|
Extensor Hallucis Brevis
The extensor hallucis brevis is a muscle on the top of the foot that helps to extend the big toe. Structure The extensor hallucis brevis is essentially the medial part of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle. Some anatomists have debated whether these two muscles are distinct entities. The extensor hallucis brevis arises from the calcaneus and inserts on the proximal phalanx of the digit 1 (the big toe). Nerve supply Nerve supplied by lateral terminal branch of Deep Peroneal Nerve (deep fibular nerve) (proximal sciatic branches S1, S2). Same innervation of Extensor Digitorum Brevis Function The extensor hallucis brevis helps to extend the big toe. See also * Extensor digitorum brevis The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (sometimes EDB) is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4. Structure The muscle originates from the forepart of the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneus (in front ... * Extensor hallucis longus Additional im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallux
Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plantigrade''; '' unguligrade'' animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes. Structure There are normally five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the proximal, middle, and distal, with the exception of the big toe (). For a minority of people, the little toe also is missing a middle bone. The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. The joints between each phalanx are the interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanx bone of each toe articulates with the metatarsal bone of the foot at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Each toe is surrounded by skin, and present on all five toes is a toenail. The toes are, from medial to lateral: * the first toe, also known as the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsalis Pedis Artery
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery (dorsal artery of foot) is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space (as the first dorsal metatarsal artery and the deep plantar artery). It carries oxygenated blood to the Dorsum (biology), dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during Anesthesia, anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve. Structure The dorsalis pedis artery is located 1/3 from malleolus, medial malleolus of the ankle. It arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint and is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery. It ends at the proximal part of the first intermetatarsal space. Here, it divides into two branches, the first dorsal metatarsal artery, and the deep plantar artery. It is covered by skin and fascia, but is fairly superficial. The dorsalis pedis communicates with the plantar blood supply of the foot through the deep plantar artery. Along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Fibular Nerve
The deep fibular nerve (also known as deep peroneal nerve) begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a ''lateral'' and a '' medial terminal branch''. Structure Lateral side of the leg The deep fibular nerve is the nerve of the anterior compartment of the leg and the dorsum of the foot. It is one of the terminal branches of the common fibular nerve. It corresponds to the posterior interosseus nerve of the forearm. It begins at the lateral side of the fibula bone, and then enters the anterior compartment by piercing the anterior intermuscular septum. It then pierces the extensor digitorum longus and lies next to the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
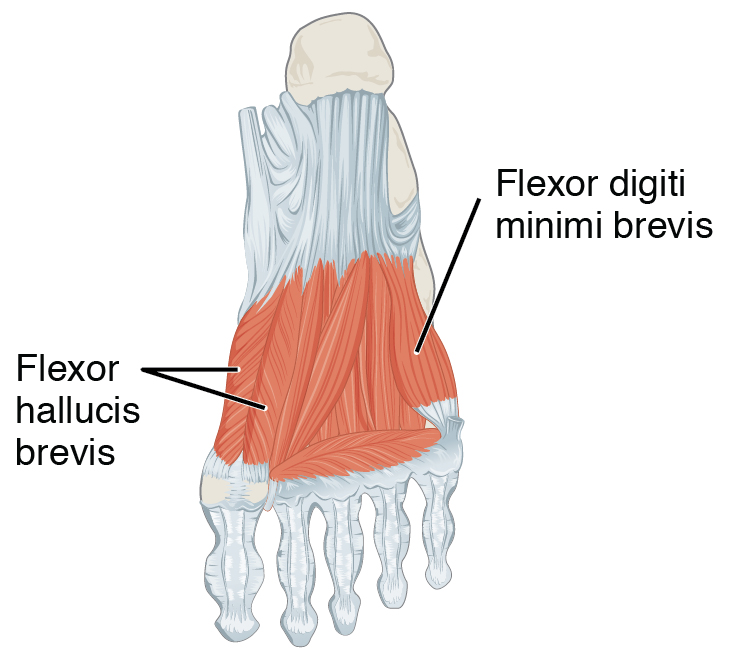
Flexor Hallucis Brevis Muscle
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe. Structure Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe, a sesamoid bone being present in each tendon at its insertion. The medial portion is blended with the abductor hallucis muscle previous to its insertion; the lateral portion (sometimes described as the first plantar interosseus) with the adductor hallucis muscle. The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle lies in a groove between the two. Its tendon usually contains two sesamoid bones at the point under the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Innervation Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Toe
Toes are the Digit (anatomy), digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plantigrade''; ''unguligrade'' animals are those that walk on hoof, hooves at the tips of their toes. Structure There are normally five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, proximal, middle, and distal, with the exception of the big toe (). For a minority of people, the little toe also is missing a middle bone. The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. The joints between each phalanx are the Interphalangeal joints of foot, interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanx bone of each toe articulates with the metatarsal bone of the foot at the Metatarsophalangeal joints, metatarsophalangeal joint. Each toe is surrounded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (sometimes EDB) is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4. Structure The muscle originates from the forepart of the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneus (in front of the groove for the peroneus brevis tendon), from the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament and the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum. The fibres pass obliquely forwards and medially across the dorsum of the foot and end in four tendons. The medial part of the muscle, also known as extensor hallucis brevis, ends in a tendon which crosses the dorsalis pedis artery and inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe. The other three tendons insert into the lateral sides of the tendons of extensor digitorum longus for the second, third and fourth toes. Nerve supply Nerve supply: lateral terminal branch of Deep Peroneal Nerve (deep fibular nerve) (proximal sciatic branches L4-L5, but most clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (sometimes EDB) is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4. Structure The muscle originates from the forepart of the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneus (in front of the groove for the peroneus brevis tendon), from the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament and the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum. The fibres pass obliquely forwards and medially across the dorsum of the foot and end in four tendons. The medial part of the muscle, also known as extensor hallucis brevis, ends in a tendon which crosses the dorsalis pedis artery and inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe. The other three tendons insert into the lateral sides of the tendons of extensor digitorum longus for the second, third and fourth toes. Nerve supply Nerve supply: lateral terminal branch of Deep Peroneal Nerve (deep fibular nerve) (proximal sciatic branches L4-L5, but most clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Hallucis Longus
The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion. Structure The muscle ends as a tendon of insertion. The tendon passes through a distinct compartment in the inferior extensor retinaculum of foot. It crosses anterior tibial vessels lateromedially near the bend of the ankle. In the foot, its tendon is situated at along the medial side of the dorsum of the foot. Opposite the metatarsophalangeal articulation, the tendon gives off a thin prolongation on either side, to cover the surface of the joint. An expansion from the medial side of the tendon is usually inserted into the base of the proximal phalanx. Origin The extensor hallucis longus muscle arises from the middle portion of the anterior surface of the fibula and adjacent interosseous membrane of the leg. Its origin is medial to the ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |