|
Faraday Cup
A Faraday cup is a metal (conductive) cup designed to catch charged particles. The resulting current can be measured and used to determine the number of ions or electrons hitting the cup. The Faraday cup was named after Michael Faraday who first theorized ions around 1830. Examples of devices which use Faraday cups include space probes (Voyager 1, & 2, Parker Solar Probe, etc.) and mass spectrometers. Faraday cups can also be used to measure charged aerosol particles. Principle of operation When a beam or packet of ions or electrons (e.g. from an electron beam) hits the metallic body of the cup, the apparatus gains a small net charge. The cup can then be discharged to measure a small current proportional to the charge carried by the impinging ions or electrons. By measuring the electric current (the number of electrons flowing through the circuit per second) in the cup, the number of charges can be determined. For a continuous beam of ions (assumed to be singly charged) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
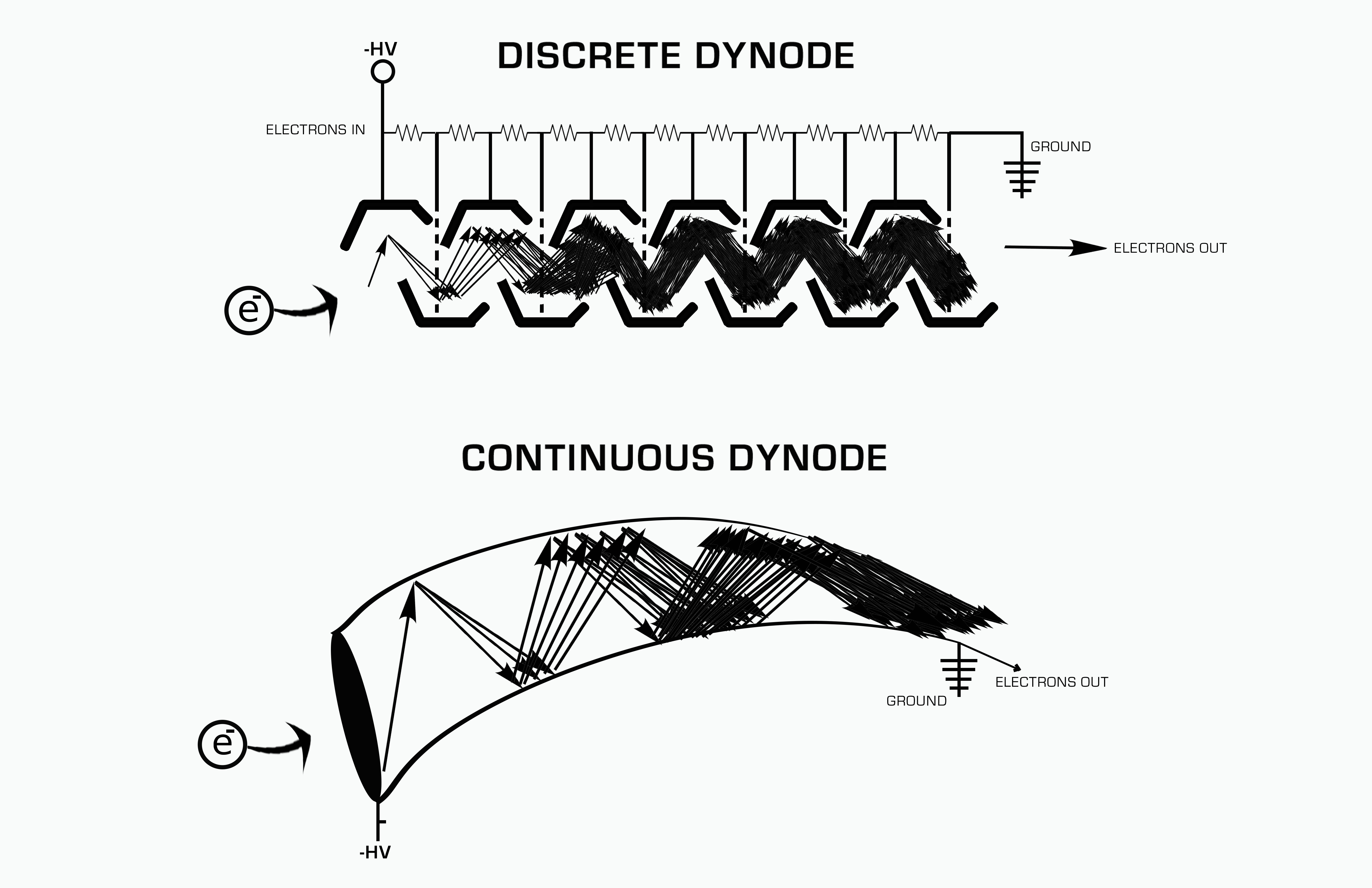
Electron Multiplier
An electron multiplier is a vacuum-tube structure that multiplies incident charges. In a process called secondary emission, a single electron can, when bombarded on secondary-emissive material, induce emission of roughly 1 to 3 electrons. If an electric potential is applied between this metal plate and yet another, the emitted electrons will accelerate to the next metal plate and induce secondary emission of still more electrons. This can be repeated a number of times, resulting in a large shower of electrons all collected by a metal anode, all having been triggered by just one. History In 1930, Russian physicist Leonid Aleksandrovitch Kubetsky proposed a device which used photocathodes combined with dynodes, or secondary electron emitters, in a single tube to remove secondary electrons by increasing the electric potential through the device. The electron multiplier can use any number of dynodes in total, which use a coefficient, σ, and created a gain of σn where n is the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elementary Charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted by , is a fundamental physical constant, defined as the electric charge carried by a single proton (+1 ''e'') or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . In SI units, the coulomb is defined such that the value of the elementary charge is exactly or 160.2176634 zeptocoulombs (zC). Since the 2019 revision of the SI, the seven SI base units are defined in terms of seven fundamental physical constants, of which the elementary charge is one. In the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS), the corresponding quantity is . Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher's oil drop experiment first directly measured the magnitude of the elementary charge in 1909, differing from the modern accepted value by just 0.6%. Under assumptions of the then-disputed atomic theory, the elementary charge had also been indirectly inferred to ~3% accuracy from blackb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Faraday Cage
A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block some electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a mesh of such materials. Faraday cages are named after scientist Michael Faraday, who first constructed one in 1836. Faraday cages work because an external electrical field will cause the electric charges within the cage's conducting material to be distributed in a way that cancels out the field's effect inside the cage. This phenomenon can be used to protect sensitive electronic equipment (for example RF receivers) from external radio frequency interference (RFI) often during testing or alignment of the device. Faraday cages are also used to protect people and equipment against electric currents such as lightning strikes and electrostatic discharges, because the cage conducts electrical current around the outside of the enclosed space and none passes through the interior. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Faraday Cup Electrometer
The Faraday cup electrometer is the simplest form of an electrical aerosol instrument used in aerosol studies. It consists of an electrometer and a filter inside a Faraday cage. Charged particles collected by the filter generate an electric current which is measured by the electrometer. Principle According to Gauss' law, the charge collected on the Faraday cup is the induced charge, that means that the filter does not need to be a conductor. It is typically used to measure particles of unipolar charge, which are particles with a net charge concentration that equals the charge concentration of positively or negatively charged particles. With an aerosol electrometer the transportation of charge by electrical charged aerosol particles can be measured as electric current. In a metal housing (Faraday cup) a particle filter is mounted on an insulator. A Faraday cup is a detector that measures the current in a beam of charged (aerosol) particles. Faraday cups are used e.g. in mass spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nanocoulombmeter
A Coulomb meter is a tool for measuring the electrostatic charge of a material. A Coulombmeter is used in combination with a Faraday cup or a metal probe for taking charge measurements of a material. A Nanocoulombmeter is a Coulombmeter that is capable of measuring electrostatic charge down to the accuracy of a fraction of a nanocoulomb (nC). The electrostatic charge of an object can be measured by placing it inside a Faraday Cup. The charge is transferred to the cup and displayed on the meter's display. The Faraday Cup of the Coulombmeter has an outer, grounded metal shield that surrounds an inner electrode. The inner electrode, which is electrically isolated from the shield, is connected to a meter to measure the charge. In the field of semiconductor design, a coulombmeter consists of a meter used in combination with a metal probe tip to pinpoint locations of excess charge on, for instance, a semiconductor device. This application of a coulombmeter is useful because e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Backscattering
In physics, backscatter (or backscattering) is the reflection of waves, particles, or signals back to the direction from which they came. It is usually a diffuse reflection due to scattering, as opposed to specular reflection as from a mirror, although specular backscattering can occur at normal incidence with a surface. Backscattering has important applications in astronomy, photography, and medical ultrasonography. The opposite effect is forward scatter, e.g. when a translucent material like a cloud diffuses sunlight, giving soft light. Backscatter of waves in physical space Backscattering can occur in quite different physical situations, where the incoming waves or particles are deflected from their original direction by different mechanisms: *Diffuse reflection from large particles and Mie scattering, causing alpenglow and gegenschein, and showing up in weather radar; *Inelastic collisions between electromagnetic waves and the transmitting medium ( Brillouin scattering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Secondary Electrons
Secondary electrons are electrons generated as ionization products. They are called 'secondary' because they are generated by other radiation In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ... (the ''primary'' radiation). This radiation can be in the form of ions, electrons, or photons with sufficiently high energy, i.e. exceeding the ionization potential. Photoelectrons can be considered an example of secondary electrons where the primary radiation are photons; in some discussions photoelectrons with higher energy (>50 eV) are still considered "primary" while the electrons freed by the photoelectrons are "secondary". Applications Secondary electrons are also the main means of viewing images in the scanning electron microscope (SEM). The range of secondary electrons de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Secondary Electron Emission
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature * Secondary emission, of particles ** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products * The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding in a transformer * Secondary (chemistry), a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds * Secondary color, color made from mixing primary colors * Secondary mirror, second mirror element/focusing surface in a reflecting telescope * Secondary craters, often called "secondaries" * Secondary consumer, in ecology * An antiquated name for the Mesozoic in geosciences * Secondary feathers, flight feathers attached to the ulna on the wings of birds Society and culture * Secondary (football), a position in American football and Canadian football * Secondary dominant in music * Secondary education, education which typically takes place after six years of primary education ** Secondary school, the type of school at the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ISM Band
The ISM radio bands are portions of the radio spectrum reserved internationally for ''industrial, scientific, and medical'' (ISM) purposes, excluding applications in telecommunications. Examples of applications for the use of radio frequency (RF) energy in these bands include RF heating, microwave ovens, and medical diathermy machines. The powerful emissions of these devices can create electromagnetic interference and disrupt radio communication using the same frequency, so these devices are limited to certain bands of frequencies. In general, communications equipment operating in ISM bands must tolerate any interference generated by ISM applications, and users have no regulatory protection from ISM device operation in these bands. Despite the intent of the original allocations, in recent years the fastest-growing use of these bands has been for short-range, low-power wireless communications systems, since these bands are often approved for such devices, which can be used w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Faraday Cup Fig
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis. Although Faraday received little formal education, as a self-made man, he was one of the most influential scientists in history. It was by his research on the magnetic field around a conductor carrying a direct current that Faraday established the concept of the electromagnetic field in physics. Faraday also established that magnetism could affect rays of light and that there was an underlying relationship between the two phenomena. the 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. He similarly discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and the laws of electrolysis. His inventions of electromagnetic rotary devices formed the foundation of electric motor technology, and it was largely due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
I-V Characteristic
IV may refer to: Businesses and organizations In the United States *Immigration Voice, an activist organization *Intellectual Ventures, a privately held intellectual property company *InterVarsity Christian Fellowship Elsewhere * Federation of Austrian Industries () *Irish Volunteers, a military organization *Italia Viva, an Italian centrist political party Music *Subdominant, in music theory Recordings * ''IV'' (The Aggrolites album), 2009 * ''IV'' (Angband album), 2020 * ''IV'' (BadBadNotGood album), 2016 * ''IV'' (Black Mountain album), 2016 * ''IV'' (Cypress Hill album), 1998 * ''IV'' (Diamond Rio album), 1996 * ''IV'' (Goatsnake album), 1998 * ''IV'' (Godsmack album), 2006 * ''IV'' (Hiroyuki Sawano album), 2021 * ''I.V.'' (Loma Prieta album), 2012 * ''IV'' (Maylene and the Sons of Disaster album), 2011 * ''IV'' (Ton Steine Scherben album), 1981 * ''IV'' (The Stranglers album), 1980 * ''IV'' (To/Die/For album), 2004 * ''IV'' (Veruca Salt album), 2006 * ''IV'' (Winger album), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |