|
Economic Production Quantity
The economic production quantity model (also known as the EPQ model) determines the quantity a company or retailer should order to minimize the total inventory costs by balancing the inventory holding cost and average fixed ordering cost. The EPQ model was developed and published by E. W. Taft, a statistical engineer working at Winchester Repeating Arms Company in New Haven, Connecticut, in 1918.Taft, E. W.The most economical production lot: Formulas for Exact and Approximate Evaluation - Handling Cost of Jigs and Interest Charges of Product Included ''Iron Age'' 101.18 (1918): pages 1410-1412, accessed 29 November 2023 This method is an extension of the economic order quantity model (also known as the EOQ model). The difference between these two methods is that the EPQ model assumes the company will produce its own quantity or the parts are going to be shipped to the company while they are being produced, therefore the orders are available or received in an incremental manner wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holding Cost
In marketing, carrying cost, carrying cost of inventory or holding cost refers to the total cost of holding inventory. This includes warehousing costs such as rent, utilities and salaries, financial costs such as opportunity cost, and inventory costs related to perishability, shrinkage, and insurance. Carrying cost also includes the opportunity cost of reduced responsiveness to customers' changing requirements, slowed introduction of improved items, and the inventory's value and direct expenses, since that money could be used for other purposes. When there are no transaction costs for shipment, carrying costs are minimized when no excess inventory is held at all, as in a just-in-time production system. Excess inventory can be held for one of three reasons. Cycle stock is held based on the re-order point, and defines the inventory that must be held for production, sale or consumption during the time between re-order and delivery. Safety stock is held to account for variability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Engineering
Statistics (from German: ', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An experimental study involves taking measurements of the syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winchester Repeating Arms Company
The Winchester Repeating Arms Company was a prominent American manufacturer of repeating firearms and ammunition. The firm was established in 1866 by Oliver Winchester and was located in New Haven, Connecticut. The firm went into receivership in 1931 and was bought by the Western Cartridge Company, a forerunner of the Olin Corporation. The Winchester brand name is still owned by the Olin Corporation, which makes ammunition under that name. The Winchester name is also used under license for firearms produced by two subsidiaries of the Herstal Group – FN Herstal of Belgium and the Browning Arms Company of Ogden, Utah. History Early history Predecessors The ancestor of the Winchester Repeating Arms Company was the Horace Smith and Daniel Wesson partnership of Norwich, Connecticut (not to be confused with the famous Smith & Wesson Revolver Company founded later by the same men). Smith and Wesson acquired Lewis Jennings' improved version of inventor Walter Hunt's 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is a city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound. With a population of 135,081 as determined by the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, New Haven is List of municipalities in Connecticut, the third largest city in Connecticut after Bridgeport, Connecticut, Bridgeport and Stamford, Connecticut, Stamford, the largest city in the South Central Connecticut Planning Region, Connecticut, South Central Connecticut Planning Region, and the principal municipality of Greater New Haven metropolitan area, which had a total population of 864,835 in 2020. New Haven was one of the first Planned community, planned cities in the U.S. A year after its founding by English Puritans in 1638, eight streets were laid out in a four-by-four Grid plan, grid, creating the "Nine Square Plan". The central common block is New Haven Green, the New Haven Green, a square at the center of Downtown New Haven. The Green is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Order Quantity
Economic order quantity (EOQ), also known as financial purchase quantity or economic buying quantity, is the order quantity that minimizes the total holding costs and ordering costs in inventory management. It is one of the oldest classical production scheduling models. The model was developed by Ford W. Harris in 1913, but the consultant R. H. Wilson applied it extensively, and he and K. Andler are given credit for their in-depth analysis. Overview The EOQ indicates the optimal number of units to order to minimize the total cost associated with the purchase, delivery, and storage of a product. EOQ applies only when demand for a product is constant over a period of time (such as a year) and each new order is delivered in full when inventory reaches zero. There is a fixed cost for each order placed, regardless of the quantity of items ordered; an order is assumed to contain only one type of inventory item. There is also a cost for each unit held in storage, commonly known as h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Time
A lead time is the latency between the initiation and completion of a process. For example, the lead time between the placement of an order and delivery of new cars by a given manufacturer might be between 2 weeks and 6 months, depending on various particularities. One business dictionary defines "manufacturing lead time" as the total time required to manufacture an item, including order preparation time, queue time, setup time, run time, move time, inspection time, and put-away time. For make-to-order products, it is the time between release of an order and the production and shipment that fulfill that order. For make-to-stock products, it is the time taken from the release of an order to production and receipt into finished goods inventory. Supply chain management A conventional definition of lead time in a supply chain management context is the time from the moment the customer places an order (the moment the supplier learns of the requirement) to the moment it is ready for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
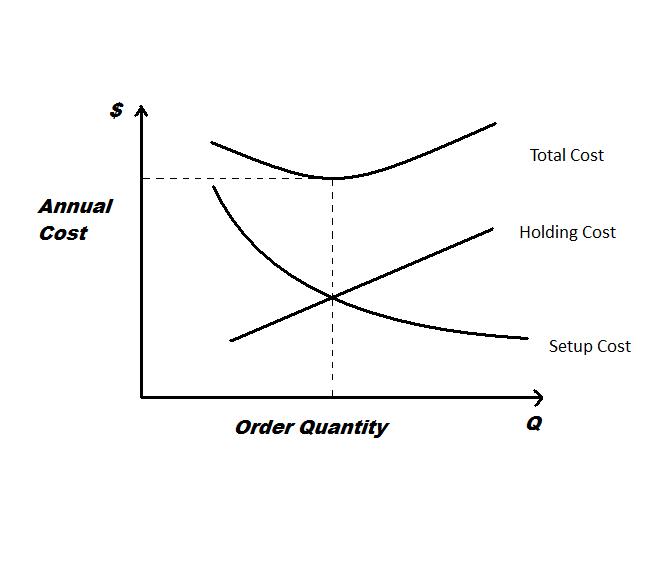
EPQ Graph
{{disambiguation ...
EPQ may refer to: * Economic production quantity * Épargne Placements Québec, an administrative unit of the Quebec Ministry of Finance * Extended Project Qualification, in the United Kingdom * Eysenck Personality Questionnaire In psychology, the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire (EPQ) is a questionnaire to assess the personality traits of a person. It was devised by psychologists Hans Jürgen Eysenck and Sybil B. G. Eysenck. Hans Eysenck's theory is based primarily on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reorder Point
The reorder point (ROP), also reorder level (ROL) or "optimal re-order level", is the level of inventory which triggers an action to replenish that particular inventory. It is a minimum amount of an item which a firm holds in stock, such that, when stock falls to this amount, the item must be reordered. It is normally calculated as the forecast usage during the replenishment lead time plus safety stock. In the EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) model, it was assumed that there is no time lag between ordering and receipt of materials. Continuous review system The reorder point for replenishment of stock occurs when the level of inventory drops down to zero. In a model with instantaneous replenishment of stock the level of inventory jumps to the original level from zero level. In real life situations there is never a zero lead time: there is always a time lag from the date of placing an order for material to the date on which materials are received. As a result, the reorder point is alwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Stock
Safety stock is a term used by logistics, logisticians to describe a level of extra inventory, stock which is maintained to mitigate the risk of stockouts, which can be caused, for example, by shortfalls in raw material availability or uncertainty in forecasting supply and demand. Adequate safety stock levels permit business operations to proceed according to their plans.Monk, Ellen and Bret Wagner. Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning. 3rd Edition. Boston: Course Technology Cengage Learning, 2009. Safety stock is held when uncertainty exists in demand, supply, or manufacturing yield, and serves as an insurance against stockouts. Safety stock is an additional quantity of an item held in the inventory to reduce the risk that the item will be out of stock. It acts as a buffer stock in case sales are greater than planned and/or the supplier is unable to deliver the additional units at the expected time. With a new product, safety stock can be used as a strategic tool until the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Order Quantity
Economic order quantity (EOQ), also known as financial purchase quantity or economic buying quantity, is the order quantity that minimizes the total holding costs and ordering costs in inventory management. It is one of the oldest classical production scheduling models. The model was developed by Ford W. Harris in 1913, but the consultant R. H. Wilson applied it extensively, and he and K. Andler are given credit for their in-depth analysis. Overview The EOQ indicates the optimal number of units to order to minimize the total cost associated with the purchase, delivery, and storage of a product. EOQ applies only when demand for a product is constant over a period of time (such as a year) and each new order is delivered in full when inventory reaches zero. There is a fixed cost for each order placed, regardless of the quantity of items ordered; an order is assumed to contain only one type of inventory item. There is also a cost for each unit held in storage, commonly known as h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Lot Size Model
The dynamic lot-size model in inventory theory, is a generalization of the economic order quantity model that takes into account that demand for the product varies over time. The model was introduced by Harvey M. Wagner and Thomson M. Whitin in 1958. Harvey M. Wagner and Thomson M. Whitin, "Dynamic version of the economic lot size model," Management Science, Vol. 5, pp. 89–96, 1958 Problem setup We have available a forecast of product demand over a relevant time horizon t=1,2,...,N (for example we might know how many widgets will be needed each week for the next 52 weeks). There is a setup cost incurred for each order and there is an inventory holding cost per item per period ( and can also vary with time if desired). The problem is how many units to order now to minimize the sum of setup cost and inventory cost. Let us denote inventory: I=I_+\sum_^x_-\sum_^d_\geq0 The functional equation representing minimal cost policy is: f_(I)=\underset\left i_I+H(x_)s_+f_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |