|
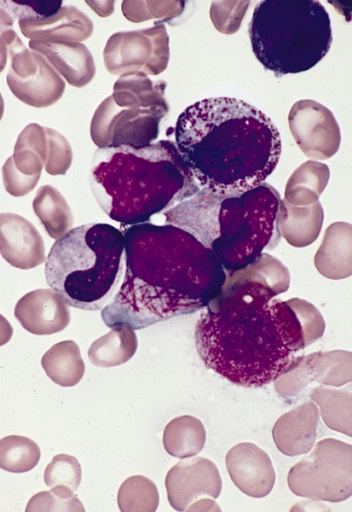
Faggot Cells
Faggot cells are cells normally found in the hypergranular form of acute promyelocytic leukemia (FAB - M3). These promyelocytes (not blast cells) have numerous Auer rods in the cytoplasm which gives the appearance of a bundle of sticks, from which the cells are given their name. See also * Buttock cell Buttock cells are cells having a notched appearance that are found in certain malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (including follicular lymphoma), mycosis fungoides, and Sézary syndrome. See also * Clue cell * Koilocyte * Large cell ... References {{Reflist Human cells Pathology Hematology Acute myeloid leukemia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faggot Cell In AML-M3
''Faggot'', often shortened to ''fag'', is a slur in the English language that was used to refer to gay men but its meaning has expanded to other members of the queer community. In American youth culture around the turn of the 21st century, its meaning extended as a broader reaching insult more related to masculinity and group power structure. The usage of ''fag'' and ''faggot'' has spread from the United States to varying extents elsewhere in the English-speaking world (especially the UK) through mass culture, including film, music, and the Internet. Etymology The first recorded use of ''faggot'' as a pejorative term for gay men was in the 1914 ''A Vocabulary of Criminal Slang'', while the shortened form ''fag'' first appeared in 1923 in ''The Hobo'' by Nels Anderson. The term faggot originated in late 16th-century English as an insult directed at women, particularly older women. Its association with homosexuality likely stems from linguistic patterns that use feminizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML, APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In APL, there is an abnormal accumulation of immature granulocytes called promyelocytes. The disease is characterized by a t(15;17) chromosomal translocation involving the retinoic acid receptor alpha (''RARA'') gene and is distinguished from other forms of AML by its responsiveness to all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA; also known as tretinoin) therapy. Acute promyelocytic leukemia was first characterized in 1957 by French and Norwegian physicians as a hyperacute fatal illness, with a median survival time of less than a week. Today, prognoses have drastically improved; 10-year survival rates are estimated to be approximately 80-90% according to one study. Signs and symptoms The symptoms tend to be similar to AML in general with the following being possible symptoms: * Anemia * Fatigue * Weakness * Chills * Depression * Difficulty breathing ( dyspnea) * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
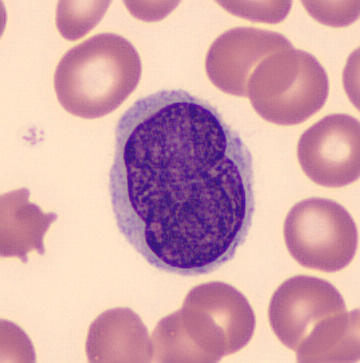
Auer Rods
Auer rods (or Auer bodies) are large, crystalline cytoplasmic inclusion bodies sometimes observed in myeloid blast cells during acute myeloid leukemia, acute promyelocytic leukemia, high-grade myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders. Composed of fused lysosomes and rich in lysosomal enzymes, Auer rods are azurophilic and can resemble needles, commas, diamonds, rectangles, corkscrews, or (rarely) granules. Eponym Although Auer rods are named for American physiologist John Auer, they were first described in 1905 by Canadian physician Thomas McCrae, then at Johns Hopkins Hospital, as Auer himself acknowledged in his 1906 paper. Both McCrae and Auer mistakenly thought that the cells containing the rods were lymphoblasts. Additional images Image:Myeloblast with Auer rod smear 2010-01-27.JPG, Bone marrow aspirate showing acute myeloid leukemia with Auer rods in several blasts Image:Myeloblast whith Auer rod 2009-09-21.JPG Image:Myeloblast with Auer Rod smear 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faggot (unit)
A faggot, in the meaning of "bundle", is an archaic English unit applied to bundles of certain items. Alternate spellings in Early Modern English include ''fagate, faget, fagett, faggott, fagot, fagatt, fagott, ffagott,'' and ''faggat''. A similar term is found in other languages (e.g. Latin: ''fascis''). Background Sometimes called a short faggot, a faggot of sticks equals a bundle of wood sticks or billets that is in length and in circumference. The measurement was standardised in ordinances by 1474. A small short faggot was also called a nicket. A brush-faggot (sometimes shortened to brush) was a bundle of similar size made of brushwood. A long faggot of sticks equals a bundle larger than long. In a book on slang used at Winchester College fire-dogs were fire basket ( andirons) that could hold long faggots, and half-faggots were smaller andirons that could only hold short faggots and were later converted for use with coal. A long faggot was also called a kidd faggot,Yax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
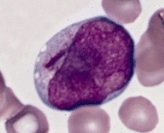
Buttock Cell
Buttock cells are cells having a notched appearance that are found in certain malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (including follicular lymphoma), mycosis fungoides, and Sézary syndrome. See also * Clue cell * Koilocyte * Large cell Large cell is a term used in oncology. It does not refer to a particular type of cell; rather it refers to cells that are larger than would be normally expected for that type. It is frequently used when describing lymphoma and lung cancer. It was ... References Blood cells Lymphoma {{oncology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Cells
The list of human cell types provides an enumeration and description of the various specialized cells found within the human body, highlighting their distinct functions, characteristics, and contributions to overall physiological processes. Cells may be classified by their physiological function, histology (microscopic anatomy), lineage, or gene expression. Total number of cells The adult human body is estimated to contain about 30 trillion (3×1013) human cells, with the number varying between 20 and 100 trillion depending on factors such as sex, age, and weight. Additionally, there are approximately an equal number of bacterial cells. The exact count of human cells has not yet been empirically measured in its entirety and is estimated using different approaches based on smaller samples of empirical observation. It is generally assumed that these cells share features with each other and thus may be organized as belonging to a smaller number of types. Classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |