|
Dimethyl Pimelimidate
Dimethyl pimelimidate (DMP) is an organic chemical compound with two functional imidate groups. It is usually available as the more stable dihydrochloride salt. It binds free amino groups at pH range 7.0-10.0 to form amidine bonds. Uses DMP is used mainly as bifunctional coupling reagent to link proteins. It is often used to prepare antibody affinity columns. The appropriate antibody is first incubated with Protein A or Protein G-agarose and allowed to bind. DMP is then added to couple the molecules together. Health effects DMP is irritating to the eyes, skin, mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. It can exert harmful effects by inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption Skin absorption is a route by which substances can enter the body through the skin. Along with inhalation, ingestion and injection, dermal absorption is a route of exposure for toxic substances and route of administration for medication. Absorpti .... References MSDS safety data also available i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemical Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon chemical bond, bonds. Due to carbon's ability to Catenation, catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate, carbonate salts and cyanide, cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered Inorganic chemistry, inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
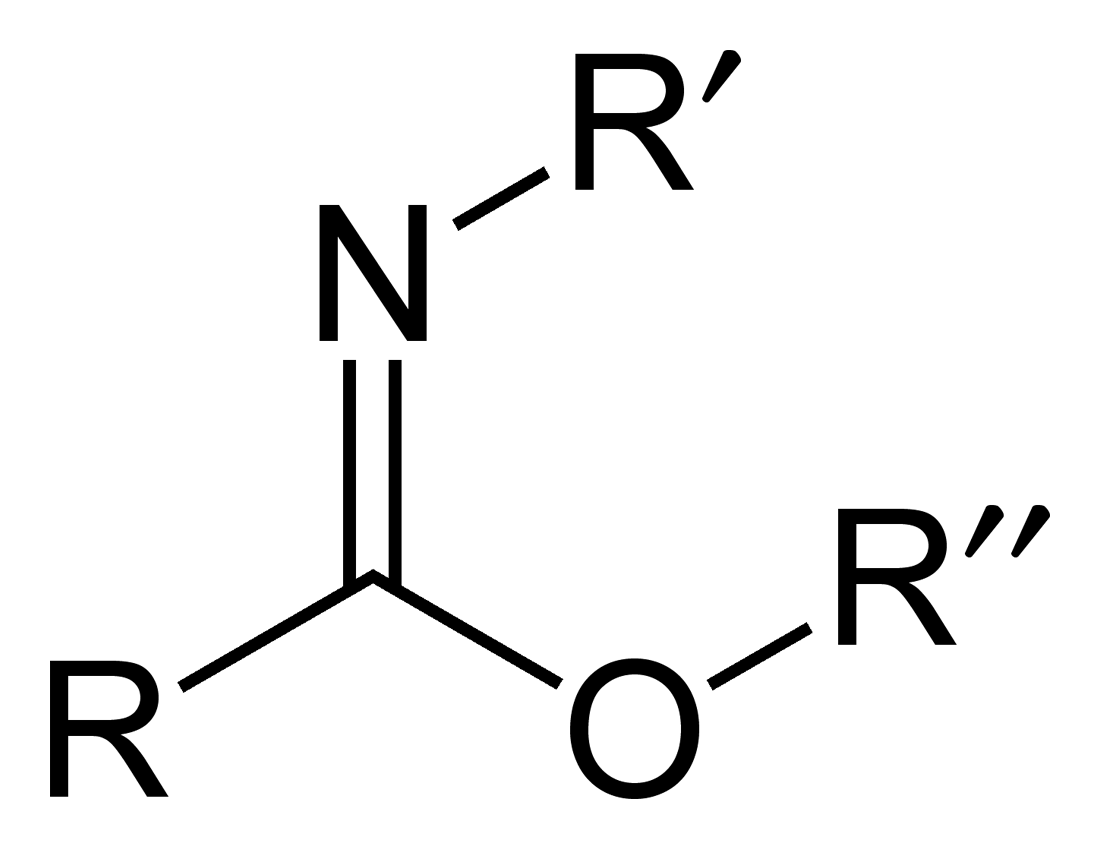
Imidate
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as esters formed between a carboximidic acid (R-C(=NR')OH) and an alcohol, with the general formula R-C(=NR')OR". They are also known as imino ethers, since they resemble imines (>C=N-) with an oxygen atom connected to the carbon atom of the C=N double bond. Synthesis Imidates may be generated by a number of synthetic routes, but are in general formed by the Pinner reaction. This proceeds via the acid catalyzed attack of nitriles by alcohols. Imidates produced in this manner are formed as their hydrochloride salts, which are sometimes referred to as Pinner salts. Carboximidates are also formed as intermediates in the Mumm rearrangement and the Overman rearrangement. Imidate/amidate anions An amidate/imidate anion is formed upon deprotonation of an amide or imidic acid. Since amides and imidic acids are tautomers, they form the same anion upon deprotonation. The two names are thus sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amines into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. Additionally, many hydrochlorides of amines have a longer shelf-life than their respective free bases. Amine hydrochlorides represent latent forms of a more reactive free base. In this regard, formation of an amine hydrochloride confers protection. This eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is Salt, table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic compound, inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic chemistry, organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic ion, monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic ion, polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amidine
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2. Examples of amidines include: * DBU * diminazene * benzamidine * Pentamidine * Paranyline Preparation A common route to primary amidines is the Pinner reaction. Reaction of the nitrile with alcohol in the presence of acid gives an iminoether. Treatment of the resulting compound with ammonia then completes the conversion to the amidine. Instead of using a Bronsted acid, Lewis acids such as aluminium trichloride promote the direct amination of nitriles. They are also generated by amination of an imidoyl chloride. They are also prepared by the addition of organolithium reagents to diimines, followed by protonation or alkylation. Dimethylformamide acetal reacts with primary amines to give amidines: :Me2NC(H)(OMe)2 + RNH2 → Me2NC=NHR + 2 MeOH Properties and appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein A
Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria ''Staphylococcus aureus''. It is encoded by the ''spa'' gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation (in relation to normal antibody function), the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis. History As a by-product of his work on type-specific staphylococcus antigens, Verwey reported in 1940 that a protein fraction prepared fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein G
Protein G is an immunoglobulin-binding protein expressed in group C and G Streptococcal bacteria much like Protein A but with differing binding specificities. It is a ~60-kDA (65 kDA for strain G148 and 58 kDa for strain C40) cell surface protein that has found application in purifying antibodies through its binding to the Fab and Fc region. The native molecule also binds albumin, but because serum albumin is a major contaminant of antibody sources, the albumin binding site has been removed from recombinant forms of Protein G. This recombinant Protein G, either labeled with a fluorophore or a single-stranded DNA strand, was used as a replacement for secondary antibodies in immunofluorescence and super-resolution imaging. Other antibody binding proteins In addition to Protein G, other immunoglobulin-binding bacterial proteins such as Protein A, Protein A/G and Protein L are all commonly used to purify, immobilize or detect immunoglobulins. Each of these immunoglobulin-binding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agarose
Agarose is a heteropolysaccharide, generally extracted from certain red seaweed. It is a linear polymer made up of the repeating unit of agarobiose, which is a disaccharide made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose. Agarose is one of the two principal components of agar, and is purified from agar by removing agar's other component, agaropectin. Agarose is frequently used in molecular biology for the separation of large molecules, especially DNA, by electrophoresis. Slabs of agarose gels (usually 0.7 - 2%) for electrophoresis are readily prepared by pouring the warm, liquid solution into a mold. A wide range of different agaroses of varying molecular weights and properties are commercially available for this purpose. Agarose may also be formed into beads and used in a number of chromatographic methods for protein purification. Structure Agarose is a linear polymer with a molecular weight of about 120,000, consisting of alternating D-galactose and 3,6-anhyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa. Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity, where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next, air moves into the pharynx, a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage, the epiglottis, that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to prevent food from moving into the airway. From the larynx, air moves into the trachea and down to the intersection known as the carina that branches to form the right and left primary (main) bronchi. Each of these bronchi branches into a secondary (lobar) bronchus that branches into tertiary (segmental) bronchi, that branch into smaller airways called bronchioles th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs. Inhalation of air Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions in some disease states) and does not need conscious control or effort. However, breathing can be consciously controlled or interrupted (within limits). Breathing allows oxygen (which humans and a lot of other species need for survival) to enter the lungs, from where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Other substances – accidental Examples of accidental inhalation includes inhalation of water (e.g. in drowning), smoke, food, vomitus and less common foreign substances (e.g. tooth fragments, coins, batteries, small toy parts, needles). Other substances – deliberate Recreational use Legal – helium, nitrous oxide (" laughing gas") Illegal – various gaseous, vaporised or aerosolized recreational drugs Medical use D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |