Guillaume Du Fay was a prominent practitioner of the form (as was John Dunstaple), and may have been its inventor. The homophony and mostly parallel harmony allows the text of the mostly liturgical lyrics to be understood clearly. Description In its simplest form, fauxbourdon consists of the cantus firmus and two other part (music), parts a Interval (music), sixth and a perfect fourth below. To prevent monotony, or create a Cadence (music), cadence, the lowest voice sometimes jumps down to the octave, and any of the accompanying voices may have minor embellishments. Usually just a small part of a composition employs the faux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending interval from C to the next F is a perfect fourth, because the note F is the fifth semitone above C, and there are four staff positions between C and F. Diminished fourth, Diminished and Tritone, augmented fourths span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (four and six, respectively). The perfect fourth may be derived from the Harmonic series (music), harmonic series as the interval between the third and fourth harmonics. The term ''perfect'' identifies this interval as belonging to the group of perfect intervals, so called because they are neither major nor minor. A perfect fourth in just intonation corresponds to a pitch ratio of 4:3, or about 498 cent (music), cents (), while in equal temperam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descant
A descant, discant, or is any of several different things in music, depending on the period in question; etymologically, the word means a voice (''cantus'') above or removed from others. The ''Harvard Dictionary of Music'' states: A descant is a form of medieval music in which one singer sang a fixed melody, and others accompanied with improvisations. The word in this sense comes from the term ' (descant "above the book"), and is a form of Gregorian chant in which only the melody is notated but an improvised polyphony is understood. The ' had specific rules governing the improvisation of the additional voices. Later on, the term came to mean the treble or soprano singer in any group of voices, or the higher pitched line in a song. Eventually, by the Renaissance, descant referred generally to counterpoint. Nowadays the counterpoint meaning is the most common. Descant can also refer to the highest pitched of a group of instruments, particularly the descant viol or recorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of France
In France, music reflects a diverse array of styles. In the field of classical music, France has produced several prominent Romantic music, romantic composers, while folk and popular music have seen the rise of the chanson and cabaret style. The oldest playable musical recordings were made in France using the earlist known sound recording device in the world, the phonautograph, which was patented by Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville in 1857. France is also the 5th largest market by value in the world, and its music industry has produced many internationally renowned artists, especially in the nouvelle chanson and French electronic music, electronic music. Classical music Medieval French music history dates back to organum in the 10th century, followed by the Notre Dame School, an organum composition style. Troubadour songs of chivalry and courtly love were composed in the Occitan language, Occitan language between the 10th and 13th centuries, and the Trouvère poet-composer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congregation
Congregation may refer to: Religion *Church (congregation), a religious organization that meets in a particular location *Congregation (Roman Curia), an administrative body of the Catholic Church *Religious congregation, a type of religious institute in the Catholic Church *Congregation (group of houses), in some religious orders of the Catholic Church Music * The Congregation (band), an English pop group * ''Congregation'' (The Afghan Whigs album), 1992, and its title song * ''Congregation'' (Kerbdog album), 2014 * ''The Congregation'' (Johnny Griffin album), 1957 * ''The Congregation'' (Leprous album), 2015 * "Congregation" (song), by Foo Fighters, 2014 Other uses *Congregation (university), a formal meeting of a university See also * Congregate (other) * Congregational church Congregationalism (also Congregational Churches or Congregationalist Churches) is a Reformed Christian (Calvinist) tradition of Protestant Christianity in which churches practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Busnois
Antoine Busnois (also Busnoys; – before 6 November 1492) was a French composer, singer and poet of early Renaissance music. Busnois and colleague Johannes Ockeghem were the leading European composers of the second half the 15th century, and central figures of the early Franco-Flemish School. While also noted as a composer of motets and other sacred music, he was one of the most renowned 15th-century composers of secular polyphonic chansons. Between Guillaume Du Fay and Claudin de Sermisy, Busnois was the most prolific and important French composer of songs. Life and career The details of Busnois's early life are largely conjectural, and nothing is certain. He was probably from the vicinity of Béthune in the Pas-de-Calais, possibly the hamlet of Busnes, to which his name seems to refer. He may have been related to the aristocratic family of Busnes; in particular, a Philippe de Busnes, canon of Notre-Dame in Lens, could have been a relative. He clearly received an excellent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilles Binchois
Gilles de Bins dit Binchois (also Binchoys; – 20 September 1460) was a Franco-Flemish composer and singer of early Renaissance music. A central figure of the Burgundian School, Binchois is renowned a melodist and miniaturist; he generally avoided large scale works, and is most admired for his shorter secular chansons. He is generally ranked below his colleague Guillaume Du Fay and the English composer John Dunstaple, but together the three were the most celebrated composers of the early European Renaissance. Binchois was born in Mons (modern-day Belgium) to an upper-class family from Binche. His youth is largely unknown, although early chorister training is likely; by late 1419 he had obtained a local organist post. By 1423 he was in Lille and probably a soldier under the Englishman William de la Pole, eventually in Paris and Hainaut. Sometime during the 1420s, Binchois settled in the culturally thriving court of Burgundy under Philip the Good, where he became a subdeacon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Benelux" countries: Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands (, which is singular). Geographically and historically, the area can also include parts of France (such as Nord (French department), Nord and Pas-de-Calais) and the Germany, German regions of East Frisia, Geldern, Guelders and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated regions are considered part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (other), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and head of state of the Holy Roman Empire. The title was held in conjunction with the title of King of Italy#Kingdom of Italy (781–962), King of Italy (''Rex Italiae'') from the 8th to the 16th century, and, almost without interruption, with the title of King of Germany (''Rex Teutonicorum'', ) throughout the 12th to 18th centuries. The Holy Roman Emperor title provided the highest prestige among Christianity in the Middle Ages, medieval Catholic monarchs, because the empire was considered by the Catholic Church to be Translatio imperii, the only successor of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. Thus, in theory and diplomacy, the emperors were considered first among equalsamong other Catholic monarchs across E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in 1437. He was elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) in 1410, and was also King of Bohemia from 1419, as well as prince-elector of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg (1378–1388 and 1411–1415). As the husband of Mary, Queen of Hungary, he was also King of Hungary and Croatia in union with Hungary, Croatia (''jure uxoris'') from 1387. He was the last male member of the House of Luxembourg. Sigismund was the son of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor and his fourth wife Elizabeth of Pomerania. He married Mary, Queen of Hungary in 1385 and was crowned King of Hungary soon after. He fought to restore and maintain authority to the throne. Mary died in 1395, leaving Sigismund the sole ruler of Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary. In 1396, Sigismund led the Battle of Nicopolis, Crusade of Nicopolis but was decisively defeated by the Ottoman Empire. Afterwards, he founded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV (; ; 1383 – 23 February 1447), born Gabriele Condulmer, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 11 March 1431 to his death, in February 1447. Condulmer was a Republic of Venice, Venetian, and a nephew of Pope Gregory XII. In 1431, he was elected pope. His tenure was marked by conflict first with the Colonna family, Colonna, relatives of his predecessor Pope Martin V, and later with the Conciliarism, Conciliar movement. In 1434, due to a complaint by Fernando Calvetos, bishop of the Canary Islands, Eugene IV issued the bull "Creator Omnium", rescinding any recognition of Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal's right to conquer those islands, rescinding any right to Christianize the natives of the island. He Excommunication, excommunicated anyone who enslaved newly Conversion to Christianity, converted Christians, the penalty to stand until the captives were restored to their liberty and possessions. In 1442, he promulgated the bull ''Dudum ad n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the preeminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to the English musicologist Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond.Margaret Bent,The Late-Medieval Motet in ''Companion to Medieval & Renaissance Music'', edited by Tess Knighton and David Fallows, 114–19 (Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1992): 114. . The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts". Etymology In the early 20th century, it was ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its Metropolitan City of Bologna, metropolitan province is home to more than 1 million people. Bologna is most famous for being the home to the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest university in continuous operation,Top Universities ''World University Rankings'' Retrieved 6 January 2010Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |