|
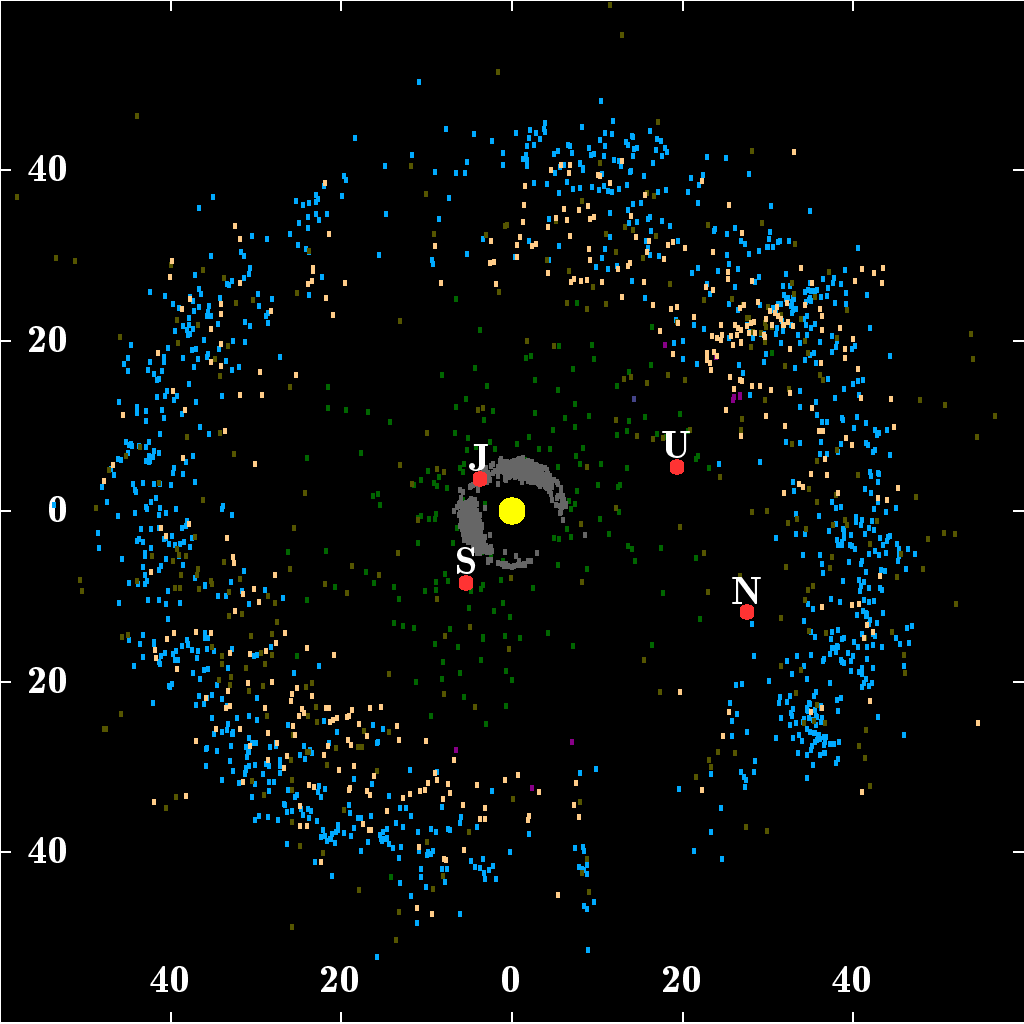
Damocloid
Damocloids are a class of minor planets such as 5335 Damocles and 1996 PW that have Halley-type or long-period highly eccentric orbits typical of periodic comets such as Halley's Comet, but without showing a cometary coma or tail. David Jewitt defines a damocloid as an object with a Jupiter Tisserand invariant (TJ) of 2 or less, while Akimasa Nakamura defines this group with the following orbital elements: * q 8.0 AU, and e > 0.75, * or alternatively, ''i'' > 90 ° However, this definition that does not focus on Jupiter excludes objects such as , , and . Using the Tisserand's parameter with respect to Jupiter of 2 or less, there are currently 220 damocloid candidates . Of these objects, 189 have orbital observation arcs greater than 30 days providing reasonably decent orbits. Their average radius is eight kilometers assuming an albedo of 0.04. The albedos of four damocloids have been measured, and they are among the darkest objects known in the Solar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1996 PW
is an exceptionally eccentric trans-Neptunian object and damocloid on an orbit typical of long-period comets but one that showed no sign of cometary activity around the time it was discovered. The unusual object measures approximately in diameter and has a rotation period of 35.4 hours and likely an elongated shape. Description orbits the Sun at a distance of 2.5–504 AU once every 4,033 years (semi-major axis of 253 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.99 and an inclination of 30 ° with respect to the ecliptic. Simulations indicate that it has most likely come from the Oort cloud, with a roughly equal probability of being an extinct comet and a rocky body that was originally scattered into the Oort cloud. The discovery of prompted theoretical research that suggests that roughly 1 to 2 percent of the Oort cloud objects are rocky. was first observed on 9 August 1996 by the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) automated search camera on Haleakala Observator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5335 Damocles
(5335) Damocles , provisional designation , is a centaur and the namesake of the damocloids, a group of minor planets which may be inactive nuclei of the Halley-type and long-period comets. It was discovered on 18 February 1991, by Australian astronomer Robert McNaught at Siding Spring Observatory in Australia. It is named after Damocles, a figure of Greek mythology. Description When ''Damocles'' was discovered, it was found to be on an orbit completely different from all others known. ''Damocles''s orbit reached from inside the aphelion of Mars to as far as Uranus. It seemed to be in transition from a near-circular outer Solar System orbit to an eccentric orbit taking it to the inner Solar System. Duncan Steel, Gerhard Hahn, Mark Bailey, and David Asher carried out projections of its long-term dynamical evolution, and found a good probability that it will become an Earth-crosser asteroid, and may spend a quarter of its life in such an orbit. ''Damocles'' has a stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20461 Dioretsa
20461 Dioretsa is a centaur and damocloid on a retrograde, cometary-like orbit from the outer Solar System. It was discovered on 8 June 1999, by members of the LINEAR team at the Lincoln Laboratory Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, United States. The highly eccentric unusual object measures approximately in diameter. It was named ''Dioretsa'', the word "asteroid" spelled backwards. Classification and orbit ''Dioretsa'' is a member of the damocloids, with a retrograde orbit and a negative TJupiter of −1.547. It is also a centaur, as its orbit has a semi-major axis in between that of Jupiter (5.5 AU) Neptune (30.1 AU). The Minor Planet Center lists it as a critical object and (other) unusual minor planet due to an orbital eccentricity of more than 0.5. It orbits the Sun at a distance of 2.4–45.4 AU once every 116 years and 10 months (42,686 days; semi-major axis of 23.9 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.90 and an inclination of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter Tisserand Invariant
Tisserand's parameter (or Tisserand's invariant) is a value calculated from several orbital elements (semi-major axis, orbital eccentricity and inclination) of a relatively small object and a larger " perturbing body". It is used to distinguish different kinds of orbits. The term is named after French astronomer Félix Tisserand, and applies to restricted three-body problems in which the three objects all differ greatly in mass. Definition For a small body with semi-major axis a\,\!, orbital eccentricity e\,\!, and orbital inclination i\,\!, relative to the orbit of a perturbing larger body with semimajor axis a_P, the parameter is defined as follows: :T_P\ = \frac + 2\cos i\sqrt The quasi-conservation of Tisserand's parameter is a consequence of Tisserand's relation. Applications * TJ, Tisserand's parameter with respect to Jupiter as perturbing body, is frequently used to distinguish asteroids (typically T_J > 3) from Jupiter-family comets (typically 2< T_J < 3).< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Comet
An extinct comet is a comet that has expelled most of its volatile ice and has little left to form a tail and coma. In a dormant comet, rather than being depleted, any remaining volatile components have been sealed beneath an inactive surface layer. Due to the near lack of a coma and tail, an extinct or dormant comet may resemble an asteroid rather than a comet and blur the distinction between these two classes of small Solar System bodies. When volatile materials such as nitrogen, water, carbon dioxide, ammonia, hydrogen and methane in the comet nucleus have evaporated away, all that remains is an inert rock or rubble pile. A comet may go through a transition phase as it comes close to extinction. Nature of extinct comets Extinct comets are those that have expelled most of their volatile ice and have little left to form a tail or coma. Over time, most of the volatile material contained in a comet nucleus evaporates away, and the comet becomes a small, dark, inert lump of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minor-planet Groups
A minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid. It is customary to name a group of asteroids after the first member of that group to be discovered, which is often the largest. Groups out to the orbit of Earth There are relatively few asteroids that orbit close to the Sun. Several of these groups are hypothetical at this point in time, with no members having yet been discovered; as such, the names they have been given are provisional. * Vulcanoid asteroids are hypothetical asteroids that orbit entirely within the orbit of Mercury (have an aphelion of less than 0.3874 AU). A few searches for vulcanoids have been conducted but none have been discovered so far. * ꞌAylóꞌchaxnim asteroids (previously named Vatira) are asteroids that orbit entirely within the orbit of Venus (have an aphelion of less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly used in the discovery and tracking of asteroids and comets. Arc length has the greatest influence on the accuracy of an orbit. The number and spacing of intermediate observations has a lesser effect. Short arcs A very short arc leaves a high uncertainty parameter. The object might be in one of many different orbits, at many distances from Earth. In some cases, the initial arc was too short to determine if the object was in orbit around the Earth, or orbiting out in the asteroid belt. With a 1-day observation arc, was thought to be a trans-Neptunian dwarf planet, but is now known to be a 1 km main-belt asteroid. With an observation arc of 3 days, was thought to be a Mars-crossing asteroid that could be a threat to Earth, but was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation. Surface albedo is defined as the ratio of radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While bi-hemispherical reflectance is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds (as obtained from flux measurements) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets— Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper-belt Object
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, may have originated in the region. The Kuiper belt was named after Dutch astronomer Gerard Kuiper, although he did not predict its existence. In 1992, minor planet (15760) Albion wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrograde Motion
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or nutation of an object's rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also refer to an object other than the primary if so described. The direction of rotation is determined by an inertial frame of reference, such as distant fixed stars. In the Solar System, the orbits around the Sun of all planets and most other objects, except many comets, are prograde. They orbit around the Sun in the same direction as the sun rotates about its axis, which is counterclockwise when observed from above the Sun's north pole. Except for Venus and Uranus, planetary rotations around their axes are also prograde. Most natural satellites have progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur (small Solar System Body)
In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body with either a perihelion or a semi-major axis between those of the outer planets (between Jupiter and Neptune). Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable (though retrograde) orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000. The first centaur to be discovered, under the definition of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)