|
Engineering Resilience
In the fields of engineering and construction, resilience is the ability to absorb or avoid damage without suffering complete failure and is an objective of design, maintenance and restoration for buildings and infrastructure, as well as communities. A more comprehensive definition is that it is the ability to respond, absorb, and adapt to, as well as recover in a disruptive event. A resilient structure/system/community is expected to be able to resist to an extreme event with minimal damages and functionality disruptions during the event; after the event, it should be able to rapidly recovery its functionality similar to or even better than the pre-event level. The concept of resilience originated from engineering and then gradually applied to other fields. It is related to that of vulnerability. Both terms are specific to the event perturbation, meaning that a system/infrastructure/community may be more vulnerable or less resilient to one event than another one. However, they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
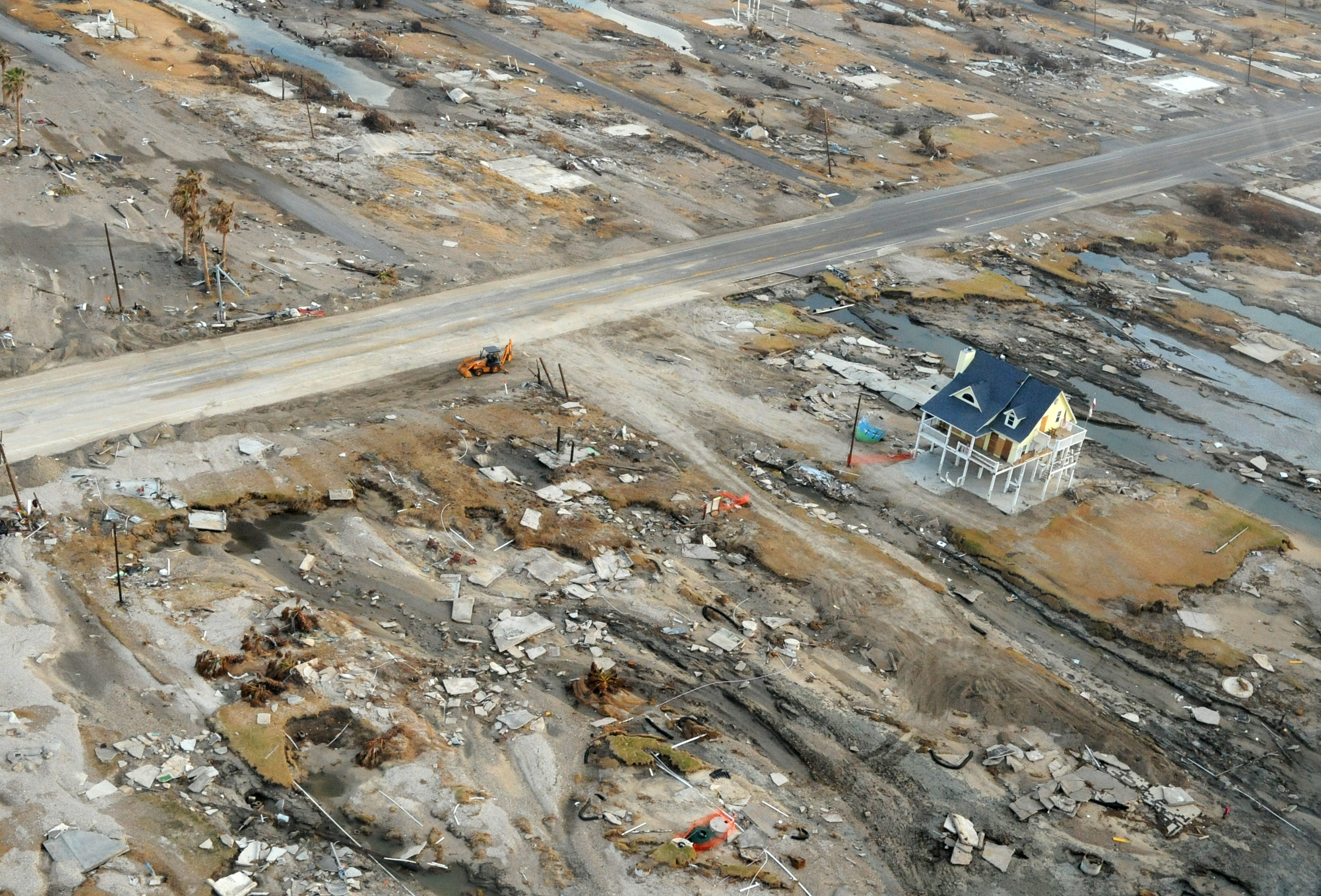
Home Designed To Resist Flood Waters
A home, or domicile, is a space used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for one or more human occupants, and sometimes various companion animals. Homes provide sheltered spaces, for instance rooms, where domestic activity can be performed such as sleeping, preparing food, eating and hygiene as well as providing spaces for work and leisure such as remote working, studying and playing. Physical forms of homes can be static such as a house or an apartment, mobile such as a houseboat, trailer or yurt or digital such as virtual space. The aspect of 'home' can be considered across scales; from the micro scale showcasing the most intimate spaces of the individual dwelling and direct surrounding area to the macro scale of the geographic area such as town, village, city, country or planet. The concept of 'home' has been researched and theorized across disciplines – topics ranging from the idea of home, the interior, the psyche, liminal space, contested space to gender an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fireproofing
Fireproofing is rendering something (Building, structures, materials, etc.) resistant to fire, or incombustible; or material for use in making anything fire-proof. It is a passive fire protection measure. "Fireproof" or "fireproofing" can be used as a noun, verb or adjective; it may be hyphenated ("fire-proof"). Applying a certification listing, certification listed fireproofing system to certain structures allows them to have a fire-resistance rating. The term "fireproofing" may be used in conjunction with standards, as reflected in common North American construction specifications. An item classed as fireproof is resistant in specified circumstances, and may burn or be rendered inoperable by fire exceeding the intensity or duration that it is designed to withstand. Markets * Commercial construction * Residential construction * Industrial construction * Marine (ships) * Offshore construction * Aerodynamics * Tunnel concrete walls and ceilings or linings * Under- and above-gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
USGBC
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), founded in 1993, is a private 501(c)(3), membership-based non-profit organization that promotes sustainability in building design, construction, and operation. USGBC is best known for its development of the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) green building rating systems and its annual Greenbuild International Conference and Expo, the world's largest conference and expo dedicated to green building. USGBC was one of eight national councils that helped found the World Green Building Council (WorldGBC). Through its partnership with the Green Business Certification Inc. (GBCI), USGBC offers a suite of LEED professional credentials that denote expertise in the field of green building. USGBC incentivizes LEED certification by awarding extra certification points to building projects completed with a LEED-certified professional on staff. History In April 1993, the USGBC was founded by David Gottfried, a real estate develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Urban Resilience
Urban resilience describes the ability of a city or urban community to withstand, recover from or adapt to man-made and natural disasters. This concept includes the resilience of physical infrastructure and social, health, and economic systems. History According to urban historian Roger W. Lotchin, World War II had a profound environmental impact on urban areas in the USA. By 1945, Pittsburgh and other cities along the Mississippi River experienced levels of air pollution that are comparable to the Dust Bowl. World War II more directly impacted many cities that were the site of battles and bombings, such as Hiroshima, Chongqing, Stalingrad, and Dresden. Environmental history first emerged as an academic research topic in the 1970's, initially focusing on rural areas. Pioneers of urban environmental history include: Martin Melosi, Christine Rosen, Joel A. Tarr, Peter Brimblecombe, Bill Luckin, and Christopher Hamlin. In recent years, the concept of resilience in the urban pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing."Toughness" Brian Larson, editor, 2001–2011, The Collaboration for NDT Education, Iowa State University [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thermal Conductivity And Resistivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials such as mineral wool or Styrofoam. Metals have this high thermal conductivity due to free electrons facilitating heat transfer. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla T is the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sustainable Design
Environmentally sustainable design (also called environmentally conscious design, eco-design, etc.) is the philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability and also aimed at improving the health and comfort of occupants in a building.McLennan, J. F. (2004), The Philosophy of Sustainable Design Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, the health and well-being of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. The basic objectives of sustainability are to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources, minimize waste, and create healthy, productive environments. Theory The sustainable design intends to "eliminate negative environmental impact through skillful sensitive design". Manifestations of sustainable design require renewable resources and innovation to impact the environment minimally, and connect people with the natural environment. "Hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
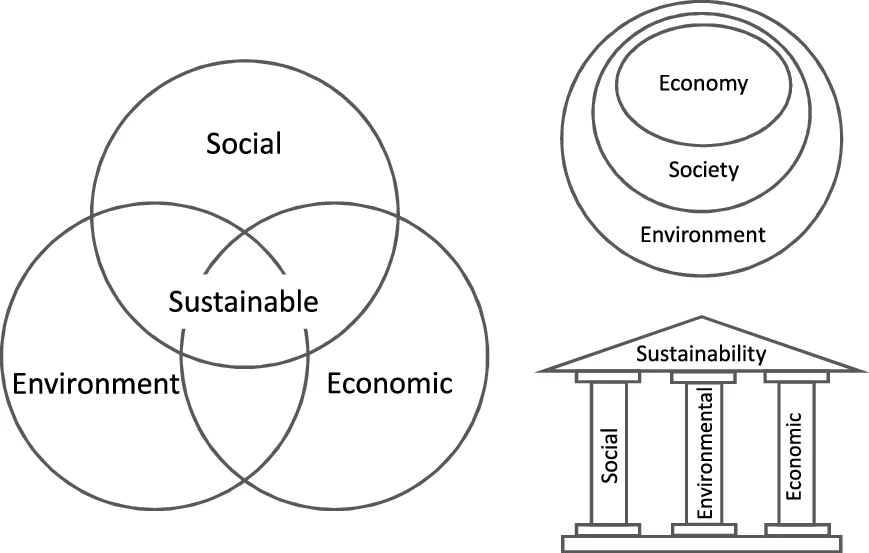
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rustproofing
Rustproofing is the prevention or delay of rusting of iron and steel objects, or the permanent wikt:protection, protection against corrosion. Typically, the protection is achieved by a process of surface finishing or treatment. Depending on mechanical wear or environmental conditions, the Chemical decomposition, degradation may not be stopped completely, unless the process is periodically repeated. The term is particularly used in the automobile industry. Vehicle rustproofing Factory In the factory, car bodies are protected with special chemical formulations. Typically, phosphate conversion coatings were used. Some firms galvanization, galvanized part or all of their car bodies before the Primer (paint), primer coat of paint was applied. If a car is body-on-frame, then the frame (chassis) must also be rustproofed. In traditional automotive manufacturing of the early- and mid-20th century, paint was the final part of the rustproofing barrier between the body shell and the atmosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rot-proof
Rot-proof or rot resistant is a condition of wikt:preservation, preservation or wikt:protection, protection, by a process or Surface finishing, treatment of materials used in industrial manufacturing or Production (economics), production to prevent biodegradation and chemical decomposition. Decomposition is a factor in which organic matter breaks down over time. It is commonly caused by fungus, Mold (fungus), mold or mildew. There are natural conditions where the environment is wikt:inhospitable, inhospitable to animals, bacteria and fungus, for example in high altitude and the freezing subzero temperatures of the Arctic and Antarctic, which creates a similar suspension. The proofing of materials may also prevent dry rot and wet rot. See also {{Wiktionary, rotproof, rot *Dust#Control, Dust resistant *Fireproofing *Rustproofing *Thermal conductivity#Resistance, Thermal resistant *Toughness *Waterproofing Chemical properties Materials science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Residual Stress
In materials science and solid mechanics, residual stresses are stresses that remain in a solid material after the original cause of the stresses has been removed. Residual stress may be desirable or undesirable. For example, laser peening imparts deep beneficial compressive residual stresses into metal components such as turbine engine fan blades, and it is used in toughened glass to allow for large, thin, crack- and scratch-resistant glass displays on smartphones. However, unintended residual stress in a designed structure may cause it to fail prematurely. Residual stresses can result from a variety of mechanisms including inelastic (plastic) deformations, temperature gradients (during thermal cycle) or structural changes ( phase transformation). Heat from welding may cause localized expansion, which is taken up during welding by either the molten metal or the placement of parts being welded. When the finished weldment cools, some areas cool and contract more than others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radiation Hardening
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation (particle radiation and high-energy electromagnetic radiation), especially for environments in outer space (especially beyond low Earth orbit), around nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, or during nuclear accidents or nuclear warfare. Most Semiconductor device, semiconductor electronic components are susceptible to radiation damage, and radiation-hardened (rad-hard) components are based on their non-hardened equivalents, with some design and manufacturing variations that reduce the susceptibility to radiation damage. Due to the low demand and the extensive development and testing required to produce a radiation-tolerant design of a microelectronics, microelectronic chip, the technology of radiation-hardened chips tends to lag behind the most recent developments. They also typically cost more than their commercial cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |