|
Diphtheritic Croup
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacteria, bacterium ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild Course (medicine), clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually start two to five days after exposure. Symptoms often come on fairly gradually, beginning with a sore throat and fever. In severe cases, a grey or white patch develops in the throat. This can block the airway and create a barking cough as in croup. The neck may swell in part due to enlarged lymph nodes. A form of diphtheria which involves the skin, eyes or genitals also exists. Complications may include myocarditis, peripheral neuropathy, inflammation of nerves, proteinuria, kidney problems, and bleeding problems due to thrombocytopenia, low levels of platelets. Myocarditis may result in an cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rate and inflammation of the nerves may r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease (medical Specialty)
Infectious diseases or ID, also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial ( healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections and is historically associated with hygiene, epidemiology, clinical microbiology, travel medicine and tropical medicine. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. Although many common infections are treated by physicians without formal expertise in infectious diseases, specialists may be consulted for cases where an infection is difficult to diagnose or manage. They may also be asked to help determine the cause of a fever of unknown origin. Specialists in infectious diseases can practice both in hospitals (inpatient) and clinics (outpatient). In hospit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or organ function depending on which nerves are affected; in other words, neuropathy affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerves result in different symptoms. More than one type of nerve may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa, African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardized geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organization describing the region (e.g. UN, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The Regions of the African Union, African Union uses a different regional breakdown, recognizing all 55 member states on the continent - grouping them into 5 distinct and standard regions. The term serves as a grouping counterpart to North Africa, which is instead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth," refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening, and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, also known as penicillin G (PenG) or BENPEN, and in military slang "Peanut Butter Shot" is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes pneumonia, strep throat, syphilis, necrotizing enterocolitis, diphtheria, gas gangrene, leptospirosis, cellulitis, and tetanus. It is not a first-line agent for pneumococcal meningitis. Due to Benzylpenicillin's limited bioavailability for oral medications, it is generally taken as an injection in the form of a sodium, potassium, benzathine, or procaine salt. Benzylpenicillin is given by injection into a vein or muscle. Two long-acting forms benzathine benzylpenicillin and procaine benzylpenicillin are available for use by injection into a muscle. Side effects include diarrhea, seizures, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. When used to treat syphilis or Lyme disease a reaction known as Jarisch–Herxheimer may occur. It is not recommended in those with a history of penicillin allergy. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used during pregnancy to prevent Group B streptococcal infection in the newborn, as well as to improve delayed stomach emptying. It can be given intravenously and by mouth. An eye ointment is routinely recommended after delivery to prevent eye infections in the newborn. Common side effects include abdominal cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea. More serious side effects may include ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis, liver problems, prolonged QT, and allergic reactions. It is generally safe in those who are allergic to penicillin. Erythromycin also appears to be safe to use during pregnancy. While generally regarded as safe during breastfeeding, its use by the mother during the first two weeks of life may increase the risk of pyloric stenosis in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antisep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertussis Vaccine
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effective. The effectiveness of the vaccines appears to decrease by between 2 and 10% per year after vaccination with a more rapid decrease with the acellular vaccines. The vaccine is only available in combination with tetanus and diphtheria vaccines. Pertussis vaccine is estimated to have saved over 500,000 lives in 2002. Vaccinating the mother during pregnancy may protect the baby. The World Health Organization and Center for Disease Control and Prevention recommend all children be vaccinated for pertussis and that it be included in routine vaccinations. Three doses starting at six weeks of age are typically recommended in young children. Additional doses may be given to older children and adults. This recommendation includes people who have H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanus Vaccine
Tetanus vaccine, also known as tetanus toxoid (TT), is a toxoid vaccine used to prevent tetanus. During childhood, five doses are recommended, with a sixth given during adolescence. After three doses, almost everyone is initially immune, but additional doses every ten years are recommended to maintain immunity. A booster shot should be given within 48 hours of an injury to people whose immunization is out of date. For people with high-risk injuries who are not fully immunized, tetanus antitoxin may also be recommended. Confirming that pregnant women are up to date on tetanus immunization during each pregnancy can prevent both maternal and neonatal tetanus. The vaccine is very safe, including during pregnancy and in those with HIV/AIDS. Redness and pain at the site of injection occur in between 25% and 85% of people. Fever, feeling tired, and minor muscle pain occurs in less than 10% of people. Severe allergic reactions occur in less than one in 100,000 people. A number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphtheria Vaccine
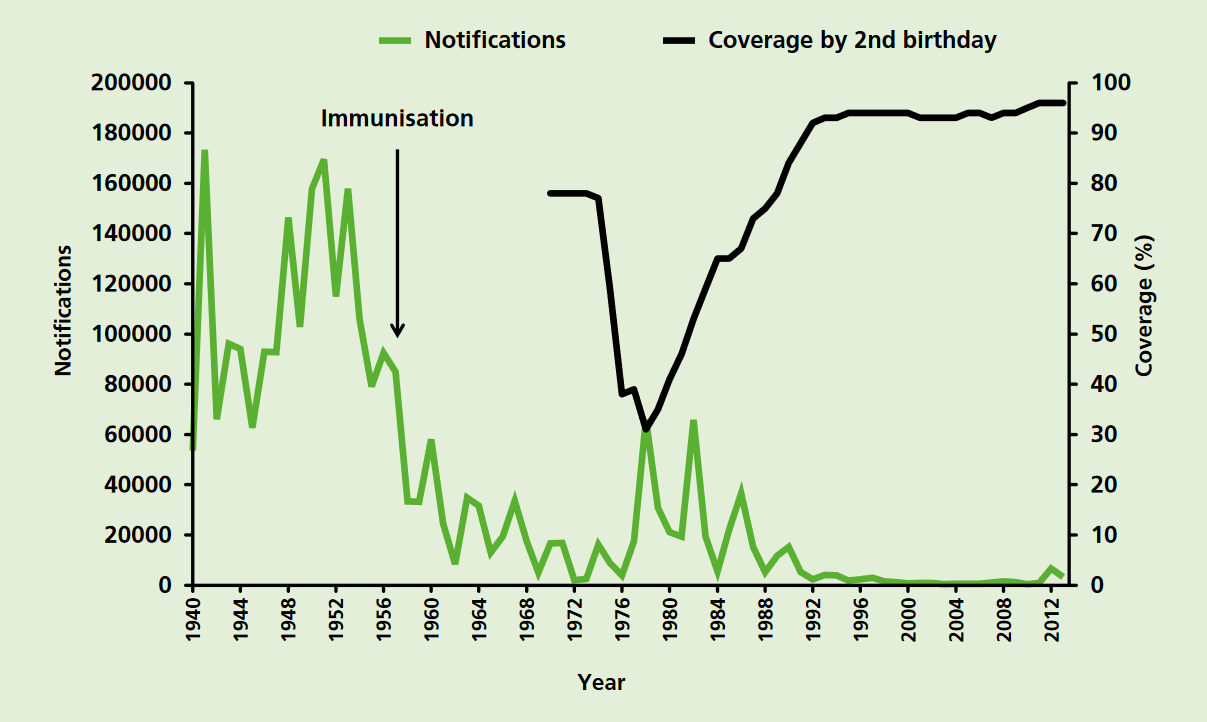
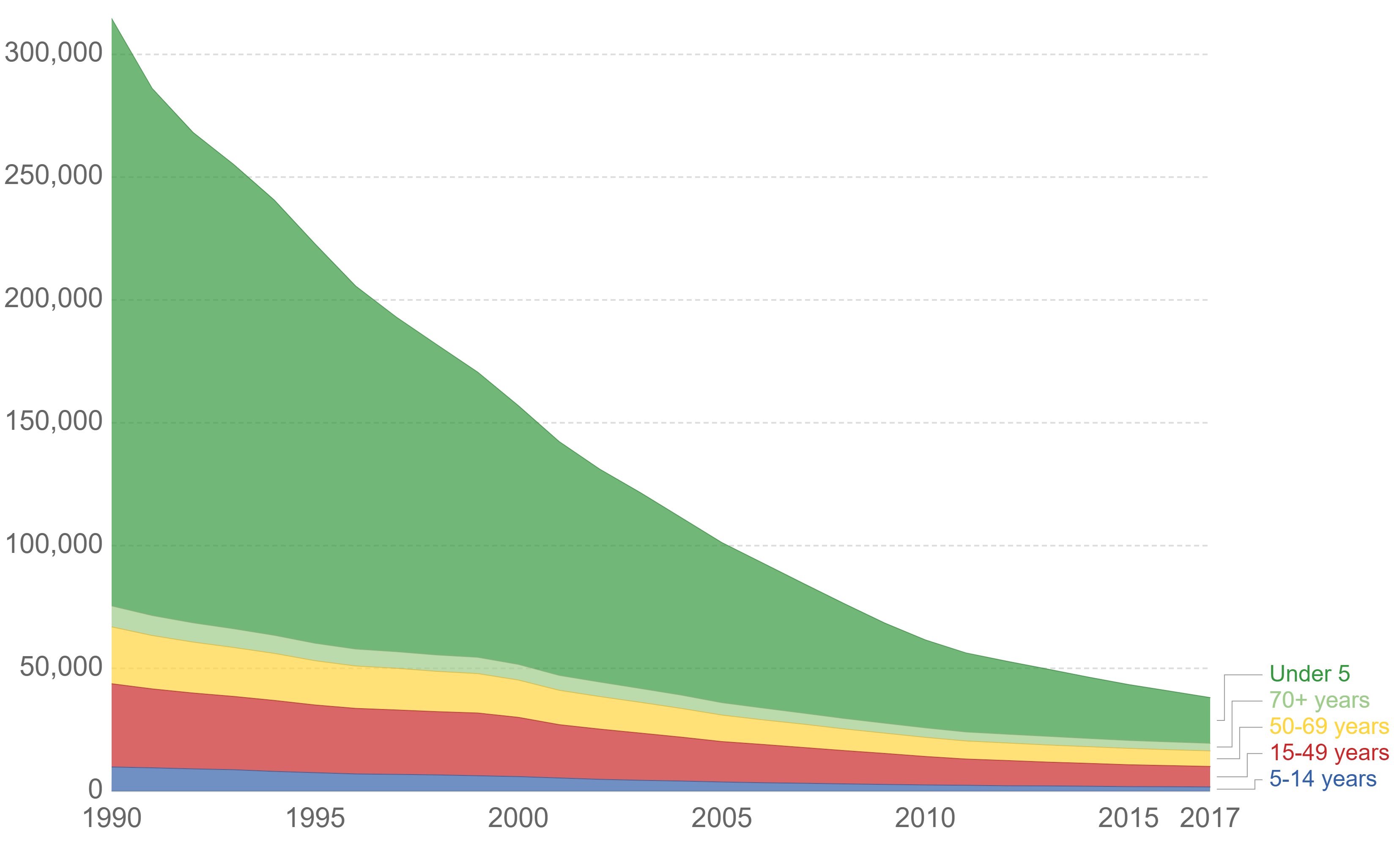
Diphtheria vaccine is a toxoid vaccine against diphtheria, an illness caused by '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Its use has resulted in a more than 90% decrease in number of cases globally between 1980 and 2000. The first dose is recommended at six weeks of age with two additional doses four weeks apart, after which it is about 95% effective during childhood. Three further doses are recommended during childhood. It is unclear if further doses later in life are needed. The diphtheria vaccine is very safe. Significant side effects are rare. Pain may occur at the injection site. A bump may form at the site of injection that lasts a few weeks. The vaccine is safe in both pregnancy and among those who have a poor immune function. The diphtheria vaccine is delivered in several combinations. Some combinations (Td and DT vaccines) include tetanus vaccine, others (known as DPT vaccine or DTaP vaccine depending on the pertussis antigen used) comes with the tetanus and pertussis va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during lysis of the cell. Gram negative pathogens may secrete outer membrane vesicles containing lipopolysaccharide endotoxin and some virulence proteins in the bounding membrane along with some other toxins as intra-vesicular contents, thus adding a previously unforeseen dimension to the well-known eukaryote process of membrane vesicle trafficking, which is quite active at the host–pathogen interface. They may exert their effect locally or produce systemic effects. Well-known exotoxins include: botulinum toxin produced by '' Clostridium botulinum''; ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' toxin, produced during life-threatening symptoms of diphtheria; tetanospasmin produced by ''Clostridium tetani''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed with some form of permanent or transient paralysis. The word "paralysis" derives from the Greek παράλυσις, meaning "disabling of the nerves" from παρά (''para'') meaning "beside, by" and λύσις (''lysis'') meaning "making loose". A paralysis accompanied by involuntary tremors is usually called "palsy". Causes Paralysis is most often caused by damage in the nervous system, especially the spinal cord. Other major causes are stroke, trauma with nerve injury, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, ALS, botulism, spina bifida, multiple sclerosis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Temporary paralysis occurs during REM sleep, and dysregulation of this system can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |