|
Dioptre
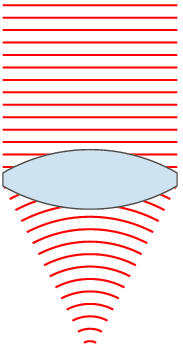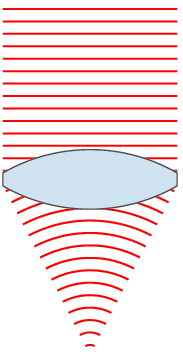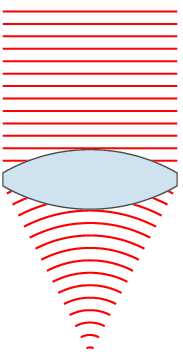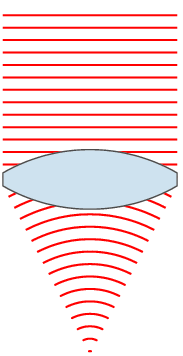
A dioptre (British spelling) or diopter (American spelling) is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dioptre = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams. The main benefit of using optical power rather than focal length is that the thin lens formula has the object distance, image distance, and focal length all as reciprocals. Additionally, when relatively thin lenses are placed close together their powers approximately add. Thus, a thin 2.0-dioptre lens placed clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vergence (optics)
In optics, vergence is the angle formed by rays of light that are not perfectly parallel to one another. Rays that move closer to the optical axis as they propagate are said to be ''converging'', while rays that move away from the axis are ''diverging''. These imaginary rays are always perpendicular to the wavefront of the light, thus the vergence of the light is directly related to the radii of curvature of the wavefronts. A convex lens or concave mirror will cause parallel rays to focus, converging toward a point. Beyond that focal point, the rays diverge. Conversely, a concave lens or convex mirror will cause parallel rays to diverge. Light does not actually consist of imaginary rays and light sources are not single-point sources, thus vergence is typically limited to simple ray modeling of optical systems. In a real system, the vergence is a product of the diameter of a light source, its distance from the optics, and the curvature of the optical surfaces. An increase in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length of the device: . High optical power corresponds to short focal length. The SI unit for optical power is the inverse metre (m−1), which is commonly called the dioptre. Converging lenses have positive optical power, while diverging lenses have negative power. When a lens is immersed in a refractive medium, its optical power and focal length change. For two or more thin lenses close together, the optical power of the combined lenses is approximately equal to the sum of the optical powers of each lens: . Similarly, the optical power of a single lens is roughly equal to the sum of the powers of each surface. These approximations are commonly used in optometry. An eye that has too much or too little refractive power to foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Metre
Reciprocal length or inverse length is a quantity or measurement used in several branches of science and mathematics. As the reciprocal of length, common units used for this measurement include the reciprocal metre or inverse metre (symbol: m−1), the reciprocal centimetre or inverse centimetre (symbol: cm−1). Quantities measured in reciprocal length include: *absorption coefficient or attenuation coefficient, in materials science *curvature of a line, in mathematics *gain, in laser physics * magnitude of vectors in reciprocal space, in crystallography *more generally any spatial frequency e.g. in cycles per unit length *optical power of a lens, in optics *rotational constant of a rigid rotor, in quantum mechanics *wavenumber, or magnitude of a wavevector, in spectroscopy *density of a linear feature in hydrology and other fields; see kilometre per square kilometre In optics, the dioptre is a unit equivalent to reciprocal metre. Measure of energy In some branches of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Monoyer
Ferdinand Monoyer (9 May 1836 – 11 July 1912) was a French ophthalmologist, known for introducing the dioptre in 1872. He invented the Monoyer chart, used to test visual acuity. He inserted his name in the random letters of the chart. It appears when one reads vertically from bottom to top on each side. Biography Monoyer was of Alsatian heritage by his mother and his father was a French military doctor. He was an associate professor of medical physics at the Faculty of Medicine, University of Strasbourg in 1871. Later, he was the director of the Ophthalmic Clinic of the Faculty of Medicine, Nancy-Université from 1872 to 1877. He was also professor of medical physics at the Faculty of Medicine, University of Lyon The University of Lyon (french: Université de Lyon), located in Lyon and Saint-Étienne, France, is a center for higher education and research comprising 11 members and 24 associated institutions. The three main universities in this center are: C ..., from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word '' lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Lens Formula
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plant), be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocal Metre
Reciprocal length or inverse length is a quantity or measurement used in several branches of science and mathematics. As the reciprocal of length, common units used for this measurement include the reciprocal metre or inverse metre (symbol: m−1), the reciprocal centimetre or inverse centimetre (symbol: cm−1). Quantities measured in reciprocal length include: *absorption coefficient or attenuation coefficient, in materials science *curvature of a line, in mathematics *gain, in laser physics *magnitude of vectors in reciprocal space, in crystallography *more generally any spatial frequency e.g. in cycles per unit length *optical power of a lens, in optics *rotational constant of a rigid rotor, in quantum mechanics *wavenumber, or magnitude of a wavevector, in spectroscopy *density of a linear feature in hydrology and other fields; see kilometre per square kilometre In optics, the dioptre is a unit equivalent to reciprocal metre. Measure of energy In some branches of ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocal Length
Reciprocal length or inverse length is a quantity or measurement used in several branches of science and mathematics. As the reciprocal of length, common units used for this measurement include the reciprocal metre or inverse metre (symbol: m−1), the reciprocal centimetre or inverse centimetre (symbol: cm−1). Quantities measured in reciprocal length include: * absorption coefficient or attenuation coefficient, in materials science *curvature of a line, in mathematics *gain, in laser physics * magnitude of vectors in reciprocal space, in crystallography *more generally any spatial frequency e.g. in cycles per unit length * optical power of a lens, in optics * rotational constant of a rigid rotor, in quantum mechanics *wavenumber, or magnitude of a wavevector, in spectroscopy *density of a linear feature in hydrology and other fields; see kilometre per square kilometre In optics, the dioptre is a unit equivalent to reciprocal metre. Measure of energy In some b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books '' Astronomia nova'', '' Harmonice Mundi'', and '' Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae''. These works also provided one of the foundations for Newton's theory of universal gravitation. Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein. Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, invented an improved version of the refracting (or Keplerian) telescop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith-Kettlewell Institute
The Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute is a nonprofit research institute in San Francisco, California, with a focus on vision science and rehabilitation engineering. It was founded in 1959 by Arthur Jampolsky and Alan B. Scott, when some members of Stanford University's Ophthalmology Department elected to stay in San Francisco rather than move to Palo Alto. Scientific contributions The Institute did early experiments in sensory substitution, especially the substitution of tactile information for visual information to help blind people navigate and other methods to obtain accessible technology. This research is often performed by scientists who are blind, such as Josh Miele. The institute's use of botulinum toxin in humans as a therapy to treat strabismus. This initial therapeutic use led to later cosmetic use in Botox. Other impactful work involved Anthony Norcia's study of vision in infants and Erich Sutter's invention of the multifocal electroretinogram and of the mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |