|
Diocese Of Boulogne
The former French Catholic diocese of Boulogne existed from 1567 to the French Revolution. It was created after the diocese of Thérouanne was suppressed because of war damage to the see; effectively this was a renaming. The Concordat of 1801 suppressed the diocese of Boulogne, transferring its territory to the diocese of Arras.Boulogne (Diocese) [Catholic-Hierarchy]/ref> The seat was the Boulogne Cathedral">atholic-Hierarchy]">Boulogne (Diocese) [Catholic-Hierarchy]/ref> The seat was the Boulogne Cathedral, demolished in 1793. Bishops * Claude-André Dormy 1567–1599 * Claude Dormy 1600–1626 * Victor Le Bouthillier 1626–1630 * Jean Dolce 1633–1643 * François Perrochel 1643–1675 * Nicolas Ladvocat-Billiard 1677–1681 * [laude Le Tonnelier de Breteuil 1682–1698 * Antoine-Girard de La Bournat 1698 * Pierre de Langle 1698–1724 * Jean-Marie Henriau 1724–1738 * Augustin-César D'Hervilly de Devise 1738–1742 * François-Joseph-Gaston de Partz de Pressy 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedrale Boulogne Enlart
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations with an episcopal hierarchy, such as the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches.New Standard Encyclopedia, 1998 by Standard Educational Corporation, Chicago, Illinois; page B-262c Church buildings embodying the functions of a cathedral first appeared in Italy, Gaul, Spain, and North Africa in the 4th century, but cathedrals did not become universal within the Western Catholic Church until the 12th century, by which time they had developed architectural forms, institutional structures, and legal identities distinct from parish churches, monastic churches, and episcopal residences. The cathedral is more important in the hierarchy than the church because it is from the cathedral that the bishop governs the area und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine-Girard De La Bournat
Antoine-Girard de La Bournat (1656, Clermont - 8 March 1702) was a French cleric and a doctor at the Sorbonne. He was put in charge of educating Louis Alexandre, Count of Toulouse by Louis XIV of France. He was already abbot of Pontlevoy Abbey when he was made bishop of Toul in 1697. He was also made bishop of Boulogne and bishop of Poitiers The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Poitiers (Latin: ''Archidioecesis Pictaviensis''; French: ''Archidiocèse de Poitiers'') is an archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church in France. The archepiscopal see is in the city of Poitiers. ..., both in 1698. Sources *Eugène Van Drival, ''Histoire des évêques de Boulogne'', Boulogne-sur-Mer, 1852 1656 births 1702 deaths Bishops of Boulogne Bishops of Toul Bishops of Poitiers {{France-bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
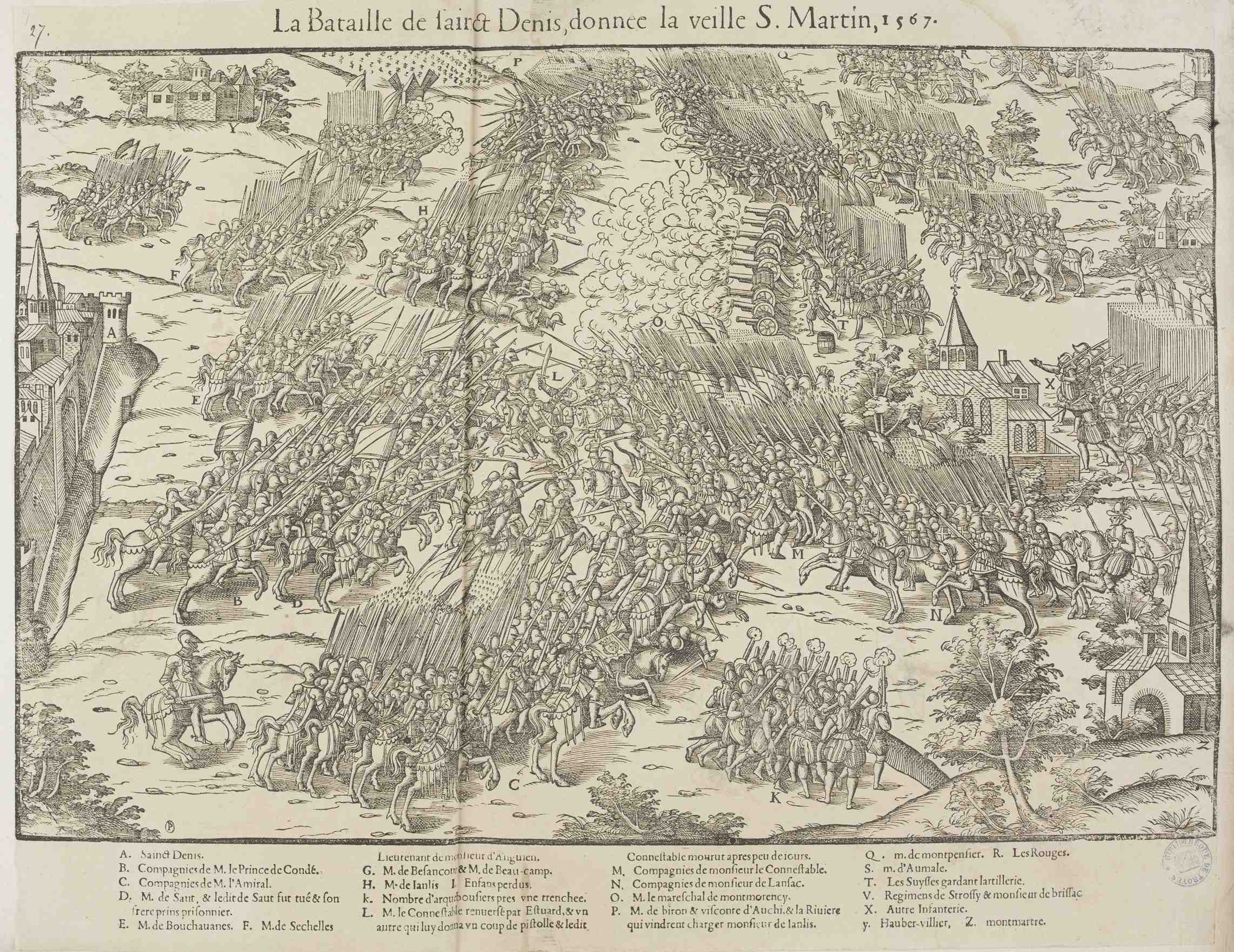
1567 Establishments In France
__NOTOC__ Year 1567 ( MDLXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January – A Spanish force under the command of Captain Juan Pardo establishes Fort San Juan, in the Native American settlement of Joara. The fort is the first European settlement in present-day North Carolina. * January 20 – Battle of Rio de Janeiro: Portuguese forces under the command of Estácio de Sá definitively drive the French out of Rio de Janeiro. * January 23 – After 45 years' reign, the Jiajing Emperor dies in the Forbidden City of China. * February 4 – The Longqing Emperor ascends the throne of the Ming Dynasty. * February 10 – Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley, husband of Mary, Queen of Scots, is murdered at the Provost's House in Kirk o' Field, Edinburgh. * March 13 – Battle of Oosterweel: A Spanish mercenary army surprises and kills a band of rebels near Antwerp in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioceses Established In The 16th Century
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Organizations Established In The 1560s
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Religions ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Roman Catholic Dioceses In France
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Catholic Dioceses In France
The Catholic Church in France mainly comprises a Metropolitan Latin Church hierarchy, joint in a national episcopal conference, consisting of * fifteen ecclesiastical provinces, each under a Metropolitan Archdioceses (15) ** with a total of 80 suffragans: seven non-Metropolitan Archdioceses, 72 bishoprics and a Territorial Prelature * two exempt non-Metropolitan Archdioceses * the (exempt) Military Ordinariate. Furthermore, it has four exempt Eastern Catholic jurisdictions : three rite-specific (of which two are transnational) and a national Ordinariate for the Faithful of Eastern Rite for all others without rite-proper Ordinary. The French overseas departments and territories, although administratively and constitutionally part of the French republic, are not part of the French church under canon law but exempt and/or part of an episcopal conference in their respective continent. There is also an Apostolic Nunciature (as papal diplomatic representation at embassy-level) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In France
, native_name_lang = fr , image = 060806-France-Paris-Notre Dame.jpg , imagewidth = 200px , alt = , caption = Cathedral Notre-Dame de Paris , abbreviation = , type = National polity , main_classification = Catholic , orientation = Christianity , scripture = Bible , theology = Catholic theology , polity = , governance = CEF , structure = , leader_title = Pope , leader_name = , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Éric de Moulins-Beaufort , leader_title2 = Primate of the Gauls , leader_name2 = Olivier de Germay , leader_title3 = Apostolic Nuncio , leader_name3 = Celestino Migliore , fellowships_type = , fellowships = , fellowships_type1 = , fellowships1 = , division_type = , division = , division_type1 = , div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-René Asseline
Jean-René Asseline (1742-1813) was a French bishop and theologian. Life His early posts were as grand vicar to Christophe de Beaumont, archbishop of Paris, and teaching scripture and theology at the Sorbonne. In 1789 he was made bishop of Boulogne and commendatory abbot of Ham Abbey - he held both posts until the following year, when the abbey and the bishopric were both suppressed. He refused to swear the oath to obey the Civil Constitution of the Clergy in 1791 and emigrated to Munster, from where he criticized the Concordat of 1801. In 1807 he was summoned by Louis XVIII Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in ... and served the French royal family until his death in 1813.Mémoires du Prince de Talleyrand, vol II, page 38, 1891 edition Works * ''Instruction pastor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Joseph-Gaston De Partz De Pressy
François-Joseph-Gaston de Partz de Pressy (22 September 1712, Équirre - 8 October 1789) was a French cleric. He was the son of François-Joseph de Partz, marquis d'Esquire, and of Jeanne Elisabeth de Beaufort. He became vicar general of Boulogne-Sur-Mer Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ..., then in 1742 bishop of Boulogne and in 1746 commendatory abbot of Ham Abbey. Sources *Eugène Van Drival, ''Histoire des évêques de Boulogne'', Boulogne-sur-Mer, 1852. 1712 births 1789 deaths Bishops of Boulogne People from Pas-de-Calais 18th-century French Roman Catholic bishops {{France-RC-bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustin-César D'Hervilly De Devise
Augustin-César d'Hervilly de Devise (1708 – 11 October 1742, in Château de Voisenon) was a French cleric. d'Hervilly de Devise was from a noble family from Picardy. he became canon and archdeacon of Cambrai and provost of Lille Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France region, the prefecture of the N ... when in 1738 he was made bishop of Boulogne and commendatory abbot of Valloires Abbey. In 1745 he was also made commendatory abbot of Ham Abbey. His secretary was canon Lesage, son of the author Alain-René Lesage. References *Eugène Van Drival, ''Histoire des évêques de Boulogne'', Boulogne-sur-Mer, 1852. Bishops of Boulogne 1708 births 1742 deaths 18th-century French Roman Catholic bishops {{France-RC-bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Marie Henriau
Jean-Marie Henriau (c.1661, Paris - 25 January 1738) was a French cleric and opponent of Jansenism. The son of a procureur to the parliament of Paris, he became conseiller-clerc to the parliament, then prior of Beaurain and canon and grand-vicar of Lisieux. He was also abbot of Valloires Abbey. He was made bishop of Boulogne in 1724 and immediately raised the interdict and set up a tribunal for penitence, chaired and run by the Capucins and Minims of Boulogne-Sur-Mer and Calais as well as the four Recollets convents shut down by his Jansenist predecessor Pierre de Langle. Also in 1724, Henriau ordered that the papal bull ''Unigenitus'' be accepted on pain of excommunication and banned reading or ownership of Pasquier Quesnel Pasquier Quesnel, CO (14 July 1634 – 2 December 1719) was a French Jansenist theologian. Life Quesnel was born in Paris, and, after graduating from the Sorbonne with distinction in 1653, he joined the French Oratory in 1657. There he soon ...'s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |