|
Downdrafts
In meteorology, an updraft is a small-scale current of rising air, often within a cloud. Overview Localized regions of warm or cool air will exhibit vertical movement. A mass of warm air will typically be less dense than the surrounding region, and so will rise until it reaches air that is either warmer or less dense than itself. The converse will occur for a mass of cool air, and is known as subsidence. This movement of large volumes of air, especially when regions of hot, wet air rise, can create large clouds, and is the central source of thunderstorms. Drafts can also be conceived by low or high pressure regions. A low pressure region will attract air from the surrounding area, which will move towards the center and then rise, creating an updraft. A high pressure region will attract air from the surrounding area, which will move towards the center and sink, spawning a downdraft. Updrafts and downdrafts, along with wind shear in general, are a major contributor to airplane cras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm Updraft
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the universal adoption of Luke H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Flank Downdraft
The rear flank downdraft (RFD) is a region of dry air wrapping around the back of a mesocyclone in a supercell thunderstorm. These areas of descending air are thought to be essential in the production of many supercellular tornadoes. Large hail within the rear flank downdraft often shows up brightly as a hook on weather radar images, producing the characteristic ''hook echo'', which often indicates the presence of a tornado. Formation The rear flank downdraft can arise owing to negative buoyancy, which can be generated by cold anomalies produced at the rear of the supercell thunderstorm by evaporative cooling of precipitation or hail melting, or injection of dry and cooler air in the cloud, and by vertical perturbation pressure gradients that can arise from vertical gradients of vertical vorticity, ''stagnation'' of environmental flow at an updraft, and pressure perturbations due to vertical buoyancy variations (which are partially due to hydrostatic effects). Vertical press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downburst
In meteorology, a downburst is a strong downward and outward gushing wind system that emanates from a point source above and blows radially, that is, in straight lines in all directions from the area of impact at surface level. Capable of producing damaging winds, it may sometimes be confused with a tornado, where high-velocity winds circle a central area, and air moves inward and upward. These usually last for seconds to minutes. Downbursts are particularly strong downdrafts within thunderstorms (or deep, moist convection as sometimes downbursts emanate from cumulonimbus or even cumulus congestus clouds that are not producing lightning). Downbursts are most often created by an area of significantly precipitation-cooled air that, after reaching the surface ( subsiding), spreads out in all directions producing strong winds. Dry downbursts are associated with thunderstorms that exhibit very little rain, while wet downbursts are created by thunderstorms with significant amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand National Airways Corporation Flight 441
New Zealand National Airways Corporation Flight 441 (NZ441) was a scheduled flight of the New Zealand National Airways Corporation from Whenuapai, Auckland to Tauranga. On 3 July 1963 at approximately 9:09 am NZST, the flight, a Douglas DC-3 Skyliner, flew into a vertical rock face in the Kaimai Ranges near Mount Ngatamahinerua, at an altitude of 2460 feet (750 m). Twenty-three people were on board. Twenty-two were killed instantly; there is evidence that one person survived the impact but died shortly afterward. Three extra passengers were supposed to be on the flight, but changed their plans at the last minute. According to Civil Aviation Authority investigators, a downdraft carried the aircraft below the level of the crests of the range, where under the very poor weather conditions prevailing at the time, the aircraft encountered an area of extreme turbulence from which it was impossible for the crew to recover altitude. On the day of the crash, another plane was caught in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Doppler Weather Radar
Terminal Doppler Weather Radar (TDWR) is a Doppler weather radar system with a three-dimensional "pencil beam" used primarily for the detection of hazardous wind shear conditions, precipitation, and winds aloft on and near major airports situated in climates with great exposure to thunderstorms in the United States. As of 2011, all were in-service with 45 operational radars, some covering multiple airports in major metropolitan locations, across the United States & Puerto Rico. Several similar weather radars have also been sold to other countries such as China (Hong Kong). Funded by the United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), TDWR technology was developed in the early 1990s at Lincoln Laboratory, part of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, to assist air traffic controllers by providing real-time wind shear detection and high-resolution precipitation data. The primary advantage of TDWRs over previous weather radars is that it has a finer range resolution—me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example of convection, specifically atmospheric convection. Thermals on Earth The Sun warms the ground, which in turn warms the air directly above. The warm air near the surface expands, becoming less dense than the surrounding air. The lighter air rises and cools due to its expansion in the lower pressure at higher altitudes. It stops rising when it has cooled to the same temperature, thus density, as the surrounding air. Associated with a thermal is a downward flow surrounding the thermal column. The downward-moving exterior is caused by colder air being displaced at the top of the thermal. The size and strength of thermals are influenced by the properties of the lower atmosphere (the ''troposphere''). When the air is cold, bubbles of wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Flank Downdraft
Forward is a relative direction, the opposite of backward. Forward may also refer to: People * Forward (surname) Sports * Forward (association football) * Forward (basketball), including: ** Point forward ** Power forward (basketball) ** Small forward * Forward (ice hockey) ** Power forward (ice hockey) * In rugby football: ** Forwards (rugby league), in rugby league football ** Forwards (rugby union), in rugby union football * Forward Sports, a Pakistan sportswear brand * BK Forward, a Swedish club for association football and bandy Politics * Avante (political party) (Portuguese for ''forward''), a political party in Brazil * Forward (Belgium), a political party in Belgium * Forward (Denmark), a political party in Denmark * Forward (Greenland), a political party in Greenland * Forward Party (United States), a centrist American political party * Kadima (Hebrew for ''forward''), a political party in Israel * La République En Marche! (sometimes translated as ''Forwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Waves
In meteorology, lee waves are atmospheric stationary waves. The most common form is mountain waves, which are atmospheric internal gravity waves. These were discovered in 1933 by two German glider pilots, Hans Deutschmann and Wolf Hirth, above the Krkonoše. They are periodic changes of atmospheric pressure, temperature and orthometric height in a current of air caused by vertical displacement, for example orographic lift when the wind blows over a mountain or mountain range. They can also be caused by the surface wind blowing over an escarpment or plateau, or even by upper winds deflected over a thermal updraft or cloud street. The vertical motion forces periodic changes in speed and direction of the air within this air current. They always occur in groups on the lee side of the terrain that triggers them. Sometimes, mountain waves can help to enhance precipitation amounts downwind of mountain ranges. Usually a turbulent vortex, with its axis of rotation parallel to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Thermodynamics
Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat-to-work transformations (and their reverse) that take place in the earth's atmosphere and manifest as weather or climate. Atmospheric thermodynamics use the laws of classical thermodynamics, to describe and explain such phenomena as the properties of moist air, the formation of clouds, atmospheric convection, boundary layer meteorology, and vertical instabilities in the atmosphere. Atmospheric thermodynamic diagrams are used as tools in the forecasting of storm development. Atmospheric thermodynamics forms a basis for cloud microphysics and convection parameterizations used in numerical weather models and is used in many climate considerations, including convective-equilibrium climate models. Overview The atmosphere is an example of a non-equilibrium system. Atmospheric thermodynamics describes the effect of buoyant forces that cause the rise of less dense (warmer) air, the descent of more dense air, and the transformation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
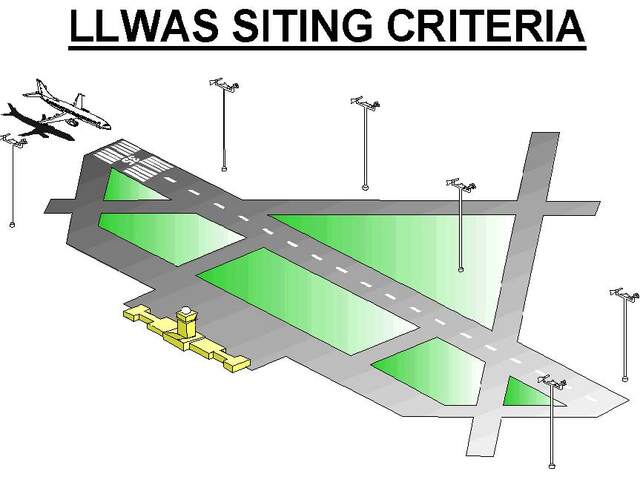
Low Level Windshear Alert System
A low-level windshear alert system (LLWAS) measures average surface wind speed and direction using a network of remote sensor stations, situated near runways and along approach or departure corridors at an airport. Wind shear is the generic term for wind differences over an operationally short distance (in relation to flight) which encompass meteorological phenomena including gust fronts, microbursts, vertical shear, and derechos. Background LLWAS compares results over its operating area to determine whether calm, steady winds, wind shifts (in relation to runways), wind gusts, divergent winds, sustained divergent winds (indicative of shear), or strong and sustained divergent winds (indicative of microbursts) are observed. A LLWAS master station polls each remote station every system cycle (nominally every ten seconds) and provides prevailing airport wind averages, runway specific winds, gusts, may set new wind shear alerts or microburst alerts and reset countdown timers of elapse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |