|
Electroglottograph
The electroglottograph, or EGG, (also referred to as a laryngograph) is a device used for the noninvasive measurement of the degree of contact between the vibrating vocal folds during voice production. Though it is difficult to verify the assumption precisely, the aspect of contact being measured by a typical EGG unit is considered to be the vocal fold contact area (VFCA). To measure VFCA, electrodes are applied on the surface of the neck so that the EGG records variations in the transverse electrical impedance of the larynx and nearby tissues by means of a small A/C electric current (in megaHertz). This electrical impedance will vary slightly with the area of contact between the moist vocal folds during the segment of the glottal vibratory cycle in which the folds are in contact. However, because the percentage variation in the neck impedance caused by vocal fold contact can be extremely small and varies considerably between subjects, no absolute measure of contact area is obtai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
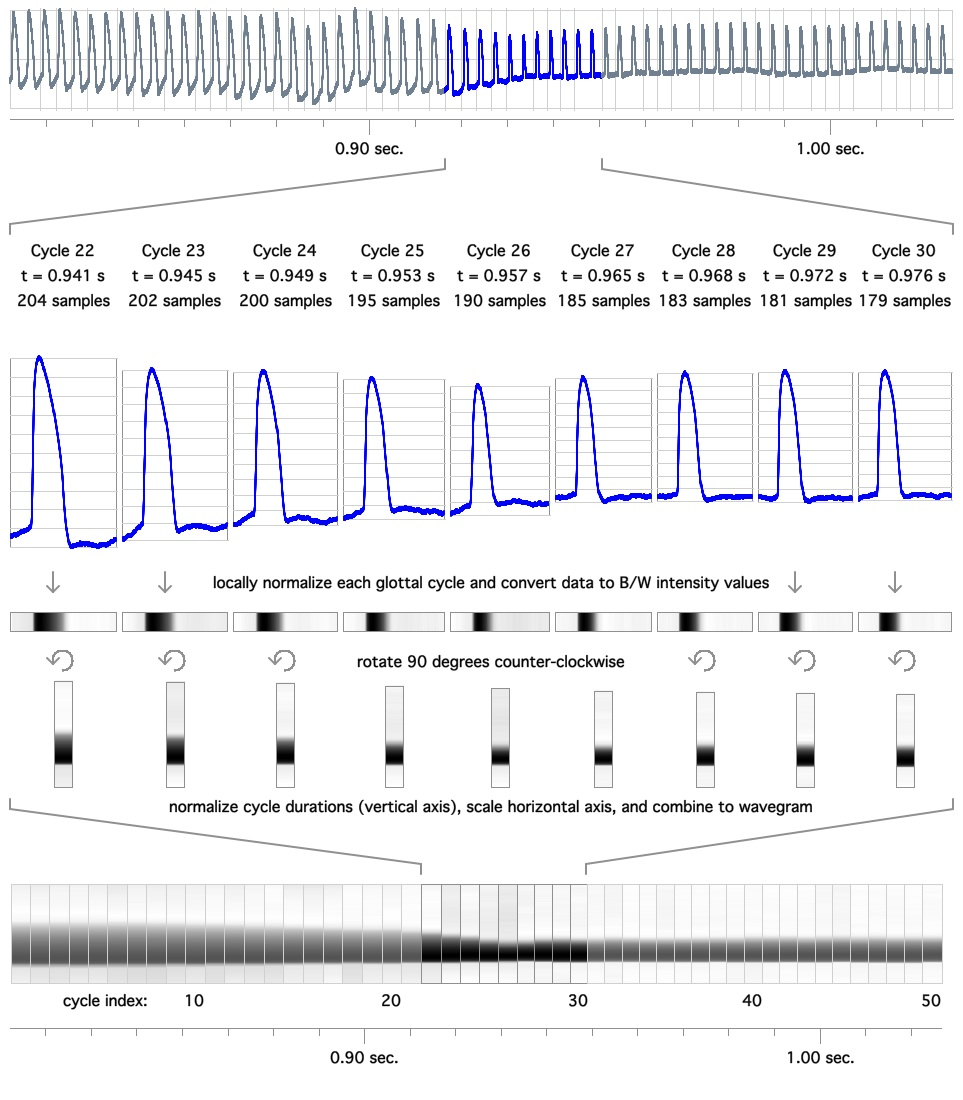
Electroglottographic Wavegram
An electroglottographic wavegram (short: EGG wavegram) is a tool for analyzing the voice source in speech and singing, based on electroglottographic (EGG) signals (and their first derivative, DEGG). Assessing the singing and speaking voice The wavegram, invented by Christian T. Herbst, provides an intuitive means for quickly assessing vocal fold contact phenomena and their variation over time. Vocal fold closings and openings appear here as a sequence of events rather than single incidents, taking place over a certain period of time, and changing with pitch, loudness and register. Wavegrams document systematic phenomena, indicating subtle changes of the vocal fold oscillatory regime. Electroglottographic wavegrams are created in 5 steps (see illustration): # extraction of consecutive glottal cycles from the EGG signal; # locally normalized data values are converted into monochrome color information, and are plotted as a strip representing one glottal cycle each; # strips are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Fold
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal nerve, recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx. They vibration, vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation. The 'true vocal cords' are distinguished from the 'false vocal folds', known as vestibular folds or ''ventricular folds'', which sit slightly superior to the more delicate true folds. These have a minimal role in normal phonation, but can produce deep sonorous tones, screams and growls. The length of the vocal fold at birth is approximately six to eight millimeters and grows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Enterprises EG2PCX Electroglottograph
{{Disambig ...
Glottal can mean: *related to the glottis *related to the vocal folds *glottal consonant *related to glottalization Glottalization is the complete or partial closure of the glottis during the articulation of another sound. Glottalization of vowels and other sonorants is most often realized as creaky voice (partial closure). Glottalization of obstruent cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EGG Signal
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilization, fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to egg incubation, incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and Mollusca, mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective eggshell, shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Enterprises EGG Electrodes
{{Disambig ...
Glottal can mean: *related to the glottis *related to the vocal folds *glottal consonant *related to glottalization Glottalization is the complete or partial closure of the glottis during the articulation of another sound. Glottalization of vowels and other sonorants is most often realized as creaky voice (partial closure). Glottalization of obstruent cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the ''fundamental'' (abbreviated as 0 or 1 ), is defined as the lowest frequency of a Periodic signal, periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch (music), pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest Harmonic series (music)#Partial, partial present. In terms of a superposition of Sine wave, sinusoids, the fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency sinusoidal in the sum of harmonically related frequencies, or the frequency of the difference between adjacent frequencies. In some contexts, the fundamental is usually abbreviated as 0, indicating the lowest frequency Zero-based numbering, counting from zero. In other contexts, it is more common to abbreviate it as 1, the first harmonic. (The second harmonic is then 2 = 2⋅1, etc.) According to Benward and Saker's ''Music: In Theory and Practice'': Explanation All sinusoidal and many non-sinusoidal waveforms repeat exactly over time – they are per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Technology
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Voice
The human voice consists of sound Voice production, made by a human being using the vocal tract, including Speech, talking, singing, Laughter, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of Voicelessness, unvoiced consonants, Click consonant, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |