|
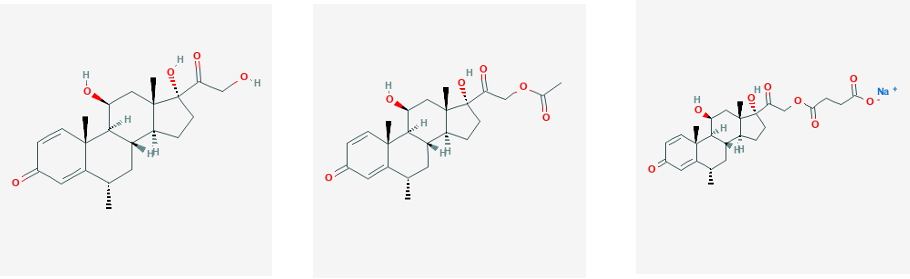
Depomedrol
Methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol, Medrol, Solu-Medrol) is a synthetic glucocorticoid, primarily prescribed for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. It is either used at low doses for chronic illnesses or used concomitantly at high doses during acute flares. Methylprednisolone and its derivatives can be administered orally or parenterally. Regardless of route of administration, methylprednisolone integrates systemically as exhibited by its effectiveness to quickly reduce inflammation during acute flares. It is associated with many adverse reactions that require tapering off the drug as soon as the disease is under control. Serious side effects include iatrogenic Cushing's Syndrome, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes, infection, and skin atrophy. Chemically, methylprednisolone is a synthetic pregnane steroid hormone derived from hydrocortisone and prednisolone. It belongs to a class of synthetic glucocorticoids and more generally, corticosteroids. It acts as a min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylprednisolone Acetate
Methylprednisolone acetate, sold under the brand names Depo-Medrol among others, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and a corticosteroid ester—specifically the C21 acetate ester of methylprednisolone—which is used in clinical and veterinary medicine. It has been formulated as an aqueous suspension for intramuscular, intra-articular, soft tissue, and intralesional injection alone and in combination with lidocaine, a local anesthetic. Methylprednisolone acetate was previously suspended with polyethylene glycol but is no longer formulated with this excipient due to concerns about possible toxicity. Depo methylprednisolone acetate is a depot injection A depot injection is a term for an injection formulation of a medication which releases slowly over time to permit less frequent administration of a medication. They are designed to increase medication adherence and consistency, especially in ... and is absorbed slowly with a duration of weeks to months with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upjohn
The Upjohn Company was a pharmaceutical manufacturing firm founded in 1886 in Hastings, Michigan, by Dr. William E. Upjohn who was an 1875 graduate of the University of Michigan medical school. The company was originally formed to make ''friable pills'', which were specifically designed to be easily digested. These could be "reduced to a powder under the thumb", a strong marketing argument at the time. History Upjohn developed a process for the large scale production of cortisone. The oxygen atom at the 11 position in this steroid is an absolute requirement for biological activity. There are however no known natural sources for starting materials that contain that feature. The only method for preparing this drug prior to 1952 was a lengthy synthesis starting from cholic acid isolated from bile. In 1952, two Upjohn biochemists, Dury Peterson and Herb Murray announced that they were able to introduce this crucial oxygen atom by fermentation of the steroid progesterone with a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
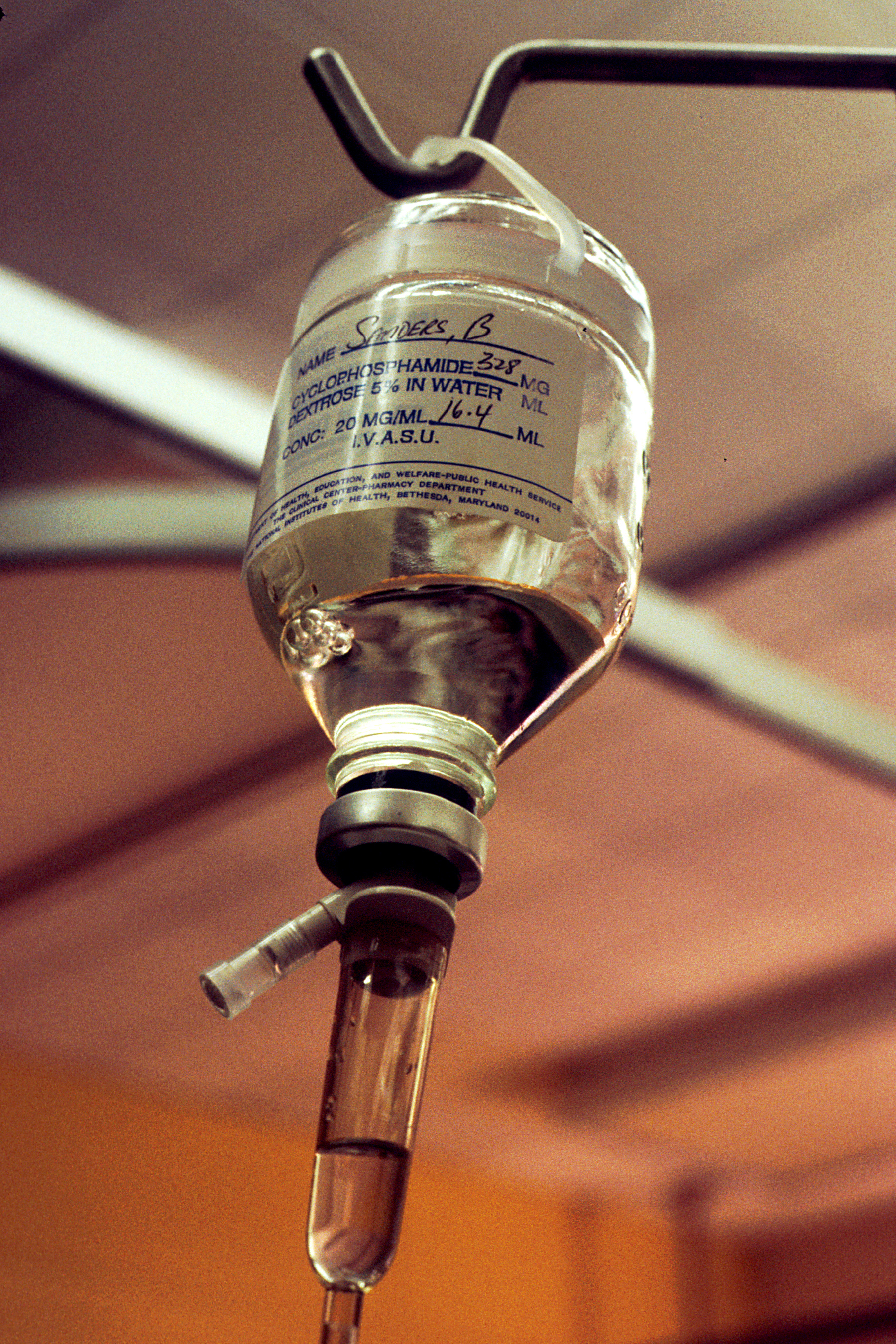
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylprednisolone Inhibits The HPA Axis
Methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol, Medrol, Solu-Medrol) is a synthetic glucocorticoid, primarily prescribed for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. It is either used at low doses for chronic illnesses or used concomitantly at high doses during acute flares. Methylprednisolone and its derivatives can be administered orally or parenterally. Regardless of route of administration, methylprednisolone integrates systemically as exhibited by its effectiveness to quickly reduce inflammation during acute flares. It is associated with many adverse reactions that require tapering off the drug as soon as the disease is under control. Serious side effects include iatrogenic Cushing's Syndrome, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes, infection, and skin atrophy. Chemically, methylprednisolone is a synthetic pregnane steroid hormone derived from hydrocortisone and prednisolone. It belongs to a class of synthetic glucocorticoids and more generally, corticosteroids. It acts as a mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukotriene
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase. Leukotrienes use lipid signaling to convey information to either the cell producing them (autocrine signaling) or neighboring cells (paracrine signaling) in order to regulate immune responses. The production of leukotrienes is usually accompanied by the production of histamine and prostaglandins, which also act as inflammatory mediators. One of their roles (specifically, leukotriene D4) is to trigger contractions in the smooth muscles lining the bronchioles; their overproduction is a major cause of inflammation in asthma and allergic rhinitis. Leukotriene antagonists are used to treat these disorders by inhibiting the production or activity of leukotrienes. History and name The name ''leukotriene'', introduced by Swedish biochemist Bengt Samuelss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues in some cases. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells present in the immediate vicinity of the site of their secreti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annexin A1
Annexin A1, also known as lipocortin I, is a protein that is encoded by the ''ANXA1'' gene in humans. Function Annexin A1 belongs to the annexin family of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins that have a molecular weight of approximately 35,000 to 40,000 Dalton and are preferentially located on the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane. Annexin A1 protein has an apparent relative molecular mass of 40 kDa with phospholipase A2 inhibitory activity. Clinical significance Effect on innate and adaptive immunity Glucocorticoids (such as budesonide, cortisol, and beclomethasone) are a class of endogenous or synthetic anti- inflammatory steroid hormones that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), which is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. They are used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an overactive immune system, including allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Because they suppress inflammatory pathways, long-term use of glucocortico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid Response Elements
Response elements are short sequences of DNA within a gene promoter or enhancer region that are able to bind specific transcription factors and regulate transcription of genes. Under conditions of stress, a transcription activator protein binds to the response element and stimulates transcription. If the same response element sequence is located in the control regions of different genes, then these genes will be activated by the same stimuli, thus producing a coordinated response. Hormone response element A hormone response element (HRE) is a short sequence of DNA within the promoter of a gene, that is able to bind to a specific hormone receptor complex and therefore regulate transcription. The sequence is most commonly a pair of inverted repeats separated by three nucleotides, which also indicates that the receptor binds as a dimer. Specifically, HRE responds to steroid hormones, as the activated steroid receptor is the transcription factor binding HRE. This regulates the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunophilins
In molecular biology, immunophilins are endogenous cytosolic peptidyl-prolyl isomerases (PPI) that catalyze the interconversion between the cis and trans isomers of peptide bonds containing the amino acid proline (Pro). They are chaperone molecules that generally assist in the proper folding of diverse "client" proteins. Immunophilins are traditionally classified into two families that differ in sequence and biochemical characteristics. These two families are: "cyclosporin-binding cyclophilins (CyPs)" and "FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs)". In 2005, a group of dual-family immunophilins (DFI) has been discovered, mostly in unicellular organisms; these DFIs are natural chimera of CyP and FKBPs, fused in either order (CyP-FKBP or FKBP-CyP). Immunophilins act as receptors for immunosuppressive drugs such as sirolimus (rapamycin), cyclosporin (such as CsA) and tacrolimus (FK506), which inhibit the prolyl isomerase activity of the immunophilins. The drug-immunophilin complexes (CsA-CyP an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shock Protein
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are a family of proteins produced by cells in response to exposure to stressful conditions. They were first described in relation to heat shock, but are now known to also be expressed during other stresses including exposure to cold, UV light and during wound healing or tissue remodeling. Many members of this group perform chaperone functions by stabilizing new proteins to ensure correct folding or by helping to refold proteins that were damaged by the cell stress. This increase in expression is transcriptionally regulated. The dramatic upregulation of the heat shock proteins is a key part of the heat shock response and is induced primarily by heat shock factor (HSF). HSPs are found in virtually all living organisms, from bacteria to humans. Heat-shock proteins are named according to their molecular weight. For example, Hsp60, Hsp70 and Hsp90 (the most widely studied HSPs) refer to families of heat shock proteins on the order of 60, 70 and 90 kilodal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction Image
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |