|
Eutherians
Eutheria (from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ), also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials. Eutherians are distinguished from non-eutherians by various phenotypic traits of the feet, ankles, jaws and teeth. All extant eutherians lack epipubic bones, which are present in all other living mammals (marsupials and monotremes). This allows for expansion of the abdomen during pregnancy, though epipubic bones are present in many primitive eutherians. Eutheria was named in 1872 by Theodore Gill; in 1880, Thomas Henry Huxley defined it to encompass a more broadly defined group than Placentalia. The earliest unambiguous eutherians are known from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation of China, dating around 120 million years ago. Two tribosphenic mammals, '' Durlstodon'' and '' Durlstotherium'' from the Berriasian age (~145–140 million years ago) of the Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtherulum
''Microtherulum'' is an extinct genus of eutherian mammal known from the Early Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of China. It is one of the earliest and most primitive eutherians. Description The genus is known from a mostly complete skeleton, including a well preserved skull, which is about long. The ear, which is among the best known in basal eutherians, is microtype, adapted for hearing high-frequency sounds. The dental formula is 5 incisors, 1 canine, 5 premolars and 3 molars The molars or molar teeth are large, flat tooth, teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammal, mammals. They are used primarily to comminution, grind food during mastication, chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, '' ... in the each half of the upper jaw, and 4 incisors, 1 canine, 5 premolars and 3 molars in each half of the lower jaw, which is typical for basal eutherians. Phylogeny ''Microtherulum'' has been placed close to the base of Eutheria. References {{Taxonbar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a relatively undeveloped state and then nurtured within a pouch on their mother's abdomen. Extant marsupials encompass many species, including Kangaroo, kangaroos, Koala, koalas, Opossum, opossums, Phalangeriformes, possums, Tasmanian devil, Tasmanian devils, Wombat, wombats, Wallaby, wallabies, and Bandicoot, bandicoots. Marsupials constitute a clade stemming from the last common ancestor of extant Metatheria, which encompasses all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to Placentalia, placentals. The evolutionary split between placentals and marsupials occurred 125-160 million years ago, in the Middle Jurassic-Early Cretaceous period. Presently, close to 70% of the 334 extant marsupial species are concentrated on the Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juramaia
''Juramaia'' is an extinct genus of a therian mammal, possibly a very basal eutherian mammal, known from the Late Jurassic ( Oxfordian stage) or Early Cretaceous deposits of western Liaoning, China. It is a small shrew-like mammal weighing around . Discovery ''Juramaia'' is known from the holotype BMNH PM1343, an articulated and nearly complete skeleton including incomplete skull preserved with full dentition. It was collected in the Daxigou site, Jianchang, from the Tiaojishan Formation dated at about . It was first named by Zhe-Xi Luo, Chong-Xi Yuan, Qing-Jin Meng and Qiang Ji in 2011 and the type species is ''Juramaia sinensis''. Classification The discovery of ''Juramaia'' provides new insight into the evolution of placental mammals by showing that their lineage diverged from that of the marsupials 35 million years earlier than previously thought. Furthermore, its discovery fills gaps in the fossil record and helps to calibrate modern, DNA-based methods of dating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placentalia
Placental mammals ( infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished from monotremes and marsupials in that the fetus is carried in the uterus of its mother to a relatively late stage of development. The name is something of a misnomer, considering that marsupials also nourish their fetuses via a placenta, though for a relatively briefer period, giving birth to less-developed young, which are then nurtured for a period inside the mother's pouch. Placentalia represents the only living group within Eutheria, which contains all mammals that are more closely related to placentals than they are to marsupials. Anatomical features Placental mammals are anatomically distinguished from other mammals by: * a sufficiently wide opening at the bottom of the pelvis to allow the birth of a large baby relative to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipubic Bone
Epipubic bones are a pair of bones projecting forward from the pelvic bones of modern marsupials, monotremes and fossil mammals like multituberculates, and even basal eutherians (the ancestors of placentals, who lack them). They first occur in non-mammalian cynodonts such as tritylodontids, suggesting that they are a synapomorphy between them and Mammaliformes. They were first described as early as 1698, but to date, their function(s) remain unresolved. Epipubic bones are often called ''marsupial bones'' because they support the mother's pouch in modern marsupials ("''marsupium''" is Latin for "pouch"). Function Some writers have suggested that the epipubic bones are a part of a kinetic link stretching from the femur on one side, to the ribs on the opposite side. This linkage is formed by a series of muscles: Each epipubic bone is connected to the femur by the pectineus muscle, and to the ribs and vertebrae by the pyramidalis, rectus abdominis, and external and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durlstodon
''Durlstodon'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Early Cretaceous of Southern England. It contains a single species, ''Durlstodon ensomi'', which is known from molars found in the Berriasian Lulworth Formation of Durlston Bay, Dorset, after which the genus was named. The species name honours Paul Ensom, discoverer of many fossil mammals from Lulworth. ''Durlstodon'' and two of its contemporaries, '' Tribactonodon'' and ''Durlstotherium'', had tribosphenidan (three-cusped) molars, which are an advanced characteristic among eutheria Eutheria (from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ), also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of Placentalia, placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials. Eutherians ...n mammals and suggest that the group emerged earlier than the Early Cretaceous. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q42860812 Prehistoric eutherians Fossil taxa described in 2017 Berriasian genera Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durlstotherium
''Durlstotherium'' is an extinct genus of mammal from the Early Cretaceous. It contains a single species, ''Durlstotherium newmani''. The type specimen was found in Durlston Bay, Dorset, after which the genus was named. ''D. newmani'' was named after a British pub landlord, Charlie Newman. ''Durlstotherium'' and two of its contemporaries, '' Tribactonodon'' and '' Durlstodon'', had tribosphenidan (three-cusped) molars, which are an advanced characteristic among eutheria Eutheria (from Greek , 'good, right' and , 'beast'; ), also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of Placentalia, placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials. Eutherians ...n mammals and suggest that the group emerged earlier than the Early Cretaceous. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q42898185 Prehistoric eutherians Fossil taxa described in 2017 Berriasian genera Early Cretaceous mammals of Europe Prehistoric mammal genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
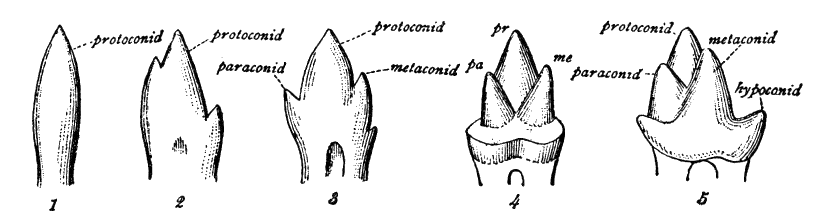
Trigonid
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third molar, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensu
''Sensu'' is a Latin word meaning "in the sense of". It is used in a number of fields including biology, geology, linguistics, semiotics, and law. Commonly it refers to how strictly or loosely an expression is used in describing any particular concept, but it also appears in expressions that indicate the convention or context of the usage. Common qualifiers ''Sensu'' is the ablative case of the noun ''sensus'', here meaning "sense". It is often accompanied by an adjective (in the same case). Three such phrases are: * – "in the strict sense", abbreviation ''s.s.'' or ''s.str.''; * – "in the broad sense", abbreviation ''s.l.''; * – "in a relaxed, generous (or 'ample') sense", a similar meaning to ''sensu lato''. Søren Kierkegaard uses the phrase ''sensu eminenti'' to mean "in the pre-eminent r most important or significantsense". When appropriate, comparative and superlative adjectives may also be used to convey the meaning of "more" or "most". Thus ''sensu stricto'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform Bones
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot: * the first or medial cuneiform * the second or intermediate cuneiform, also known as the middle cuneiform * the third or lateral cuneiform They are located between the navicular bone and the first, second and third metatarsal bones and are medial to the cuboid bone. Structure There are three cuneiform bones: # The medial cuneiform (also known as first cuneiform) is the largest of the cuneiforms. It is situated at the medial side of the foot, anterior to the navicular bone and posterior to the base of the first metatarsal. Lateral to it is the intermediate cuneiform. It articulates with four bones: the navicular, second cuneiform, and first and second metatarsals. The tibialis anterior and fibularis longus muscle inserts at the medial cuneiform bone. # The intermediate cuneiform (second cuneiform or middle cuneiform) is shaped like a wedge, the thin end pointing downwards. The intermediate cuneiform is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |