|
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor–speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. It is a condition in which problems effectively occur with the muscles that help produce speech, often making it very difficult to pronounce words. It is unrelated to problems with understanding language (that is, dysphasia or aphasia), although a person can have both. Any of the speech subsystems ( respiration, phonation, resonance, prosody, and articulation) can be affected, leading to impairments in intelligibility, audibility, naturalness, and efficiency of vocal communication. Dysarthria that has progressed to a total loss of speech is referred to as anarthria. The term ''dysarthria'' was formed from the Greek components ''dys-'' "dysfunctional, impaired" and ''arthr-'' "joint, vocal articulation". Neurological injury due to damage in the central or peripheral nervous system may result in wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy, Dysarthria, And Ophthalmoparesis
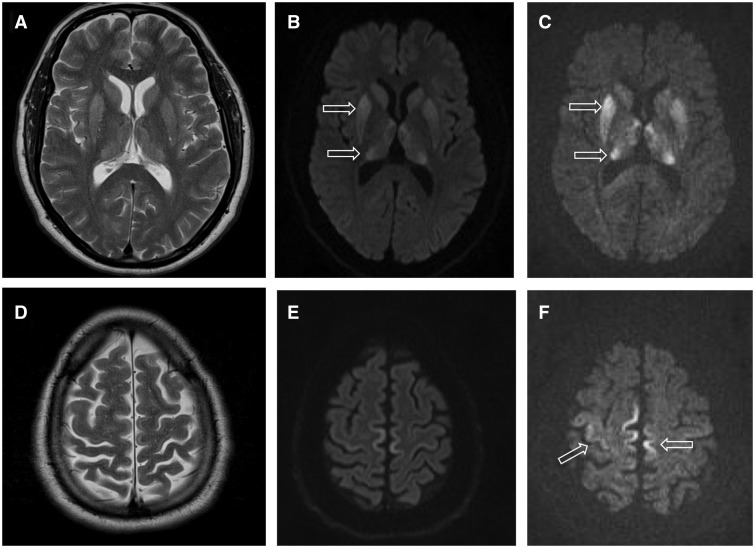
Sensory ataxic neuropathy, dysarthria, and ophthalmoparesis, also known as SANDO syndrome, is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by ocular and nerve anomalies. Signs and symptoms This disorder is characterized by the adult-onset triad consisting of the following symptoms: sensory ataxic neuropathy, dysarthria, and ophthalmoparesis. MRIS often reveals white matter abnormalities and bilateral thalamus lesions. Other symptoms include generalized myopathy, epilepsy, and deafness Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is writte .... Causes It is caused by autosomal recessive mutations in the POLG gene. Epidemiology According to OMIM, approximately 29 cases have been described in medical literature. Most of these cases came from Europe. References Genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apraxia Of Speech
Apraxia of speech (AOS), also called verbal apraxia, is a speech sound disorder affecting an individual's ability to translate conscious speech plans into motor plans, which results in limited and difficult speech ability. By the definition of apraxia, AOS affects volitional (willful or purposeful) movement pattern. However, AOS usually also affects automatic speech. People with AOS have difficulty connecting speech messages from the brain to the mouth. AOS is a loss of prior speech ability resulting from a brain injury such as a stroke or progressive illness. Developmental verbal dyspraxia (DVD), also known as childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) and developmental apraxia of speech (DAS), is an inability to utilize motor planning to perform movements necessary for speech during a child's language learning process. Although the causes differ between AOS and DVD, the main characteristics and treatments are similar. Presentation Apraxia of speech (AOS) is a neurogenic communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Speech Disorder
Motor speech disorders are a class of speech disorders that disturb the body's natural ability to speak due to neurologic impairments. Altogether, motor speech disorders are a group of speech output dysfunctions due to neurological complications. These neurologic impairments make it difficult for individuals with motor speech disorders to plan, program, control, coordinate, and execute speech productions. Disturbances to the individual's natural ability to speak vary in their etiology based on the integrity and integration of cognitive, neuromuscular, and musculoskeletal activities. Speaking is an act dependent on thought and timed execution of airflow and oral motor / oral placement of the lips, tongue, and jaw that can be disrupted by weakness in oral musculature (dysarthria) or an inability to execute the motor movements needed for specific speech sound production (apraxia of speech or developmental verbal dyspraxia). Such deficits can be related to pathology of the nervous sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasia
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person's ability to comprehend or formulate language because of dysfunction in specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in developed countries. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, epilepsy, autoimmune neurological diseases, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's language must be significantly impaired in one or more of the four aspects of communication. In the case of progressive aphasia, a noticeable decline in language abilities over a short period of time is required. The four aspects of communication include spoken language production, spoken language comprehension, written language production, and written language comprehension. Impairments in any of these aspects can impact functional communication. The difficulties o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Sound Disorder
A speech sound disorder (SSD) is a speech disorder affecting the ability to pronounce speech sounds, which includes Articulatory phonetics, speech articulation disorders and Phoneme, phonemic disorders, the latter referring to some sounds (phonemes) not being produced or used correctly. The term "protracted phonological development" is sometimes preferred when describing children's speech, to emphasize the continuing development while acknowledging the delay. A study in the United States estimated that amongst 6 year olds, 5.3% of African American children and 3.8% of White children have a speech sound disorder. Classification Speech sound disorders may be further subdivided into two primary types, articulation disorders (also called phonetic production disorders) and phonemic disorders (also called phonological disorders). However, some may have a mixed disorder in which both articulation and phonological problems exist. Though speech sound disorders are associated with childh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tay–Sachs Disease
Tay–Sachs disease is an Genetic disorder, inherited fatal lysosomal storage disease that results in the destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. The most common form is infantile Tay–Sachs disease, which becomes apparent around the age of three to six months of age, with the infant losing the ability to turn over, sit, or crawl. This is then followed by seizures, hearing loss, and paralysis, inability to move, with death usually occurring by the age of three to five. Less commonly, the disease may occur later in childhood, adolescence, or adulthood (juvenile or late-onset). These forms tend to be less severe, but the juvenile form typically results in death by the age of 15. Tay–Sachs disease is caused by a genetic mutation in the ''HEXA'' gene on chromosome 15, which codes a Protein subunit, subunit of the hexosaminidase enzyme known as hexosaminidase A. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. The mutation disrupts the activity of the enzyme, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
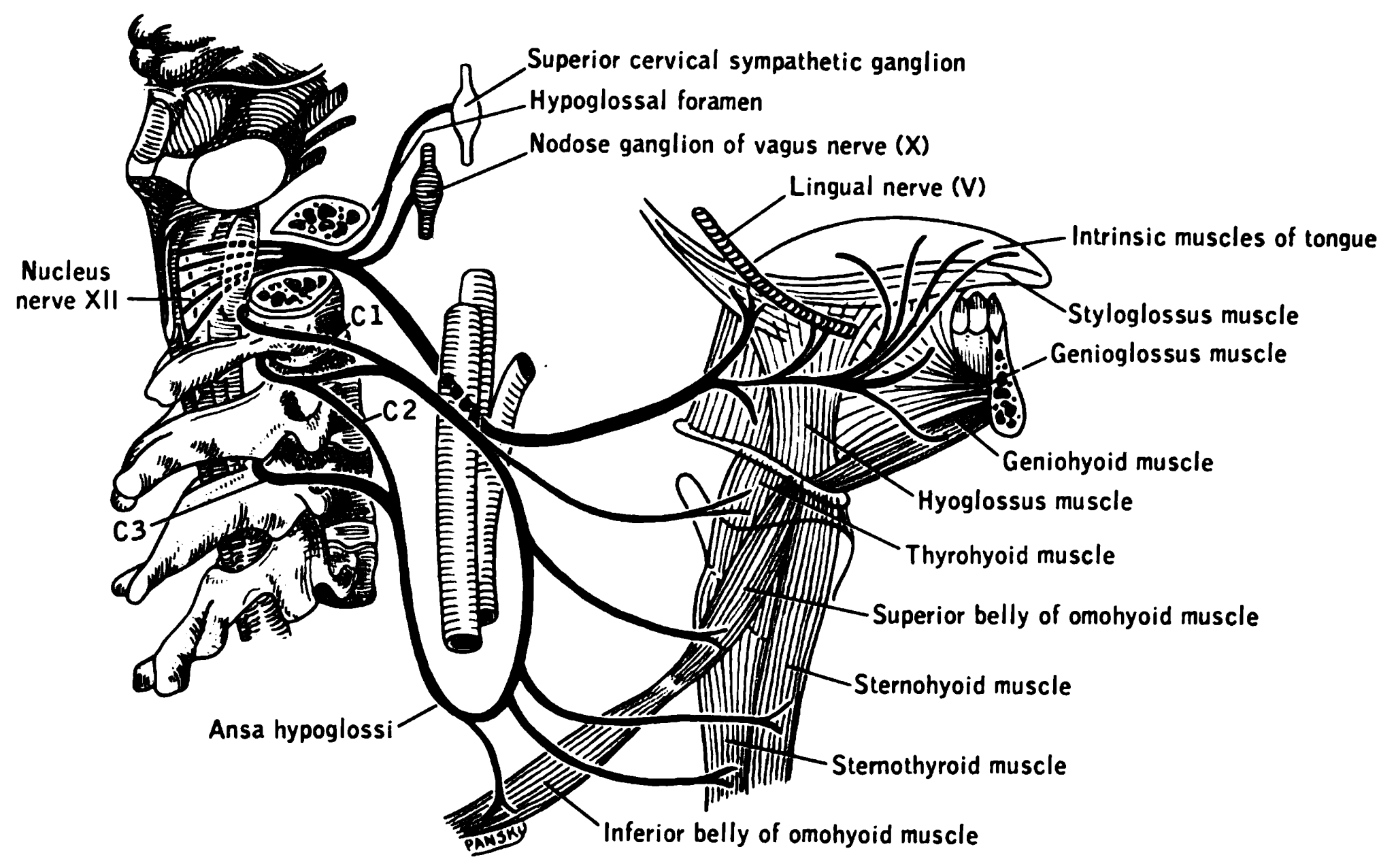
Hypoglossal Nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve was by Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Metal Poisoning
A toxic heavy metal is a common but misleading term for a metal-like element noted for its potential toxicity. Not all heavy metals are toxic and some toxic metals are not heavy. Elements often discussed as toxic include cadmium, mercury and lead, all of which appear in the World Health Organization's list of 10 chemicals of major public concern. Other examples include chromium and nickel, thallium, bismuth, arsenic, antimony and tin. These toxic elements are found naturally in the earth. They become concentrated as a result of human caused activities and can enter plant and animal (including human) tissues via inhalation, diet, and manual handling. Then, they can bind to and interfere with the functioning of vital cellular components. The toxic effects of arsenic, mercury, and lead were known to the ancients, but methodical studies of the toxicity of some heavy metals appear to date from only 1868. In humans, heavy metal poisoning is generally treated by the administration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) is an incurable, always fatal neurodegenerative disease belonging to the transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) group. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, visual disturbances and auditory disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, deafness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of sufferers die within a year of diagnosis. The name "Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease" was introduced by Walther Spielmeyer in 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob. CJD is caused by abnormal folding of a protein known as a prion. Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded. About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in the Northern Hemisphere. Infections are most common in the spring and early summer. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and fatigue (medical), tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include Facial nerve paralysis, loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, arthritis, joint pains, Meningitis, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later, repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally, shootin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson's Disease
Wilson's disease (also called hepatolenticular degeneration) is a genetic disorder characterized by the excess build-up of copper in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build-up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin, and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis. Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (''ATP7B'') gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for people to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests, and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. Wilson's disease is typically tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Sense
In linguistics, a word sense is one of the meanings of a word. For example, a dictionary may have over 50 different senses of the word "play", each of these having a different meaning based on the context of the word's usage in a sentence, as follows: In each sentence different collocates of "play" signal its different meanings. People and computers, as they read words, must use a process called word-sense disambiguationR. Navigli''Word Sense Disambiguation: A Survey'' ACM Computing Surveys, 41(2), 2009, pp. 1-69. to reconstruct the likely intended meaning of a word. This process uses context to narrow the possible senses down to the probable ones. The context includes such things as the ideas conveyed by adjacent words and nearby phrases, the known or probable purpose and register of the conversation or document, and the orientation (time and place) implied or expressed. The disambiguation is thus context-sensitive. Advanced semantic analysis has resulted in a sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |