|
Expectminimax Tree
The expectiminimax algorithm is a variation of the minimax algorithm, for use in artificial intelligence systems that play two-player zero-sum games, such as backgammon, in which the outcome depends on a combination of the player's skill and chance elements such as dice rolls. In addition to "min" and "max" nodes of the traditional minimax tree, this variant has "chance" ("move by nature") nodes, which take the expected value of a random event occurring. In game theory terms, an expectiminimax tree is the game tree of an extensive-form game of perfect, but incomplete information. In the traditional minimax method, the levels of the tree alternate from max to min until the depth limit of the tree has been reached. In an expectiminimax tree, the "chance" nodes are interleaved with the max and min nodes. Instead of taking the max or min of the utility values of their children, chance nodes take a weighted average, with the weight being the probability that child is reached. The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Algorithm
In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm designed to solve a search problem. Search algorithms work to retrieve information stored within particular data structure, or calculated in the Feasible region, search space of a problem domain, with Continuous or discrete variable, either discrete or continuous values. Although Search engine (computing), search engines use search algorithms, they belong to the study of information retrieval, not algorithmics. The appropriate search algorithm to use often depends on the data structure being searched, and may also include prior knowledge about the data. Search algorithms can be made faster or more efficient by specially constructed database structures, such as search trees, hash maps, and database indexes. Search algorithms can be classified based on their mechanism of searching into three types of algorithms: linear, binary, and hashing. Linear search algorithms check every record for the one associated with a target key i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Michie
Donald Michie (; 11 November 1923 – 7 July 2007) was a British researcher in artificial intelligence. During World War II, Michie worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, contributing to the effort to solve " Tunny", a German teleprinter cipher. He founded The Turing Institute in Glasgow in 1982, alongside Peter Mowforth and Tim Niblett. In 1984, the institute worked under contract from Radian Corp to develop code for the Space Shuttle auto-lander. Early life and education Michie was born in Rangoon, Burma. He attended Rugby School and won a scholarship to study classics at Balliol College, Oxford. In early 1943, however, looking for some way to contribute to the war effort, Michie instead attempted to enrol on a Japanese language course in Bedford for intelligence officers. On arrival, it transpired that he had been misinformed, and instead he trained in cryptography, displaying a natural aptitude for the subject. Six weeks later, he was recr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Artificial Intelligence
In video games, artificial intelligence (AI) is used to generate responsive, adaptive or intelligent behaviors primarily in non-playable characters (NPCs) similar to human-like intelligence. Artificial intelligence has been an integral part of video games since their inception in 1948, first seen in the game ''Nim''. AI in video games is a distinct subfield and differs from academic AI. It serves to improve the game-player experience rather than machine learning or decision making. During the golden age of arcade video games the idea of AI opponents was largely popularized in the form of graduated difficulty levels, distinct movement patterns, and in-game events dependent on the player's input. Modern games often implement existing techniques such as pathfinding and decision trees to guide the actions of NPCs. AI is often used in mechanisms which are not immediately visible to the user, such as data mining and procedural-content generation. One of the most infamous examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Algorithms
In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm designed to solve a search problem. Search algorithms work to retrieve information stored within particular data structure, or calculated in the search space of a problem domain, with either discrete or continuous values. Although search engines use search algorithms, they belong to the study of information retrieval, not algorithmics. The appropriate search algorithm to use often depends on the data structure being searched, and may also include prior knowledge about the data. Search algorithms can be made faster or more efficient by specially constructed database structures, such as search trees, hash maps, and database indexes. Search algorithms can be classified based on their mechanism of searching into three types of algorithms: linear, binary, and hashing. Linear search algorithms check every record for the one associated with a target key in a linear fashion. Binary, or half-interval, searches repeatedly target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, expectation operator, mathematical expectation, mean, expectation value, or first Moment (mathematics), moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean, mean of the possible values a random variable can take, weighted by the probability of those outcomes. Since it is obtained through arithmetic, the expected value sometimes may not even be included in the sample data set; it is not the value you would expect to get in reality. The expected value of a random variable with a finite number of outcomes is a weighted average of all possible outcomes. In the case of a continuum of possible outcomes, the expectation is defined by Integral, integration. In the axiomatic foundation for probability provided by measure theory, the expectation is given by Lebesgue integration. The expected value of a random variable is often denoted by , , or , with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
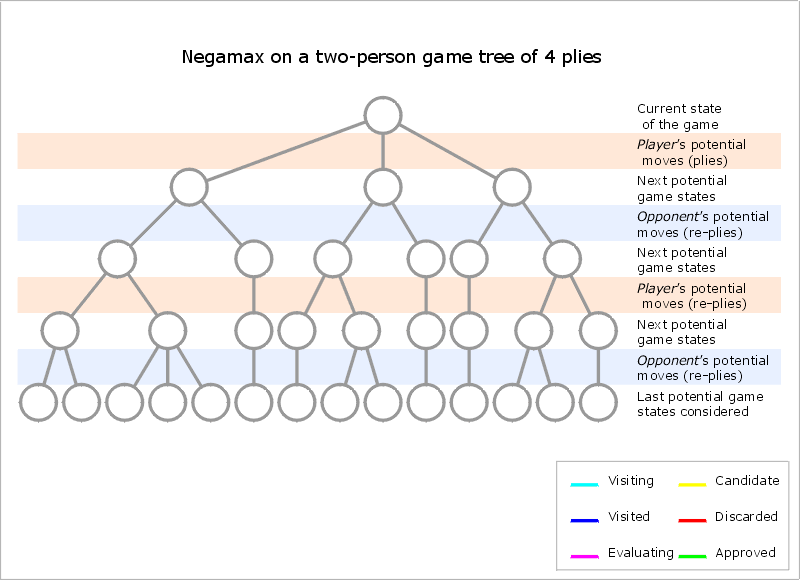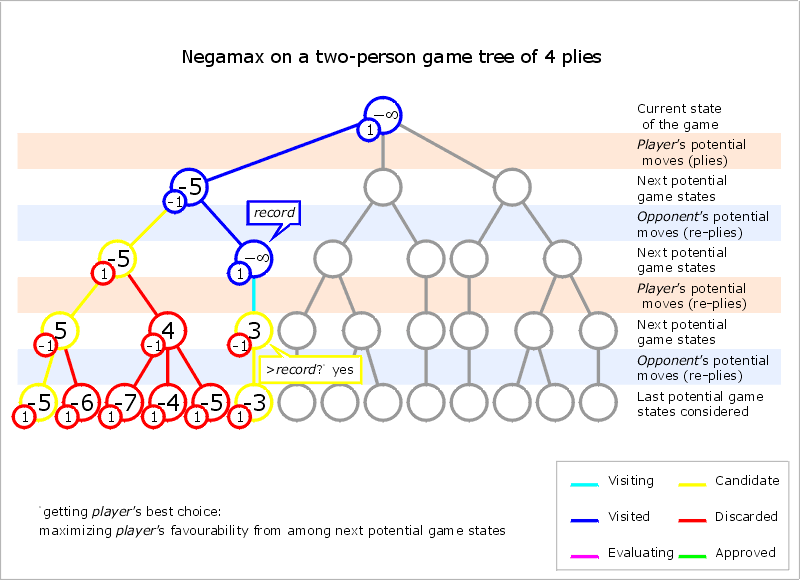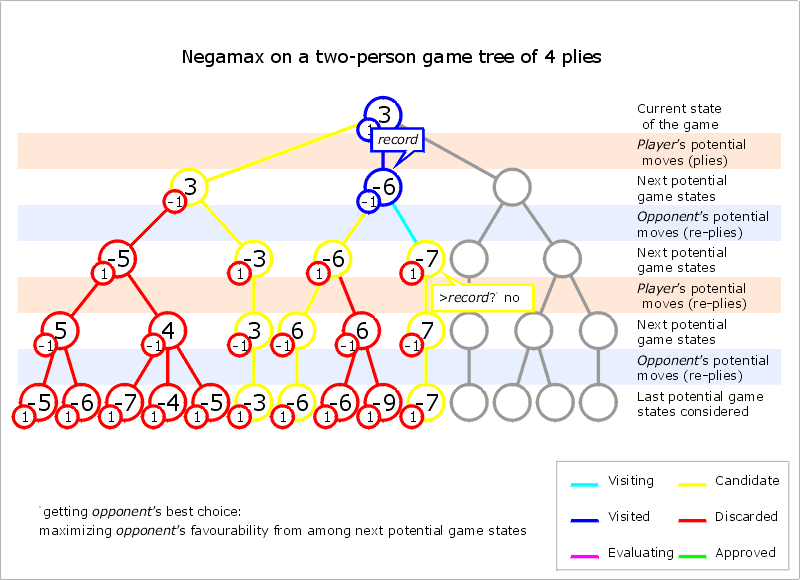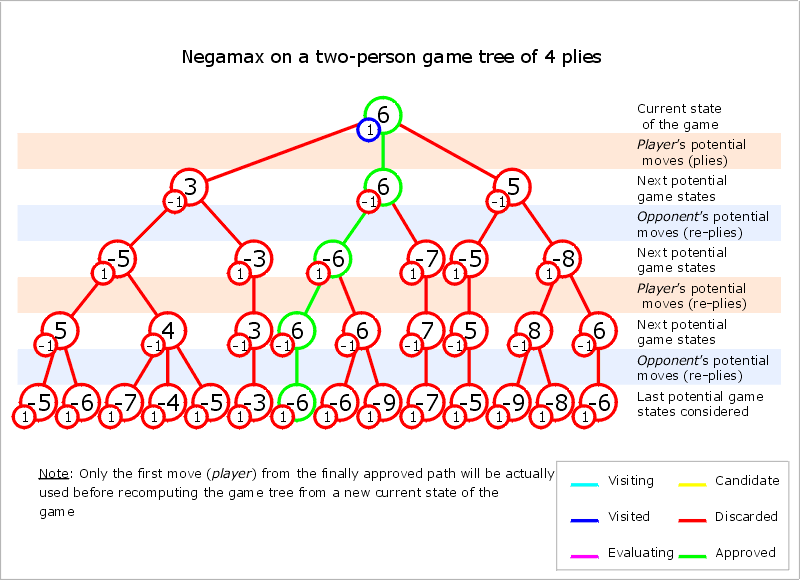
Negamax
Negamax search is a variant form of minimax search that relies on the Zero-sum (Game theory), zero-sum property of a two-player game. This algorithm relies on the fact that to simplify the implementation of the minimax algorithm. More precisely, the value of a position to player A in such a game is the negation of the value to player B. Thus, the player on move looks for a move that maximizes the negation of the value resulting from the move: this successor position must by definition have been valued by the opponent. The reasoning of the previous sentence works regardless of whether A or B is on move. This means that a single procedure can be used to value both positions. This is a coding simplification over minimax, which requires that A selects the move with the maximum-valued successor while B selects the move with the minimum-valued successor. It should not be confused with negascout, an algorithm to compute the minimax or negamax value quickly by clever use of alpha–beta p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha–beta Pruning
Alpha–beta pruning is a search algorithm that seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the Minimax#Minimax algorithm with alternate moves, minimax algorithm in its game tree, search tree. It is an adversarial search algorithm used commonly for machine playing of two-player Combinatorial game theory, combinatorial games (Tic-tac-toe, Chess, Connect 4, etc.). It stops evaluating a move when at least one possibility has been found that proves the move to be worse than a previously examined move. Such moves need not be evaluated further. When applied to a standard minimax tree, it returns the same move as minimax would, but prunes away branches that cannot possibly influence the final decision. History John McCarthy during the Dartmouth workshop, Dartmouth Workshop met Alex Bernstein of IBM, who was writing a chess program. McCarthy invented alpha–beta search and recommended it to him, but Bernstein was "unconvinced". Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon who us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimax
Minimax (sometimes Minmax, MM or saddle point) is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, combinatorial game theory, statistics, and philosophy for ''minimizing'' the possible loss function, loss for a Worst-case scenario, worst case (''max''imum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" – to maximize the minimum gain. Originally formulated for several-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. Game theory In general games The maximin value is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action. Its formal definition is: :\underline = \max_ \min_ W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-beta Pruning
Alphabeta or Alpha Beta may also refer to: * Alphabeta, an Israeli musical group * Alpha Beta, a former chain of Californian supermarkets * The Greek alphabet, from ''Alpha'' (Αα) and ''Beta'' (Ββ), the first two letters * Alpha and beta anomers (chemistry) * Alpha–beta pruning, a type of search algorithm * Alpha–beta transformation, a mathematical transformation in electrical engineering * α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compound, a class of organic compounds * Alpha beta filter, a predictive filter * Alpha (finance) and Beta (finance) In finance, the beta ( or market beta or beta coefficient) is a statistic that measures the expected increase or decrease of an individual stock price in proportion to movements of the stock market as a whole. Beta can be used to indicate the c ..., two measures characterizing the return of an investment portfolio * The Alpha Betas, a fraternity in the '' Revenge of the Nerds'' film series * ''Alpha Betas,'' an animated webseries created by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Hutter
Marcus Hutter (born 14 April 1967 in Munich) is a computer scientist, professor and artificial intelligence researcher. As a senior researcher at DeepMind, he studies the mathematical foundations of artificial general intelligence. Hutter studied physics and computer science at the Technical University of Munich. In 2000 he joined Jürgen Schmidhuber's group at the Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence Research in Manno, Switzerland. He developed a mathematical formalism of artificial general intelligence named AIXI. He has served as a professor at the College of Engineering, Computing and Cybernetics of the Australian National University in Canberra, Australia. Research Starting in 2000, Hutter developed and published a mathematical theory of artificial general intelligence, AIXI, based on idealised intelligent agents and reward-motivated reinforcement learning. His first book ''Universal Artificial Intelligence: Sequential Decisions Based on Algorithmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocode
In computer science, pseudocode is a description of the steps in an algorithm using a mix of conventions of programming languages (like assignment operator, conditional operator, loop) with informal, usually self-explanatory, notation of actions and conditions. Although pseudocode shares features with regular programming languages, it is intended for human reading rather than machine control. Pseudocode typically omits details that are essential for machine implementation of the algorithm, meaning that pseudocode can only be verified by hand. The programming language is augmented with natural language description details, where convenient, or with compact mathematical notation. The reasons for using pseudocode are that it is easier for people to understand than conventional programming language code and that it is an efficient and environment-independent description of the key principles of an algorithm. It is commonly used in textbooks and scientific publications to document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both economists and ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally related. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person has a preference ordering. A utility fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |