|
Ethoxylation
In organic chemistry, ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide () adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates. In the usual application, alcohols and phenols are converted into , where ''n'' ranges from 1 to 10. Such compounds are called alcohol ethoxylates. Alcohol ethoxylates are often converted to related species called ethoxysulfates. Alcohol ethoxylates and ethoxysulfates are surfactants, used widely in cosmetic and other commercial products. The process is of great industrial significance, with more than 2,000,000 metric tons of various ethoxylates produced worldwide in 1994. Production The process was developed at the Ludwigshafen laboratories of IG Farben by Conrad Schöller and during the 1930s. Alcohol ethoxylates Industrial ethoxylation is primarily performed upon alcohols. Lower alcohols react to give glycol ethers which are commonly used as solvents, while l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxide
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy''. However, few if any of the epoxy groups i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Laureth Sulfate
Sodium laureth sulfate (SLES), an accepted contraction of sodium lauryl ether sulfate, also called sodium alkylethersulfate, is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many personal care products (soaps, shampoos, toothpaste, etc.) and for industrial uses. SLES is an inexpensive and very effective foaming agent.Kurt Kosswig,"Surfactants" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, 2005, Weinheim. SLES, sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS), and sodium pareth sulfate are surfactants that are used in many cosmetic products for their cleaning and emulsifying properties. It is derived from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. In herbicides, it is used as a surfactant to improve absorption of the herbicidal chemicals and reduces time the product takes to be rainfast, when enough of the herbicidal agent will be absorbed. Its chemical formula is . Sometimes the number represented by ''n'' is specified in the name, for example laureth-2 sulfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene Oxide
Propylene oxide is an epoxide with the molecular formula C3H6O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture. This compound is sometimes called 1,2-propylene oxide to distinguish it from its isomer 1,3-propylene oxide, better known as oxetane. Production Industrial production of propylene oxide starts from propylene. Two general approaches are employed, one involving chlorohydrin formation and the other involving oxidation. In 2005, about half of the world production was through chlorohydrin technology and one half via oxidation routes. The latter approach is growing in importance. Chlorohydrin route The traditional route proceeds via the conversion of propylene to propylene chlorohydrin according to the following simplified sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
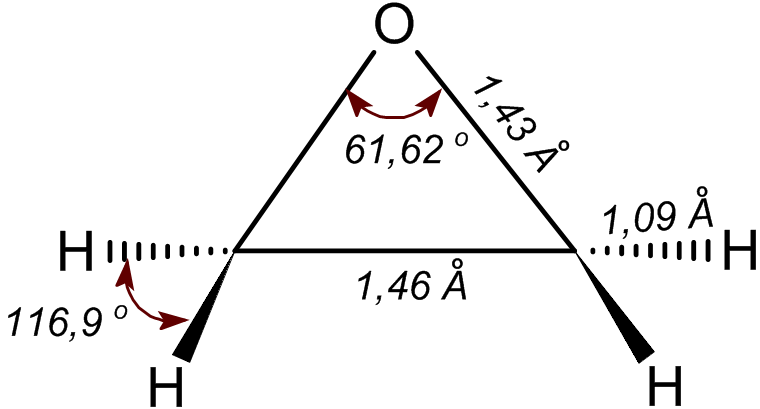
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxylation
Alkoxylation is a chemical reaction that involves the addition of an epoxide to another compound. The usual manifestation of this reaction is ethoxylation of alcohols (ROH), in which case ethylene oxide is the alkoxylating agent: :ROH + C2H4O → ROCH2CH2OH Another industrially significant epoxide is propylene oxide (PO, OCH2CHCH3). PO is mainly used for alkoxylation to produce polyether polyols. The alkoxylation process is shown in simplified form: :ROH + n OCH2CHCH3 → R(OCH2CHCH3)nOH Polyols derived from PO have complex stereochemistry owing to the chirality of the propylene oxide. These polyols are used on a large scale to produce polyurethanes, by condensation with diisocyanate In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyan ...s.Norbert Adam et al. "Polyurethane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfate
In organosulfur chemistry, organosulfates are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the structure . The core is a sulfate group and the R group is any organic residue. All organosulfates are formally esters derived from alcohols and sulfuric acid () although many are not prepared in this way. Many sulfate esters are used in detergents, and some are useful reagents. Alkyl sulfates consist of a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain, a polar sulfate group (containing an anion) and either a cation or amine to neutralize the sulfate group. Examples include: sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sulfuric acid mono dodecyl ester sodium salt) and related potassium and ammonium salts. Applications Alkyl sulfates are commonly used as anionic surfactants in liquid soaps and detergents used to clean wool, as surface cleaners, and as active ingredients in laundry detergents, shampoos and conditioners. They can also be found in household products such as toothpas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-range Ethoxylate
Narrow-range ethoxylates (NREs) in chemistry are fatty alcohol polyglycol ethers with a narrow homolog distribution and are known nonionic surfactants. They can be produced industrially, for example, by the addition of ethylene oxide onto fatty alcohols in the presence of suitable catalysts (layer compounds which have been calcined or hydrophobized with fatty acids). This process can also be carried out on a variety of other hydrophobes and using different alkoxylating compounds (e.g., propylene oxide and butylene oxide) by modifying the catalyst properties. Example An ethoxylation reaction proceeds under an inert atmosphere with an amount of heat depending on the starting material. The reaction proceeds via the epoxide (in this case ethylene oxide) ring opening and activation of the nucleophile, ring, or combination thereof via the catalyst. With conventional catalysts (i.e. potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeat Unit
A repeat unit or repeating unit , or mer, is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain (except for the end groups) by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the beads of a necklace. A repeat unit is sometimes called a mer (or mer unit) in polymer chemistry. "Mer" originates from the Greek word ''meros'', which means "a part". The word polymer derives its meaning from this, which means "many mers". The mer is not the same thing as a monomer—a mer is a repeating unit within a larger molecule, whereas a monomer is an actual molecule that exists independently, either prior to polymerization or after decomposition.Callister, William D. (2007). ''Materials science and engineering : an introduction'' (7th ed.) New York : John Wiley & Sons. Overview One of the simplest repeat units is that of the addition polymer polyvinyl chloride, - H2-CHClsub>n-, whose repeat unit is - H2-CHCl. In this case the repeat unit has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Production Volume Chemicals Programme
High production volume chemicals (HPV chemicals) are produced or imported into the United States in quantities of 1 million pounds or 500 tons per year. In OECD countries, HPV chemicals are defined as being produced at levels greater than 1,000 metric tons per producer/importer per year in at least one member country/region. A list of HPV chemicals serves as an overall priority list, from which chemicals are selected to gather data for a screening information dataset (SIDS), for testing and for initial hazard assessment. History OECD countries including EU In 1987, member countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development decided to investigate existing chemicals. In 1991, they agreed to begin by focusing on High production volume (HPV) chemicals, where production volume was used as a surrogate for data on occupational, consumer, and environmental exposure. Each country agreed to "sponsor" the assessment of a proportion of the HPV chemicals. Countries also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |