|
Exotic Option
In finance, an exotic option is an option which has features making it more complex than commonly traded vanilla options. Like the more general exotic derivatives they may have several triggers relating to determination of payoff. An exotic option may also include a non-standard underlying instrument, developed for a particular client or for a particular market. Exotic options are more complex than options that trade on an exchange, and are generally traded over-the-counter. Etymology The term "exotic option" was popularized by Mark Rubinstein's 1990 working paper (published 1992, with Eric Reiner) "Exotic Options", with the term based either on exotic wagers in horse racing, or due to the use of international terms such as "Asian option", suggesting the "exotic Orient". Journalist Brian Palmer used the "successful $1 bet on the superfecta" in the 2010 Kentucky Derby that "paid a whopping $101,284.60" as an example of the controversial high-risk, high-payout exotic bets th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lookback Option
Lookback options, in the terminology of finance, are a type of exotic option with path dependency, among many other kind of options. The payoff depends on the optimal (maximum or minimum) underlying asset's price occurring over the life of the option. The option allows the holder to "look back" over time to determine the payoff. There exist two kinds of lookback options: with floating strike and with fixed strike. Lookback option with floating strike As the name introduces it, the option's strike price is floating and determined at maturity. The floating strike is the optimal value of the underlying asset's price during the option life. The payoff is the maximum difference between the market asset's price at maturity and the floating strike. For the call, the strike price is fixed at the asset's lowest price during the option's life, and, for the put, it is fixed at the asset's highest price. Note that these options are not really options, as they will be always exercised by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are ''linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the so-called demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed. The annual interest rate is the rate over a period of one year. Other interest rates apply over different periods, such as a month or a day, but they are usually annualized. The interest rate has been characterized as "an index of the preference . . . for a dollar of present ncomeover a dollar of future income." The borrower wants, or needs, to have money sooner rather than later, and is willing to pay a fee—the interest rate—for that privilege. Influencing factors Interest rates vary according to: * the government's directives to the central bank to accomplish the government's goals * the currency of the principal sum lent or borrowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Credit Rating
A credit rating is an evaluation of the credit risk of a prospective debtor (an individual, a business, company or a government), predicting their ability to pay back the debt, and an implicit forecast of the likelihood of the debtor defaulting. The credit rating represents an evaluation of a credit rating agency of the qualitative and quantitative information for the prospective debtor, including information provided by the prospective debtor and other non-public information obtained by the credit rating agency's analysts. Credit reporting (or credit score) – is a subset of credit rating – it is a numeric evaluation of an ''individual's'' credit worthiness, which is done by a credit bureau or consumer credit reporting agency. Sovereign credit ratings A sovereign credit rating is the credit rating of a sovereign entity, such as a national government. The sovereign credit rating indicates the risk level of the investing environment of a country and is used by investors when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company is divided, or these shares considered together" "When a company issues shares or stocks ''especially AmE'', it makes them available for people to buy for the first time." (Especially in American English, the word "stocks" is also used to refer to shares.) A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares. This typically entitles the shareholder (stockholder) to that fraction of the company's earnings, proceeds from liquidation of assets (after discharge of all senior claims such as secured and unsecured debt), or voting power, often dividing these up in proportion to the amount of money each stockholder has invested. Not all stock is necessarily equal, as certain clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
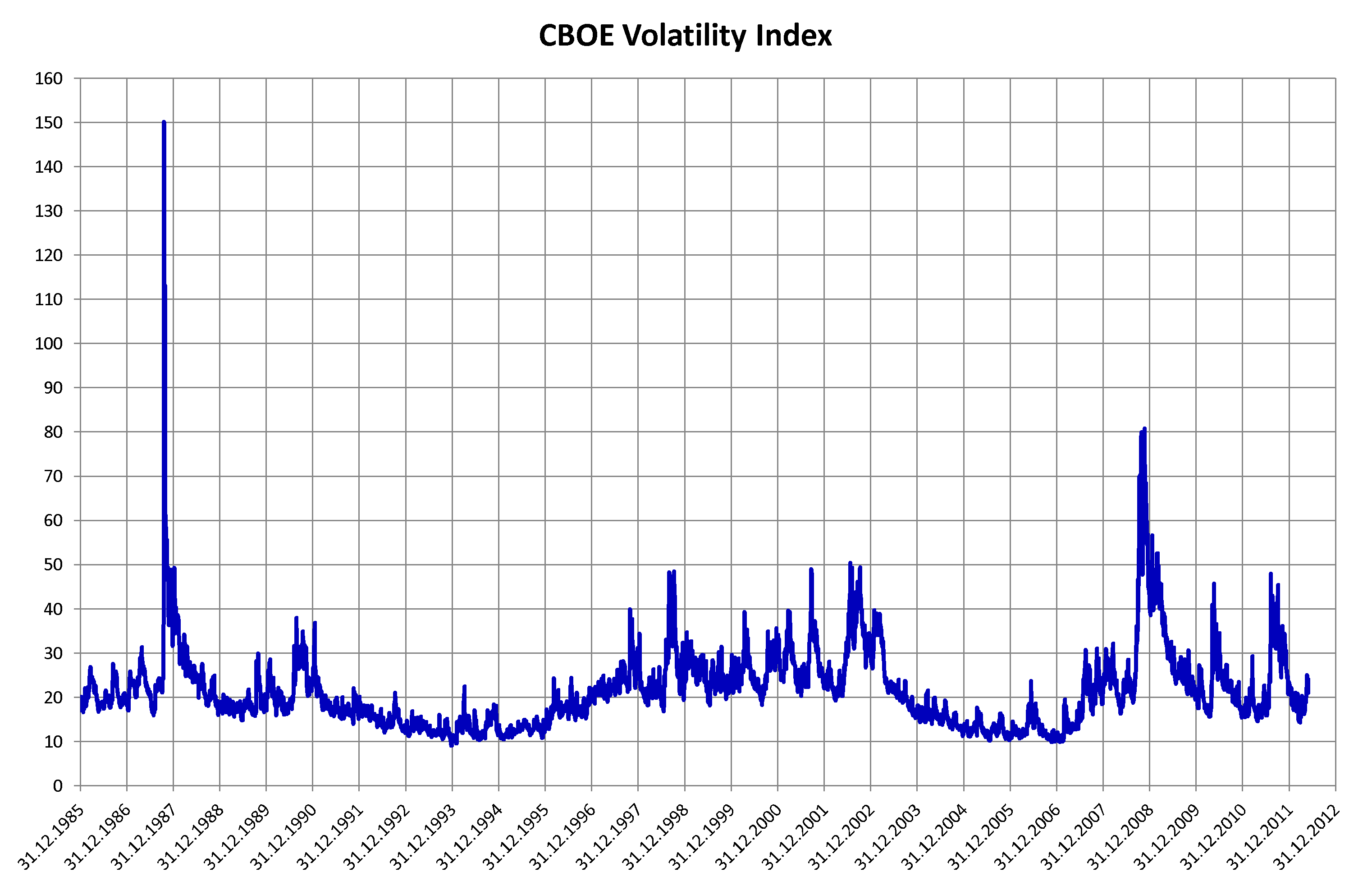
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn calculated using the sum of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convertible Bond
In finance, a convertible bond or convertible note or convertible debt (or a convertible debenture if it has a maturity of greater than 10 years) is a type of bond that the holder can convert into a specified number of shares of common stock in the issuing company or cash of equal value. It is a hybrid security with debt- and equity-like features. It originated in the mid-19th century, and was used by early speculators such as Jacob Little and Daniel Drew to counter market cornering. Convertible bonds are most often issued by companies with a low credit rating and high growth potential. Convertible bonds are also considered debt security because the companies agree to give fixed or floating interest rate as they do in common bonds for the funds of investor. To compensate for having additional value through the option to convert the bond to stock, a convertible bond typically has a coupon rate lower than that of similar, non-convertible debt. The investor receives the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quanto
A quanto is a type of derivative in which the underlying is denominated in one currency, but the instrument itself is settled in another currency at some rate. Such products are attractive for speculators and investors who wish to have exposure to a foreign asset, but without the corresponding exchange rate risk. Quantos are attractive because they shield the purchaser from exchange rate fluctuations. If a US investor were to invest directly in the Japanese stocks that comprise the Nikkei, he would be exposed to both fluctuations in the Nikkei index and fluctuations in the USD/JPY exchange rate. Essentially, a quanto has an embedded currency forward with a variable notional amount. It is that variable notional amount that give quantos their name—"quanto" is short for "quantity adjusting option". Quanto options have both the strike price and underlier denominated in the foreign currency. At exercise, the value of the option is calculated as the option's intrinsic value in the forei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cash Or Share Option
Cash or Share Option is a specialized form of warrant where the settlement is either cash or physical delivery of shares depending if the option expires in the money or out of the money. Normally, the holder of the certificate receives the exercise price in cash when option is in the money, that is price of the underlying at expiry is equal or above the exercise price, and physical delivery of the underlying when the option is out of the money In finance, moneyness is the relative position of the current price (or future price) of an underlying asset (e.g., a stock) with respect to the strike price of a derivative, most commonly a call option or a put option. Moneyness is firstly a thr ..., that is the price of the underlying at expiry is below the exercise price. Then the holder is the one giving the option. {{Derivatives market Options (finance) Equity securities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moneyness
In finance, moneyness is the relative position of the current price (or future price) of an underlying asset (e.g., a stock) with respect to the strike price of a derivative, most commonly a call option or a put option. Moneyness is firstly a three-fold classification: * If the derivative would have positive intrinsic value if it were to expire today, it is said to be in the money; * If the derivative would be worthless if expiring with the underlying at its current price, it is said to be out of the money; * And if the current underlying price and strike price are equal, the derivative is said to be at the money. There are two slightly different definitions, according to whether one uses the current price (spot) or future price (forward), specified as "at the money spot" or "at the money forward", etc. This rough classification can be quantified by various definitions to express the moneyness as a number, measuring how far the asset is in the money or out of the money with re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basket Option
A basket option is a financial derivative, more specifically an exotic option, whose underlying is a weighted sum or average of different assets that have been grouped together in a basket. A basket option is similar to an index option, where a number of stocks have been grouped together in an index and the option is based on the price of the index, but differs in that the members and weightings of an index can change over time while those in a basket option do not. Unlike a rainbow option which considers a group of assets but ultimately pays out on the level of one, a basket option is written on a basket of underlying assets but will pay out on a weighted average gain of the basket as a whole. Like rainbow options basket options are most commonly written on a basket of equity indices, though they are frequently written on a basket of individual equities as well. For example, a call option could be written on a basket of ten healthcare stocks, where the basket was composed of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |