|
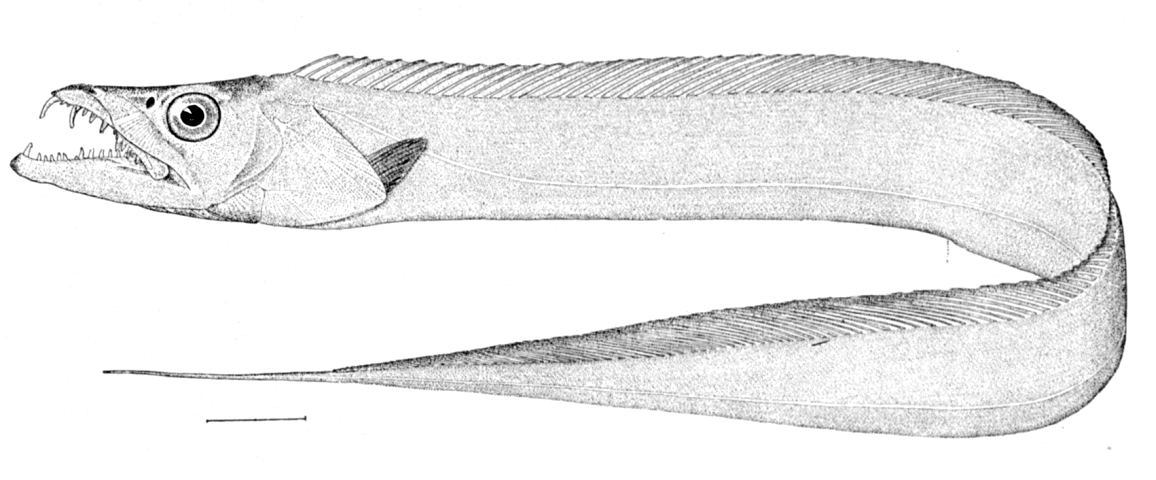
Escolar
The escolar, ''Lepidocybium flavobrunneum'', a species of fish in the family Gempylidae, is found in deep (200–885 metres, or 656–2,904 ft) tropical and temperate waters around the world. It is also known as snake mackerel, ' ( Hawaiian, sometimes written '), and is sometimes sold as " butterfish" or " white tuna". Biology The escolar is dark brown, growing darker with age until it is quite black. It is a fast-swimming fish with a prominent lateral keel and four to six finlets after the anal and second dorsal fins. Escolar can grow to over in length. Like its relative the oilfish (''Ruvettus pretiosus''), escolar cannot metabolize the wax esters (gempylotoxin) naturally found in its diet. This gives the escolar an oil content of 14–25% in its flesh. Health effects The escolar's wax ester content can cause keriorrhea (Greek: flow of wax), also called gempylotoxism or gempylid fish poisoning. Symptoms range from stomach cramps to rapid loose bowel mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seafood Mislabeling
Seafood species can be mislabelled in misleading ways. This article examines the history and types of mislabelling, and looks at the current state of the law in different locations. History in the United States Proper species identification of seafood has been important to consumers since ancient times. The Jewish dietary laws, known as kashrut, require the Jews to identify certain types of fish to maintain a kosher diet. Kashrut does not require rabbis to "bless" fish to make it kosher, but rather to identify the features the fish must have to meet kosher requirements (among others) and confirm their existence. In the 13th century, the King of England passed first law concerning proper labelling requirements, the Assize of Bread and Ale, regulating weight and quality of bread and ale. These laws were codified in the colonies, being a part of Britain, in some form. For instance, in 1758, the Georgia Legislature passed the Act for Regulating the Assize of Bread requiring bakers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oilfish
Oilfish (''Ruvettus pretiosus'') are a species of snake mackerel with a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and temperate oceans. They can be found at depths from , but most often between . Oilfish can grow to a length of , though most do not exceed . It is the only known member of its genus. Description Oilfish are large, fusiform fish which often grow to and a maximum of . Other distinctive features of this fish include the large fangs, rough scales, two pairs of finlets, and a uniformly brown coloration. Oilfish meat is extremely oily, containing high lipid concentrations. Though edible, the oil mainly consists of wax esters, which makes the meat act as a laxative if consumed in large quantities. Habitat and ecology Oilfish are distributed throughout tropical and temperate waters across the world, being recorded in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans, including the Mediterranean Sea. They are found in the deep water benthic environments of continental slopes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gempylidae
The Gempylidae are a family of scombriform ray-finned fishes commonly known as snake mackerels or escolars. The family includes about 25 species. They are elongated fishes with a similar appearance to barracudas, having a long dorsal fin, usually with one or finlets trailing it. The largest species, including the Thyrsites, snoek (''Thyrsites atun''), grow up to 2 m long, and the oilfish (''Ruvettus pretiosus'') can reach 3 m, though they rarely surpass 150 cm. Like the barracudas, they are predators, with fang-like teeth. Taxonomy * Subfamily Clade 1 Mthethwa, 2023 ** Genus ''Diplospinus'' *** ''Diplospinus multistriatus'' Günther Maul, Maul, 1948 (Striped escolar) ** Genus ''Gempylus'' *** ''Gempylus serpens'' Georges Cuvier, G. Cuvier, 1829 (Snake mackerel) ** Genus ''Nealotus'' *** ''Nealotus tripes'' James Yate Johnson, J. Y. Johnson, 1865 (Black Snake mackerel) ** Genus ''Nesiarchus'' *** ''Nesiarchus nasutus'' J. Y. Johnson, 1862 (Black gemfish) ** Genus ''Paradiplos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Nicholas Gill
Theodore Nicholas Gill (March 21, 1837 – September 25, 1914) was an American ichthyologist, mammalogist, malacologist, and librarian. Career Born and educated in New York City under private tutors, Gill early showed interest in natural history. He was associated with J. Carson Brevoort in the arrangement of the latter's entomological and ichthyological collections before going to Washington, DC, in 1863 to work at the Smithsonian Institution. He catalogued mammals, fishes, and mollusks most particularly, although he maintained proficiency in other orders of animals. He was librarian at the Smithsonian and also senior assistant to the Library of Congress. He was elected as a member of the American Philosophical Society in 1867. Gill was professor of zoology at George Washington University. He was also a member of the Megatherium Club at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. Fellow members frequently mocked him for his vanity. He was president of the American Associati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceana (non-profit Group)
Oceana, inc. is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit ocean conservation organization focused on influencing specific policy decisions on the national level to preserve and restore the world's oceans. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., with offices in Juneau, Monterey, Fort Lauderdale, New York, Portland, Toronto, Mexico City, Madrid, Brussels, Copenhagen, Geneva, London, Manila, Belmopan, Brasília, Santiago, and Lima, and it is the largest international advocacy group dedicated entirely to ocean conservation. Currently, Oceana has a staff of about 200 and 6,000 volunteers, and it has almost 50 million dollars of revenue (as of 2017). Oceana takes a multi-faceted approach to ocean conservation; It conducts its own scientific research in addition to making policy recommendations, lobbying for specific legislation, and filing and litigating lawsuits. History Oceana was established in 2001 by an international group of leading foundations including the Rockefeller Brothers Fund, Sandler F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steatorrhea
Steatorrhea (or steatorrhoea) is the presence of excess fat in Human feces, feces. Stools may be bulky and difficult to flush, have a pale and oily appearance, and can be especially foul-smelling. An oily anal leakage or some level of fecal incontinence may occur. There is increased fat excretion, which can be measured by determining the fecal fat level. Causes Impaired digestion or absorption can result in fatty stools. Possible causes include exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, with poor digestion from lack of lipases, loss of bile salts, which reduces micelle formation, and small intestinal disease-producing malabsorption. Various other causes include certain medicines that block fat absorption or indigestible or excess oil/fat in diet. The absence of bile secretion can cause the feces to turn gray or pale. Bile is responsible for the brownish color of feces. In addition to this, bile also plays a role in fat absorption, where dietary lipids are combined so that pancreatic lipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keriorrhea
Keriorrhea is the production of greasy, orange-colored stools which results from the consumption of indigestible wax esters found in oilfish and escolar. See also * Steatorrhea Steatorrhea (or steatorrhoea) is the presence of excess fat in Human feces, feces. Stools may be bulky and difficult to flush, have a pale and oily appearance, and can be especially foul-smelling. An oily anal leakage or some level of fecal incon ... * Rectal discharge References Feces Diarrhea Gastrointestinal tract disorders Steatorrhea-related diseases {{Symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wax Ester
A wax ester (WE) is an ester of a fatty acid and a fatty alcohol. Wax esters are the main components of three commercially important waxes: carnauba wax, candelilla wax, and beeswax.. Wax esters are formed by combining one fatty acid with one fatty alcohol: :RCOOH + R'OH RCOOR' + H2O Some wax esters are saturated, and others contain unsaturated centers. Saturated wax esters have higher melting points and are more likely to be solid at room temperature. Unsaturated wax esters have a lower melting point and are more likely to be liquid at room temperature. Both fatty acids and fatty alcohols may be made of different carbon chain length. In the end, there are many different possible combinations of fatty acids and fatty alcohols and each combination will have a unique set of properties in terms of steric orientation and phase transition. The chain lengths of fatty acids and fatty alcohols in naturally occurring wax esters vary. The fatty acids in wax esters derived from plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Anatomy
Fish anatomy is the study of the form or Morphology (biology), morphology of fish. It can be contrasted with fish physiology, which is the study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. In practice, fish anatomy and fish physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the latter dealing with how those components function together in living fish. The anatomy of fish is often shaped by the physical characteristics of water, the medium in which fish live. Water is much density, denser than air, holds a relatively small amount of dissolved oxygen, and absorbs more light than air does. The body of a fish is divided into a head, trunk and tail, although the divisions between the three are not always externally visible. The skeleton, which forms the support structure inside the fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |