|
Erniettomorphs
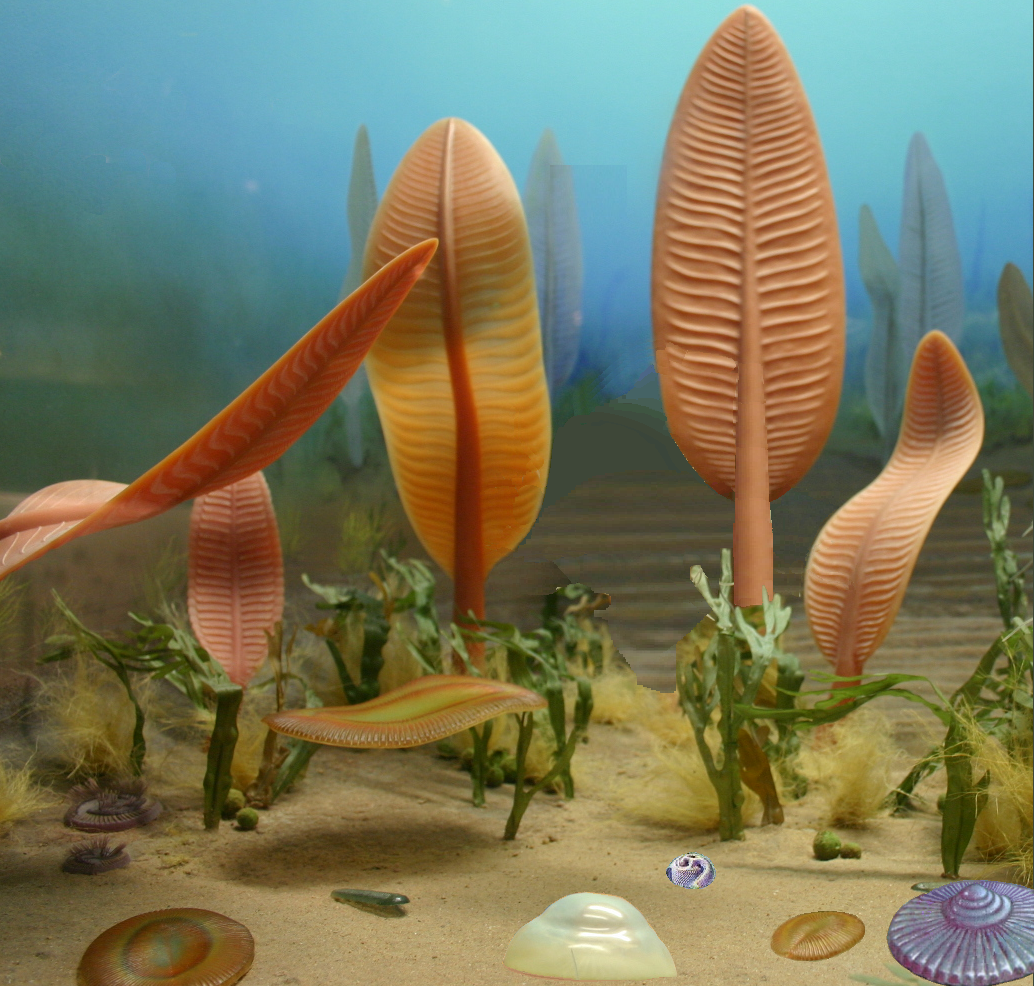
The Erniettomorphs are a form of Ediacaran fossil consisting of rows of airbed-like tubes arranged along a midline with a glide symmetry, vaguely resembling plant leaves in shape. Representative genera include '' Ernietta'', ''Phyllozoon'', ''Pteridinium'', ''Swartpuntia'', and '' Tulaneia''. Undisputed Erniettomorphs were Ediacaran, but the species ''Erytholus'', ''Rutgersella'', and ''Protonympha'', who have by some been included in this group but are by no means clear members, are found through to the Late Devonian. Their affinity is uncertain; they probably form a clade and are most likely a sister group to the rangeomorphs, which bear a similar (though fractal) construction. Placements within the metazoan crown-group have been rebutted, and it is most likely that these peculiar organisms lie in the stem group to the animals. There is no evidence that they possessed a mouth or gut. Because they may have been found in water which was too deep to permit photosynthesis – and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernietta
''Ernietta'' is an extinct genus of Ediacaran organisms with an infaunal lifestyle. Fossil preservations and modeling indicate this organism was sessile and “sack”-shaped. It survived partly buried in substrate, with an upturned bell-shaped frill exposed above the sediment-water interface. ''Ernietta'' have been recovered from present-day Namibia, and are a part of the Ediacaran biota, a late Proterozoic radiation of multicellular organisms. They are among the earliest complex multicellular organisms and are known from the late Ediacaran (ca. 548 Ma to 541 Ma). ''Ernietta plateauensis'' remains the sole species of the genus. Biology and paleoecology Fossil specimens show individuals to have lived partly buried in the substrate, as well as filled to some degree by substrate material. An exposed frill extended out of the substrate and was thought to have conducted feeding in the water column. Modeling based on fossil specimens show that the frill possessed an “upturned bell� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran Life
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The term "Ediacara biota" has received criticism from some scientists due to its alleged inconsistency, arbitrary exclusion of certain fossils, and inability to be precisely defined. The Ediacaran biota may have undergone evolutionary radiation in a proposed event called the Avalon explosion, . This was after the Earth had thawed from the Cryogenian period's extensive glaciation. This biota largely disappeared with the rapid increase in biodiversity known as the Cambrian explosion. Most of the currently existing body plans of animals first appeared in the fossil record of the Cambrian rather than the Ediacaran. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
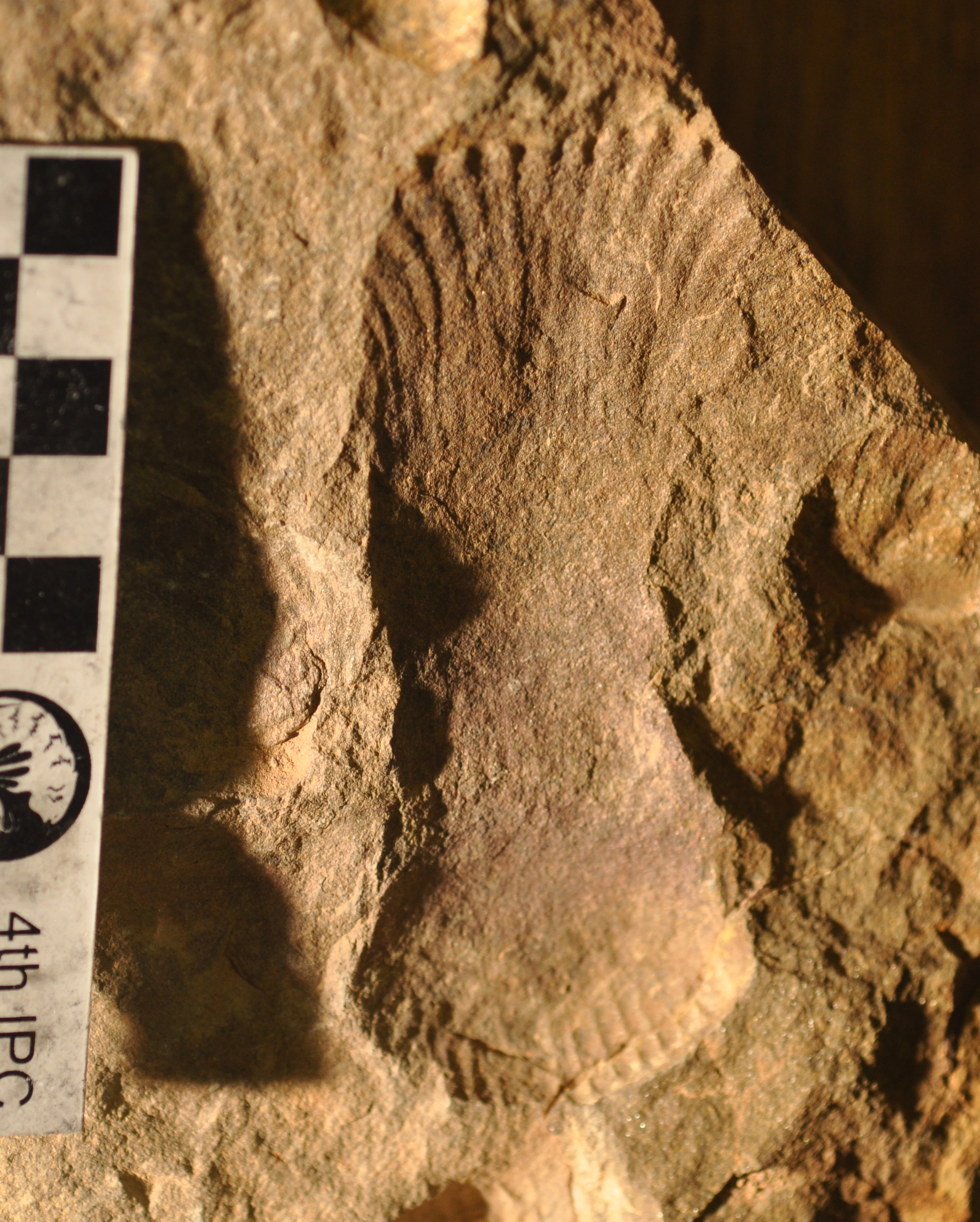
Nasepia
''Nasepia altae'' is a species of Ediacaran erniettomorph which was described in 1973 from the farms of Vrede and Chamis, Namibia. ''Nasepia'' has an appearance similar to that of most other erniettomorphs from Namibia, with it having a leaf-like body with thin ribs and spindle-shaped bodies, however it differentiates itself from other taxa such as ''Pteridinium'' and ''Rangea'' in the sense that it has smaller petaloids and with the configuration of the ribs being sub-parallel to its axis. Description ''Nasepia altae'' represents an erniettomorph with a morphology similar to that of a tiny leaf-like being, with it being made up of a bundle of spindle-shaped bodies, as well as fine ribs that are sub-parallel to a long axis that possess clearly marked margins on its sides. Germs (1973) also noted the appearance of transverse ribs on the body that only appear in some parts of ''Nasepia''. The body fossils of it also share a similarity between '' Pteridinium simplex'' and '' R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ediacaran Genera
The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin himself recognized the challenge it posed for his theory of evolution. While reports of Precambrian organisms have been made since Alexander Murray's 1868 discovery of ''Aspidella'', it wasn't until the discovery of ''Charnia'' in 1956 that considerable evidence of Precambrian life had been presented. The period immediately preceding the Cambrian, the Ediacaran, is now widely accepted of containing animal life. It spans from 635 to 540 million years ago, and covers approximately 2% of Earth's history. Taxonomists have purported a total of 245 described genera from the Ediacaran, 162 of which are accepted as valid. Key * Valid genus - Genera that are accepted by the scientific community * Synonym (taxonomy), Junior synonym - Alternative name for an already existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacara Biota
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The term "Ediacara biota" has received criticism from some scientists due to its alleged inconsistency, arbitrary exclusion of certain fossils, and inability to be precisely defined. The Ediacaran biota may have undergone evolutionary radiation in a proposed event called the Avalon explosion, . This was after the Earth had thawed from the Cryogenian period's extensive glaciation. This biota largely disappeared with the rapid increase in biodiversity known as the Cambrian explosion. Most of the currently existing body plans of animals first appeared in the fossil record of the Cambrian rather than the Ediacara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangeomorphs
The rangeomorphs are a group of Ediacaran fossils. Ediacarans are the oldest large fossil organisms on earth, and many are not self-evidently related to anything else that has ever lived. However, some Ediacarans clearly resemble each other. Palentologists have not been able to agree on what else, if anything, is related to these organisms, so Ediacarans are usually classified into groups based on their appearance. These "form taxa" allow scientists to study and discuss Ediacarans when they cannot know what kind of living things they were, or how they were genetically related to each other. Rangeomorphs look roughly like fern fronds or feathers arranged around a central axis; the group is defined as Ediacarans with a similar appearance and structure to the genus ''Rangea''. Some researchers, such as Pflug and Narbonne, believe all rangeomorphs were more closely related to each other than to anything else. If true, this would make the group a natural taxon called Rangeomorpha (just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, near-bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as ''Dickinsonia'', '' Vendia'', '' Cephalonega'', '' Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangeomorpha
The rangeomorphs are a group of Ediacaran fossils. Ediacarans are the oldest large fossil organisms on earth, and many are not self-evidently related to anything else that has ever lived. However, some Ediacarans clearly resemble each other. Palentologists have not been able to agree on what else, if anything, is related to these organisms, so Ediacarans are usually classified into groups based on their appearance. These " form taxa" allow scientists to study and discuss Ediacarans when they cannot know what kind of living things they were, or how they were genetically related to each other. Rangeomorphs look roughly like fern fronds or feathers arranged around a central axis; the group is defined as Ediacarans with a similar appearance and structure to the genus '' Rangea''. Some researchers, such as Pflug and Narbonne, believe all rangeomorphs were more closely related to each other than to anything else. If true, this would make the group a natural taxon called Rangeomorpha (jus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Water
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium () and chloride () ions). The average density at the surface is 1.025 kg/L. Seawater is denser than both fresh water and pure water (density 1.0 kg/L at ) because the dissolved salts increase the mass by a larger proportion than the volume. The freezing point of seawater decreases as salt concentration increases. At typical salinity, it freezes at about . The coldest seawater still in the liquid state ever recorded was found in 2010, in a stream under an Antarctic glacier: the measured temperature was . Seawater pH is typically limited to a range between 7.5 and 8.4. However, there is no universally accepted reference pH-scale for seawater and the difference between measurements b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
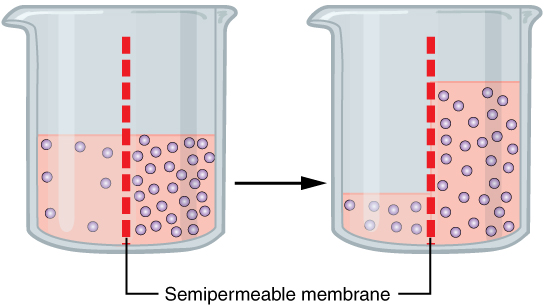
Osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do Work (physics), work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to prevent net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative properties, colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biology, bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants. The concept was developed by Willi Hennig, the formulator of phylogenetic systematics, as a way of classifying living organisms relative to their extinct relatives in his "Die Stammesgeschichte der Insekten", and the "crown" and "stem" group terminology was coined by R. P. S. Jefferies in 1979. Though formulated in the 1970s, the term was not commonly used until its reintroduction in 2000 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen. Contents of the crown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozoa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |