|
Extreme Learning Machine
Extreme learning machines are feedforward neural networks for classification, regression, clustering, sparse approximation, compression and feature learning with a single layer or multiple layers of hidden nodes, where the parameters of hidden nodes (not just the weights connecting inputs to hidden nodes) need to be tuned. These hidden nodes can be randomly assigned and never updated (i.e. they are random projection but with nonlinear transforms), or can be inherited from their ancestors without being changed. In most cases, the output weights of hidden nodes are usually learned in a single step, which essentially amounts to learning a linear model. The name "extreme learning machine" (ELM) was given to such models by Guang-Bin Huang who originally proposed for the networks with any type of nonlinear piecewise continuous hidden nodes including biological neurons and different type of mathematical basis functions. The idea for artificial neural networks goes back to Frank Rosenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Feedforward Neural Network
Feedforward refers to recognition-inference architecture of neural networks. Artificial neural network architectures are based on inputs multiplied by weights to obtain outputs (inputs-to-output): feedforward. Recurrent neural networks, or neural networks with loops allow information from later processing stages to feed back to earlier stages for sequence processing. However, at every stage of inference a feedforward multiplication remains the core, essential for backpropagationRumelhart, David E., Geoffrey E. Hinton, and R. J. Williams.Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. David E. Rumelhart, James L. McClelland, and the PDP research group. (editors), Parallel distributed processing: Explorations in the microstructure of cognition, Volume 1: Foundation. MIT Press, 1986. or backpropagation through time. Thus neural networks cannot contain feedback like negative feedback or positive feedback where the outputs feed back to the ''very same'' inputs and modify them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
QR Decomposition
In linear algebra, a QR decomposition, also known as a QR factorization or QU factorization, is a decomposition of a matrix ''A'' into a product ''A'' = ''QR'' of an orthonormal matrix ''Q'' and an upper triangular matrix ''R''. QR decomposition is often used to solve the linear least squares (LLS) problem and is the basis for a particular eigenvalue algorithm, the QR algorithm. Cases and definitions Square matrix Any real square matrix ''A'' may be decomposed as : A = QR, where ''Q'' is an orthogonal matrix (its columns are orthogonal unit vectors meaning and ''R'' is an upper triangular matrix (also called right triangular matrix). If ''A'' is invertible, then the factorization is unique if we require the diagonal elements of ''R'' to be positive. If instead ''A'' is a complex square matrix, then there is a decomposition ''A'' = ''QR'' where ''Q'' is a unitary matrix (so the conjugate transpose If ''A'' has ''n'' linearly independent columns, then the first ''n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Random Projection
In mathematics and statistics, random projection is a technique used to reduce the dimensionality of a set of points which lie in Euclidean space. According to theoretical results, random projection preserves distances well, but empirical results are sparse. They have been applied to many natural language tasks under the name random indexing. Dimensionality reduction Dimensionality reduction, as the name suggests, is reducing the number of random variables using various mathematical methods from statistics and machine learning. Dimensionality reduction is often used to reduce the problem of managing and manipulating large data sets. Dimensionality reduction techniques generally use linear transformations in determining the intrinsic dimensionality of the manifold as well as extracting its principal directions. For this purpose there are various related techniques, including: principal component analysis, linear discriminant analysis, canonical correlation analysis, discrete cosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reservoir Computing
Reservoir computing is a framework for computation derived from recurrent neural network theory that maps input signals into higher dimensional computational spaces through the dynamics of a fixed, non-linear system called a reservoir. After the input signal is fed into the reservoir, which is treated as a "black box," a simple readout mechanism is trained to read the state of the reservoir and map it to the desired output. The first key benefit of this framework is that training is performed only at the readout stage, as the reservoir dynamics are fixed. The second is that the computational power of naturally available systems, both classical and quantum mechanical, can be used to reduce the effective computational cost. History The first examples of reservoir neural networks demonstrated that randomly connected recurrent neural networks could be used for sensorimotor sequence learning, and simple forms of interval and speech discrimination. In these early models the memory in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
RBF Network
In the field of mathematical modeling, a radial basis function network is an artificial neural network that uses radial basis functions as activation functions. The output of the network is a linear combination of radial basis functions of the inputs and neuron parameters. Radial basis function networks have many uses, including function approximation, time series prediction, classification, and system control. They were first formulated in a 1988 paper by Broomhead and Lowe, both researchers at the Royal Signals and Radar Establishment. Network architecture Radial basis function (RBF) networks typically have three layers: an input layer, a hidden layer with a non-linear RBF activation function and a linear output layer. The input can be modeled as a vector of real numbers \mathbf \in \mathbb^n. The output of the network is then a scalar function of the input vector, \varphi : \mathbb^n \to \mathbb , and is given by :\varphi(\mathbf) = \sum_^N a_i \rho(, , \mathbf-\mathbf_i, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Black-box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The term can be used to refer to many inner workings, such as those of a transistor, an engine, an algorithm, the human brain, or an institution or government. To analyze an open system with a typical "black box approach", only the behavior of the stimulus/response will be accounted for, to infer the (unknown) ''box''. The usual representation of this "black box system" is a data flow diagram centered in the box. The opposite of a black box is a system where the inner components or logic are available for inspection, which is most commonly referred to as a white box (sometimes also known as a "clear box" or a "glass box"). History The modern meaning of the term "black box" seems to have entered the English language around 1945. In electroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
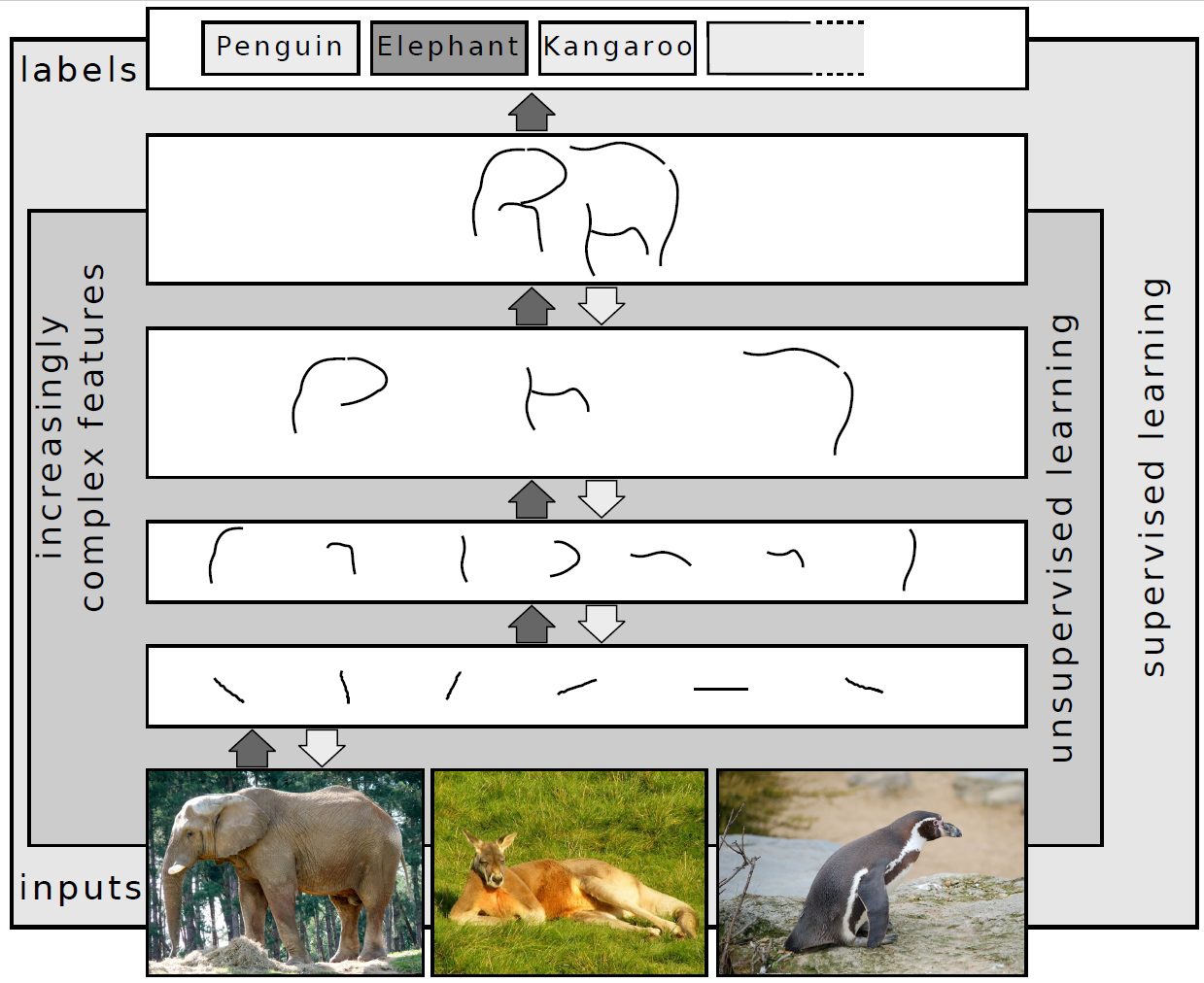
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Design Matrix
In statistics and in particular in regression analysis, a design matrix, also known as model matrix or regressor matrix and often denoted by X, is a matrix of values of explanatory variables of a set of objects. Each row represents an individual object, with the successive columns corresponding to the variables and their specific values for that object. The design matrix is used in certain statistical models, e.g., the general linear model. It can contain indicator variables (ones and zeros) that indicate group membership in an ANOVA, or it can contain values of continuous variables. The design matrix contains data on the independent variables (also called explanatory variables), in a statistical model that is intended to explain observed data on a response variable (often called a dependent variable). The theory relating to such models uses the design matrix as input to some linear algebra : see for example linear regression. A notable feature of the concept of a design matrix i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Least-squares Fit
The method of least squares is a mathematical optimization technique that aims to determine the best fit function by minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed values and the predicted values of the model. The method is widely used in areas such as regression analysis, curve fitting and data modeling. The least squares method can be categorized into linear and nonlinear forms, depending on the relationship between the model parameters and the observed data. The method was first proposed by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1805 and further developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss. History Founding The method of least squares grew out of the fields of astronomy and geodesy, as scientists and mathematicians sought to provide solutions to the challenges of navigating the Earth's oceans during the Age of Discovery. The accurate description of the behavior of celestial bodies was the key to enabling ships to sail in open seas, where sailors could no longer rely on la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaussian Noise
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below. There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymous adjective ''Gaussian'' is pronounced . Mathematics Algebra and linear algebra Geometry and differential geometry Number theory Cyclotomic fields *Gaussian period *Gaussian rational *Gauss sum, an exponential sum over Dirichlet characters **Elliptic Gauss sum, an analog of a Gauss sum **Quadratic Gauss sum Analysis, numerical analysis, vector calculus and calculus of variations Complex analysis and convex analysis *Gauss–Lucas theorem *Gauss's continued fraction, an analytic continued fraction derived from the hypergeometric functions *Gauss's test, Gauss's criterion – described oEncyclopedia of Mathematics*Gauss's hypergeometric theorem, an identity on hypergeometric series *Gauss plane Statistics *Gaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |