|
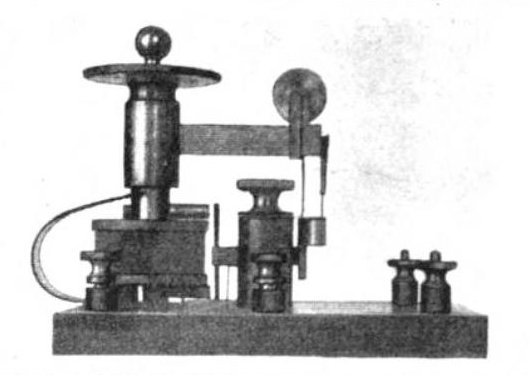
Electrolytic Detector
An electrolytic detector, or liquid barretter, is a type of detector (demodulator) used in early radio receivers. It was first used by Canadian radio researcher Reginald Fessenden in 1903, and used until about 1913, after which it was superseded by crystal detectors and vacuum tube detectors such as the Fleming valve and Audion (triode). It was considered very sensitive and reliable compared to other detectors available at the time such as the magnetic detector and the coherer. It was one of the first rectifying detectors, able to receive AM (sound) transmissions. On December 24, 1906, US Naval ships with radio receivers equipped with Fessenden's electrolytic detectors received the first AM radio broadcast from Fessenden's Brant Rock, Massachusetts transmitter, consisting of a program of Christmas music. History Fessenden, more than any other person, is responsible for developing amplitude modulation (AM) radio transmission around 1900. While working to develop AM transmitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Demodulate
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. There are many types of modulation, and there are many types of demodulators. The signal output from a demodulator may represent sound (an analog signal, analog audio signal), images (an analog video signal) or binary signal, binary data (a Digital signal (electronics), digital signal). These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers, but many other systems use many kinds of demodulators. For example, in a modem, which is a contraction of the terms modulator/demodulator, a demodulator is used to extract a serial digital data stream from a carrier signal which is used to carry it through a telephone line, coaxial cable, or optical fiber. History Demodulation was first used in radio rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of chemical element, elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores using an electrolytic cell. The voltage that is needed for electrolysis to occur is called the decomposition potential. The word "lysis" means to separate or break, so in terms, electrolysis would mean "breakdown via electricity." Etymology The word "electrolysis" was introduced by Michael Faraday in 1834, using the Greek language, Greek words "amber", which since the 17th century was associated with electrical phenomena, and ' meaning "dissolution". Nevertheless, electrolysis, as a tool to study chemical reactions and obtain pure chemical element, elements, precedes the coinage of the term and formal description by Faraday. History In the early nineteenth century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Biasing
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC (direct current) operating conditions (current and voltage) of an electronic component that processes time-varying signals. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying ( AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called ''bias''. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage. The operating point of a device, also known as bias point, quiescent point, or Q-point, is the DC voltage or current at a specified terminal of an active device (a transistor or vacuum tube) with no input signal applied. A bias circuit is a portion of the device's circuit that supplies this steady current or voltage. Overview In electronics, 'biasing' usually refers to a fixed DC voltage or current applied to a terminal of an electronic component such as a diode, transistor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), work needed per unit of Electric charge, charge to move a positive Test particle#Electrostatics, test charge from the first point to the second point. In the SI unit, International System of Units (SI), the SI derived unit, derived unit for voltage is the ''volt'' (''V''). The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a Electric generator, generator). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. Since it is the difference in electric potential, it is a physical Scalar (physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, electrical insulation, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron beam, electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A archaism, term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains Electronics, electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish language, Spanish , a diminutive of "silver". Platinum is a member of the platinum group of elements and group 10 element, group 10 of the periodic table of elements. It has six naturally occurring isotopes. It is one of the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, rarer elements in Earth's crust, with an average abundance of approximately 5 microgram, μg/kg, making platinum about 30 times rarer than gold. It occurs in some nickel and copper ores along with some Native element mineral, native deposits, with 90% of current production from deposits across Russia's Ural Mountains, Colombia, the Sudbury Basin, Sudbury basin of Canada, and a large reserve in South Africa. Because of its scarcity in Earth's crust, only a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hugo Gernsback
Hugo Gernsback (; born Hugo Gernsbacher, August 16, 1884 – August 19, 1967) was a Luxembourgish American editor and magazine publisher whose publications included the first science fiction magazine, ''Amazing Stories''. His contributions to the genre as publisher were so significant that, along with the novelists Jules Verne and H. G. Wells, he is sometimes called "The Father of Science Fiction". In his honor, annual awards presented at the World Science Fiction Convention are named the "Hugo Award, Hugos". Gernsback emigrated to the U.S. in 1904 and later became a citizen. He was also a significant figure in the electronics and radio industries, even starting a radio station, WRNY, and the world's first magazine about electronics and radio, ''Modern Electrics''. Gernsback died in New York City in 1967. Personal life Gernsback was born in 1884 in Luxembourg City, to Berta (Dürlacher), a housewife, and Moritz Gernsbacher, a winemaker. His family was Jewish. Gernsback emigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Michael I
Michael I may refer to: * Pope Michael I of Alexandria, Coptic Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark in 743–767 * Michael I Rangabe, Byzantine Emperor (died in 844) * Michael I Cerularius, Patriarch Michael I of Constantinople (c. 1000–1059) * Michael I of Duklja, Prince and King of Duklja and (d. 1081) * Mikhail of Vladimir (died in 1176) * Michael I Komnenos Doukas (died in 1215) * Michael I of Russia (1596–1645) * Michael I of Poland (Michał Korybut Wiśniowiecki), King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania (1640-1673) * Michael I of Portugal (1802–1866) * Michael I of Serbia (1823–1868) * Mihály Cseszneky de Milvány et Csesznek, Michael I of Macedonia (1910–1975) * Michael I of Romania Michael I ( ; 25 October 1921 – 5 December 2017) was the last King of Romania, reigning from 20 July 1927 to 8 June 1930 and again from 6 September 1940 until his forced abdication on 30 December 1947. Shortly after Michael's birth, his f ... ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wollaston Wire
Wollaston wire is a very fine (c. 0.001 mm thick) platinum wire clad in silver and used in electrical instruments. For most uses, the silver cladding is etched away by acid to expose the platinum core. History The wire is named after its inventor, William Hyde Wollaston, who first produced it in England in the early 19th century. Platinum wire is drawn through successively smaller dies until it is about in diameter. It is then embedded in the middle of a silver wire having a diameter of about . This composite wire is then drawn until the silver wire has a diameter of about , causing the embedded platinum wire to be reduced by the same 50:1 ratio to a final diameter of . Removal of the silver coating with an acid bath leaves the fine platinum wire as a product of the process. Uses Wollaston wire was used in early radio detectors known as electrolytic detector An electrolytic detector, or liquid barretter, is a type of detector (demodulator) used in early radio rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hot-wire Barretter
The hot-wire barretter was a demodulating detector, invented in 1902 by Reginald Fessenden, that found limited use in early radio receivers. In effect, it was a highly sensitive thermoresistor, which could demodulate amplitude-modulated signals, something that the coherer (the standard detector of the time) could not do. Tapan K. Sarkar, Robert Mailloux, Arthur A. Oliner, Magdalena Salazar Palma, Dipak L. Sengupta, "History of Wireless", , January 2006, Wiley-IEEE Press, page 369. The first device used to demodulate amplitude modulated signals, it was later superseded by the electrolytic detector, also generally attributed to Fessenden. The barretter principle is still used as a detector for microwave radiation, similar to a bolometer. Description and construction Fessenden's 1902 patent describes the construction of the device. A fine platinum wire, about in diameter, is embedded in the middle of a silver tube having a diameter of about . This compound wire is then drawn un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solvent like water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |