|
Estimand
An estimand is a quantity that is to be estimated in a statistical analysis. The term is used to distinguish the target of inference from the method used to obtain an approximation of this target (i.e., the estimator) and the specific value obtained from a given method and dataset (i.e., the estimate). For instance, a normally distributed random variable X has two defining parameters, its mean \mu and variance \sigma^. A variance estimator: s^ = \sum_^ \left. \left( x_ - \bar \right)^ \right/ (n-1), yields an estimate of 7 for a data set x = \left\; then s^ is called an estimator of \sigma^, and \sigma^ is called the estimand. Definition In relation to an estimator, an estimand is the outcome of different treatments of interest. It can formally be thought of as any quantity that is to be estimated in any type of experiment. Overview An estimand is closely linked to the purpose or objective of an analysis. It describes what is to be estimated based on the question of interes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Missing Data
In statistics, missing data, or missing values, occur when no data value is stored for the variable in an observation. Missing data are a common occurrence and can have a significant effect on the conclusions that can be drawn from the data. Missing data can occur because of nonresponse: no information is provided for one or more items or for a whole unit ("subject"). Some items are more likely to generate a nonresponse than others: for example items about private subjects such as income. Attrition is a type of missingness that can occur in longitudinal studies—for instance studying development where a measurement is repeated after a certain period of time. Missingness occurs when participants drop out before the test ends and one or more measurements are missing. Data often are missing in research in economics, sociology, and political science because governments or private entities choose not to, or fail to, report critical statistics, or because the information is not avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
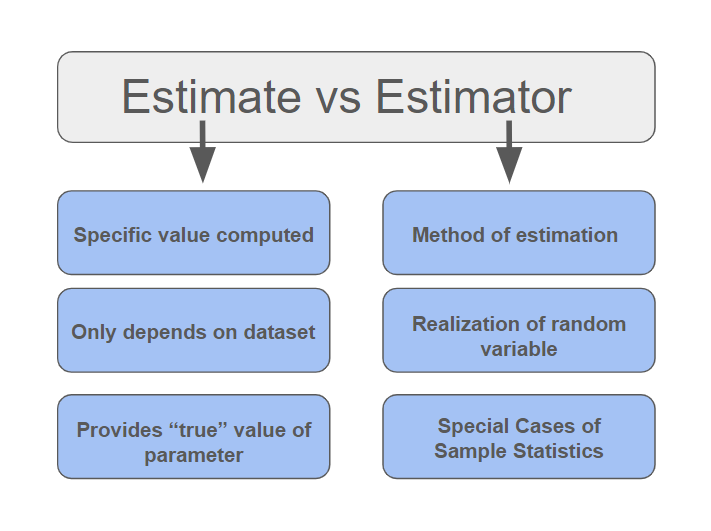
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quantity
Quantity or amount is a property that can exist as a multitude or magnitude, which illustrate discontinuity and continuity. Quantities can be compared in terms of "more", "less", or "equal", or by assigning a numerical value multiple of a unit of measurement. Mass, time, distance, heat, and angle are among the familiar examples of quantitative properties. Quantity is among the basic classes of things along with quality, substance, change, and relation. Some quantities are such by their inner nature (as number), while others function as states (properties, dimensions, attributes) of things such as heavy and light, long and short, broad and narrow, small and great, or much and little. Under the name of multitude comes what is discontinuous and discrete and divisible ultimately into indivisibles, such as: ''army, fleet, flock, government, company, party, people, mess (military), chorus, crowd'', and ''number''; all which are cases of collective nouns. Under the name of magni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Survival Analysis
Survival analysis is a branch of statistics for analyzing the expected duration of time until one event occurs, such as death in biological organisms and failure in mechanical systems. This topic is called reliability theory, reliability analysis or reliability engineering in engineering, duration analysis or duration modelling in economics, and event history analysis in sociology. Survival analysis attempts to answer certain questions, such as what is the proportion of a population which will survive past a certain time? Of those that survive, at what rate will they die or fail? Can multiple causes of death or failure be taken into account? How do particular circumstances or characteristics increase or decrease the probability of survival? To answer such questions, it is necessary to define "lifetime". In the case of biological survival, death is unambiguous, but for mechanical reliability, failure may not be well-defined, for there may well be mechanical systems in which failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drug Development
Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug. The entire process—from concept through preclinical testing in the laboratory to clinical trial development, including Phase I–III trials—to approved vaccine or drug typically takes more than a decade. New chemical entity development Broadly, the process of drug development can be divided into preclinical and clinical work. Pre-clinical New chemical entities (NCEs, also known as new molecular entities or NMEs) are compounds that emerge from the process of drug discovery. These h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
International Council For Harmonisation Of Technical Requirements For Pharmaceuticals For Human Use
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is an initiative that brings together regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry to discuss scientific and technical aspects of pharmaceutical product development and registration. The mission of the ICH is to promote public health by achieving greater harmonisation through the development of technical guidelines and requirements for pharmaceutical product registration. Harmonisation leads to a more rational use of human, animal and other resources, the elimination of unnecessary delay in the global development, and availability of new medicines while maintaining safeguards on quality, safety, efficacy, and regulatory obligations to protect public health. Junod notes in her 2005 treatise on clinical drug trials that " ove all, the ICH has succeeded in aligning clinical trial requirements." History In the 1980s, the European Union began harmonising regulatory requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lost To Follow-up
In the clinical research trial industry, lost to follow-up refers to patients who at one point in time were actively participating in a clinical research trial, but have become lost (either by error in a computer tracking system or by being unreachable) at the point of follow-up in the trial. These patients can become lost for many reasons. Without properly informing the investigator associated with the clinical trial, they may have opted to withdraw from the clinical trial, moved away from the particular study site during the clinical trial, become ill and unable to communicate, are missing or are deceased. __TOC__ Adverse effects Patients who become lost to follow-up during a clinical research trial result in many negative effects on the outcome of the trial and on the pharmaceutical company sponsoring the clinical research trial. Patients who are lost-to-follow-up lead to incomplete study results, which in turn can put a bias on the result of the study as well as a bias on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is the study of how the uncertainty in the output of a mathematical model or system (numerical or otherwise) can be divided and allocated to different sources of uncertainty in its inputs. This involves estimating sensitivity indices that quantify the influence of an input or group of inputs on the output. A related practice is uncertainty analysis, which has a greater focus on uncertainty quantification and propagation of uncertainty; ideally, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis should be run in tandem. Motivation A mathematical model (for example in biology, climate change, economics, renewable energy, agronomy...) can be highly complex, and as a result, its relationships between inputs and outputs may be faultily understood. In such cases, the model can be viewed as a black box, i.e. the output is an "opaque" function of its inputs. Quite often, some or all of the model inputs are subject to sources of uncertainty, including errors of measurement, er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hazard Ratio
In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions characterised by two distinct levels of a treatment variable of interest. For example, in a clinical study of a drug, the treated population may die at twice the rate of the control population. The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating a higher hazard of death from the treatment. To illustrate how hazard ratio is linked to projected risk: in a population where the incidence of a disease is 10% by age 65 (eg: Dementia), a hazard ratio of 4.42 (eg: Aripiprazole medication) results in an expected incidence of 37.3% by age 65. For example, a scientific paper might use an HR to state something such as: "Adequate COVID-19 vaccination status was associated with significantly decreased risk for the composite of severe COVID-19 or mortality with a[n] HR of 0.20 (95% CI, 0.17–0.22)." In essence, the hazard for the composite outcome was 80% lower among the vaccinated relative to tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Statistical Inference
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of a population, for example by testing hypotheses and deriving estimates. It is assumed that the observed data set is sampled from a larger population. Inferential statistics can be contrasted with descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics is solely concerned with properties of the observed data, and it does not rest on the assumption that the data come from a larger population. In machine learning, the term ''inference'' is sometimes used instead to mean "make a prediction, by evaluating an already trained model"; in this context inferring properties of the model is referred to as ''training'' or ''learning'' (rather than ''inference''), and using a model for prediction is referred to as ''inference'' (instead of ''prediction''); se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |