|
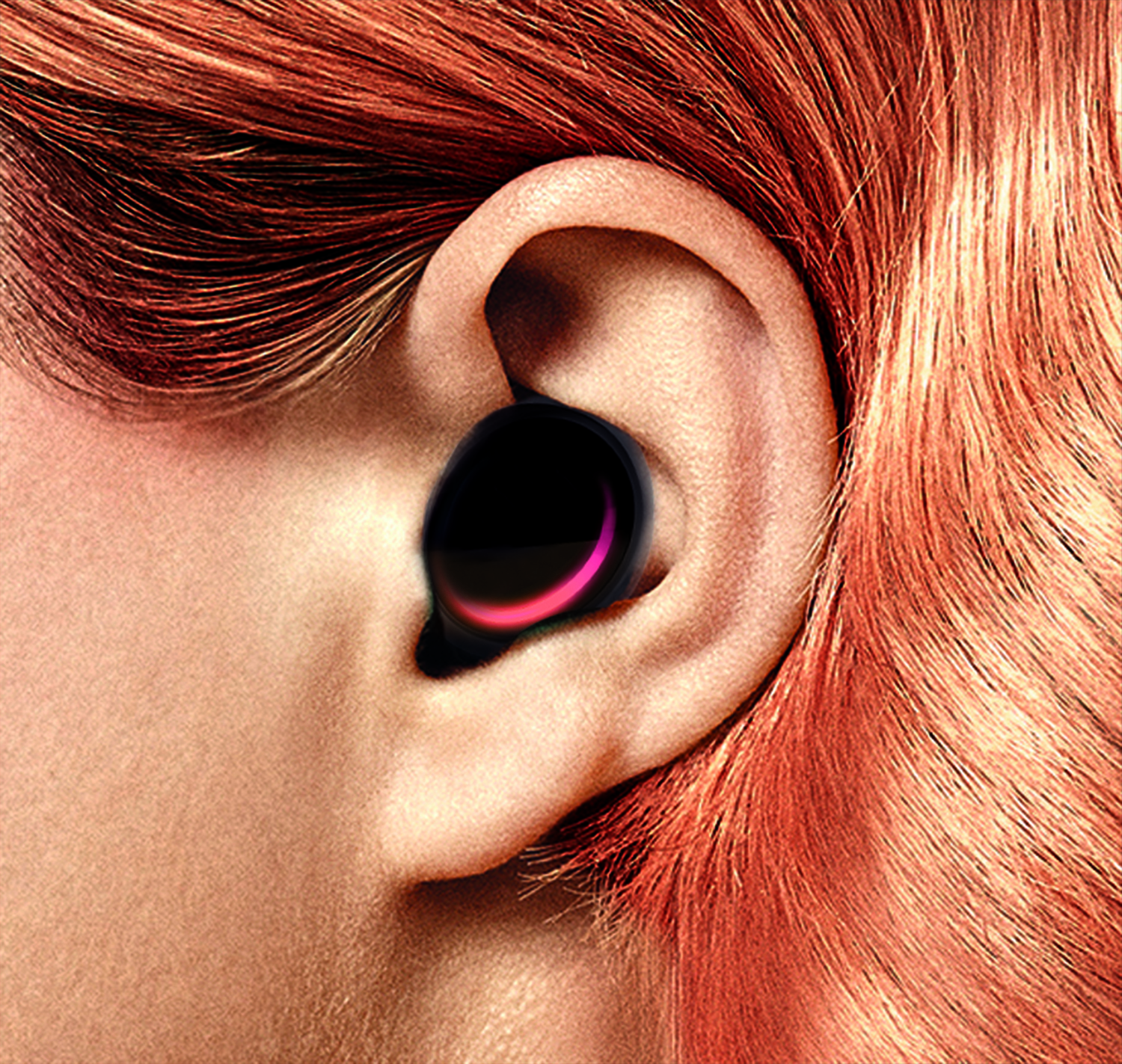
Ear-EEG
Ear-EEG is a method for measuring dynamics of brain activity through the minute voltage changes observable on the skin, typically by placing electrodes on the scalp. In ear-EEG, the electrodes are exclusively placed in or around the outer ear, resulting in both a much greater invisibility and wearer mobility compared to full scalp electroencephalography (EEG), but also significantly reduced signal amplitude, as well as reduction in the number of brain regions in which activity can be measured. It may broadly be partitioned into two groups: those using electrode positions exclusively within the concha and ear canal, and those also placing electrodes close to the ear, usually hidden behind the ear lobe. Generally speaking, the first type will be the most invisible, but also offer the most challenging (noisy) signal. Ear-EEG is a good candidate for inclusion in a hearable device, however, due to the high complexity of ear-EEG sensors, this has not yet been done. History Ear-EEG wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearables
Hearables or smart headphones or earbuds are electronic in-ear devices designed for multiple purposes. The category is split between hearables for hearing health, and hearables for other applications. Terminology The neologism "hearable" is a hybrid of the terms wearable and headphone, as hearables combine major assets of wearable technology with the basic principle of audio-based information services, conventional rendition of music and wireless telecommunication. The term was introduced in April 2014 simultaneously by Apple in the context of the company's acquisition of Beats Electronics and product designer and wireless application specialist Nick Hunn in a blogpost for a wearable technologies internet platform. Hearables are often referenced as a subset of wearables. Sometimes the terms "smart headphones" or "smart advisors" are also used to denominate hearables. The news agency Reuters in its "Journalism media and technology predictions 2015" ranked voice-driven virtual as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widex
Widex A/S is the world’s sixth largest hearing aid manufacturer. In close collaboration with international audiological researchers and specialists, the company has developed a wide range of digital hearing aids. They introduced the world's first commercially available 100% digital in-the-ear hearing aid in 1995 based on the research model developed by Oticon that same year. The Danish company was founded in 1956 by the Tøpholm and Westermann families, and is still owned by the relatives of the company’s original founders. The CEO of Widex is Jan Makela, who was appointed in July 2024. Widex hearing aids are sold in almost 100 countries and the company employs approximately 3,800 people around the world. Widex’s new headquarters are located in Allerød Municipality, Denmark, north of Copenhagen. The new headquarters use groundwater for cooling in the summer and heating in the winter. Widex also placed an energy-generating wind turbine beside the building. In 2018, Widex a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
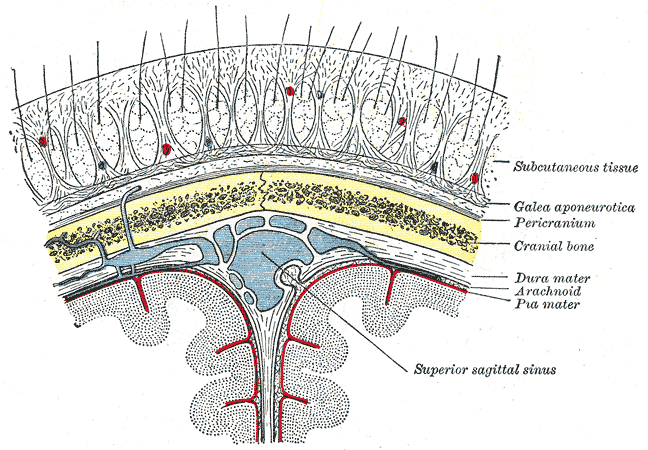
Scalp Topography And Ear-topographies
The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology. Structure Layers The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can be remembered using the mnemonic 'SCALP': * S: Skin. The skin of the scalp contains numerous hair follicles and sebaceous glands. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: Aponeurosis. The epicranial aponeurosis or galea aponeurotica is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which anchors the above layers in place. It runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis posteriorly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysomnography
Polysomnography (PSG) is a multi-parameter type of sleep study and a diagnostic tool in sleep medicine. The test result is called a polysomnogram, also abbreviated PSG. The name is derived from Greek and Latin roots: the Greek πολύς (''polus'' for "many, much", indicating many channels), the Latin ''somnus'' ("sleep"), and the Greek γράφειν (''graphein'', "to write"). Type I polysomnography is a sleep study performed overnight with the patient continuously monitored by a credentialed technologist. It records the physiological changes that occur during sleep, usually at night, though some labs can accommodate shift workers and people with circadian rhythm sleep disorders who sleep at other times. The PSG monitors many body functions, including brain activity ( EEG), eye movements ( EOG), muscle activity or skeletal muscle activation ( EMG), and heart rhythm ( ECG). After the identification of the sleep disorder sleep apnea in the 1970s, breathing functions, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. Symptoms can remain even soon after raised blood level. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is diabetes medication, medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin (medication), insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driver Drowsiness Detection
Driver drowsiness detection (also known as "driver alertness monitoring") is a car safety technology which helps prevent accidents caused by the driver getting drowsy. Various studies have suggested that around 20% of all road accidents are fatigue-related, up to 50% on certain roads. Drowsiness can impair a driver’s mental stability, reducing their ability to make sound decisions and potentially leading to physical harm and financial losses for both the driver and passengers. From 2024, the EU mandates drowsiness detection systems in all new vehicles to enhance road safety. Technology Various technologies can be used to try to detect driver drowsiness. Steering pattern monitoring Primarily uses steering input from electric power steering system. Monitoring a driver this way only works as long as a driver actually steers a vehicle actively instead of using an automatic lane-keeping system. Vehicle position in lane monitoring Uses a lane monitoring camera. Monitoring a drive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain–computer Interface
A brain–computer interface (BCI), sometimes called a brain–machine interface (BMI), is a direct communication link between the brain's electrical activity and an external device, most commonly a computer or robotic limb. BCIs are often directed at researching, Brain mapping, mapping, assisting, Augmented cognition, augmenting, or repairing human Cognitive skill, cognitive or Sensory-motor coupling, sensory-motor functions. They are often conceptualized as a human–machine interface that skips the intermediary of moving body parts (e.g. hands or feet). BCI implementations range from non-invasive (EEG, Magnetoencephalography, MEG, MRI) and partially invasive (ECoG and endovascular) to invasive (microelectrode array), based on how physically close electrodes are to brain tissue. Research on BCIs began in the 1970s by Jacques Vidal at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) under a grant from the National Science Foundation, followed by a contract from the Defense Adva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from [see the Electron#Etymology, etymology of "electron"]; ; and ) is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cell (biology), cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnostic medicine, electrodiagnosis and monitoring (medicine), monitoring. Definition and scope Classical electrophysiological techniques Principle and mechanisms Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that pertains broadly to the flow of ions (ion current) in biological tissues and, in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |