|
Diffuse Supernova Neutrino Background
The diffuse supernova neutrino background (DSNB) is a theoretical population of neutrinos (and anti-neutrinos) cumulatively originating from all core-collapse supernovae events throughout the history of the universe. Though it has not yet been directly detected, the DSNB is theorized to be isotropic and consists of neutrinos with typical energies on the scale of 107 eV. Current detection efforts are limited by the influence of background noise in the search for DSNB neutrinos and are therefore limited to placing limits on the parameters of the DSNB, namely the neutrino flux. Restrictions on these parameters have gotten more strict in recent years, but many researchers are looking to make direct observations in the near future with next generation detectors. The DSNB is not to be confused with the cosmic neutrino background (CNB), which is comprised by relic neutrinos that were produced during the Big Bang and have much lower energies (10−4 to 10−6 eV). Sources In a core collap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is an elementary particle that interacts via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles (excluding massless particles). The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the electromagnetic interaction or the strong interaction. Consequently, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and with no detectable effect. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: # electron neutrino, # muon neutrino, # tau neutrino, Each flavor is associated with the correspondingly named charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photomultiplier Tube
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible light, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times or 108 (i.e., 160 decibel, dB),Decibels are power ratios. Power is proportional to I2 (current squared). Thus a current gain of 108 produces a power gain of 1016, or 160 decibel, dB in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low. The combination of high Gain (electronics), gain, low Noise (electronics), noise, high frequency response or, equivalently, ultra-fast response, and large area of collection has maintained photomultipliers an essential place in Spectroscopy, low light level spectroscopy, confocal microscopy, Raman spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cosmic Neutrino Background
The cosmic neutrino background is a proposed background particle radiation composed of neutrinos. They are sometimes known as relic neutrinos or sometimes abbreviated CNB or CB, where the symbol is the Greek letter '' nu'', standard particle physics symbol for a ''neutrino''. The CB is a relic of the Big Bang; while the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) dates from when the universe was 379,000 years old, the CB decoupled (separated) from matter when the universe was just one second old. It is estimated that today, the CB has a temperature of roughly . As neutrinos rarely interact with matter, these neutrinos still exist today. They have a very low energy, around 10 to 10 eV. Even high energy neutrinos are notoriously difficult to detect, and the CB has energies around 1010 times smaller, so the CB may not be directly observed in detail for many years, if at all. However, Big Bang cosmology makes many predictions about the CB, and there is very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Laboratori Nazionali Del Gran Sasso
Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS) is the largest underground research center in the world. Situated below Gran Sasso mountain in Italy, it is well known for particle physics research by the INFN. In addition to a surface portion of the laboratory, there are extensive underground facilities beneath the mountain. The nearest towns are L'Aquila and Teramo. The facility is located about 120 km from Rome. The primary mission of the laboratory is to host experiments that require a low background environment in the fields of astroparticle physics and nuclear astrophysics and other disciplines that can profit of its characteristics and of its infrastructures. The LNGS is, like the three other European underground astroparticle laboratories ( Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane, Laboratorio subterráneo de Canfranc, and Boulby Underground Laboratory), a member of the coordinating group ILIAS. Facilities The laboratory consists of a surface facility, located within the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
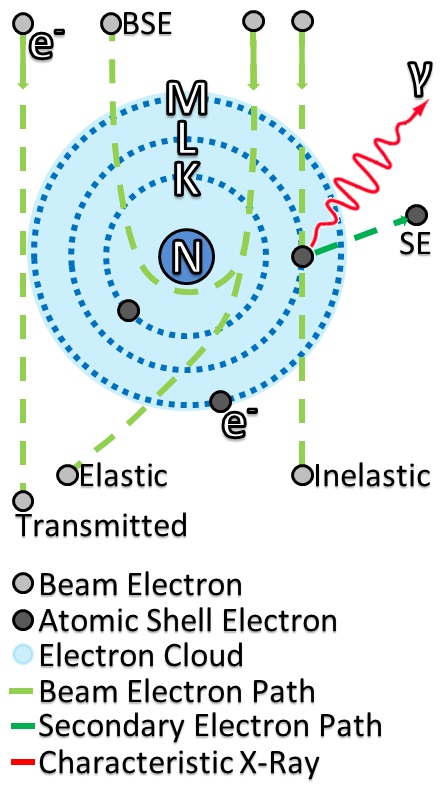
Electron Scattering
Electron scattering occurs when electrons are displaced from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors. Electron scattering has many applications ranging from the use of swift electron in Electron microscope, electron microscopes to very high energies for hadronic systems that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand many details about the atomic structure, from the ordering of atoms to that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks. Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways: * Not at all: no electron scatte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neutral Current
Weak neutral current interactions are one of the ways in which subatomic particles can interact by means of the weak force. These interactions are mediated by the Z boson. The discovery of weak neutral currents was a significant step toward the unification of electromagnetism and the weak force into the electroweak force, and led to the discovery of the W and Z bosons. In simple terms The weak force is best known for its role in nuclear decay. It has very short range but (apart from gravity) is the only force to interact with neutrinos. Like other subatomic forces, the weak force is mediated via exchange particles. Perhaps the most well known of the exchange particles for the weak force is the W particle which is involved in beta decay. W particles have electric charge – there are both positive and negative W particles – however the Z boson is also an exchange particle for the weak force but does ''not'' have any electrical charge. Exchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heavy Water
Heavy water (deuterium oxide, , ) is a form of water (molecule), water in which hydrogen atoms are all deuterium ( or D, also known as ''heavy hydrogen'') rather than the common hydrogen-1 isotope (, also called ''protium'') that makes up most of the hydrogen in normal water. The presence of the heavier isotope gives the water different nuclear properties, and the increase in mass gives it slightly different physical and chemical properties when compared to normal water. Deuterium is a heavy Isotopes of hydrogen, hydrogen isotope. Heavy water contains deuterium atoms and is used in nuclear reactors. Semiheavy water (HDO) is more common than pure heavy water, while heavy-oxygen water is denser but lacks unique properties. Tritiated water is radioactive due to tritium content. Heavy water has different physical properties from regular water, such as being 10.6% denser and having a higher melting point. Heavy water is less Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated at a given temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'' (''ApJ'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015. Since 1953, ''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'' (''ApJS'') has been published in conjunction with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', with generally longer articles to supplement the material in the journal. It publishes six volumes per year, with two 280-page issues per volume. ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters'' (''ApJL''), established in 1967 by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar as Part 2 of ''The Astrophysical Journal'', is now a separate journal focusing on the rapid publication of high-impact astronomical research. The three journals were published by the University of Chicago Press for the American Astronomical Society until, in January 2009, publication was transferred to IOP Publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatter counterpart) of the electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more photons. Positrons can be created by positron emission radioactive decay (through weak interactions), or by pair production from a sufficiently energetic photon which is interacting with an atom in a material. History Theory In 1928, Paul Dirac published a paper proposing that electrons can have both a positive and negative charge. This paper introduced the Dirac equation, a unification of quantum mechanics, special relativity, and the then-new concept of electron Spin (physics), spin to explain the Zeeman effect. The paper did not explicitly predict a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inverse Beta Decay
In nuclear and particle physics, inverse beta decay, commonly abbreviated to IBD, is a nuclear reaction involving an electron antineutrino scattering off a proton, creating a positron and a neutron. This process is commonly used in the detection of electron antineutrinos in neutrino detectors, such as the first detection of antineutrinos in the Cowan–Reines neutrino experiment, or in neutrino experiments such as KamLAND and Borexino. It is an essential process to experiments involving low-energy neutrinos (< 60 MeV) such as those studying neutrino oscillation, reactor neutrinos, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kamioka Observatory
The is a neutrino and gravitational waves laboratory located underground in the Mozumi mine of the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. near the Kamioka section of the city of Hida in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. A set of groundbreaking neutrino experiments have taken place at the observatory over the past two decades. All of the experiments have been very large and have contributed substantially to the advancement of particle physics, in particular to the study of neutrino astronomy and neutrino oscillation. The mine The Mozumi mine is one of two adjacent mines owned by the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. (a subsidiary of the Mitsui Mining and Smelting Co. Mitsui Kinzoku''). The mine is famous as the site of one of the greatest mass-poisonings in Japanese history. From 1910 to 1945, the mine operators released cadmium from the processing plant into the local water. This cadmium caused what the locals called itai-itai disease. The disease caused weakening of the bones and extreme pain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary physics, spallation describes meteoritic impacts on a planetary surface and the effects of stellar winds and cosmic rays on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. In the context of mining or geology, spallation can refer to pieces of rock breaking off a rock face due to the internal stresses in the rock; it commonly occurs on mine shaft walls. In the context of metal oxidation, spallation refers to the breaking off of the oxide layer from a metal. For example, the flaking off of rust from iron. In the context of anthropology, spallation is a process used to make stone tools such as arrowheads by knapping. In nuclear physics, spallation is the process in which a heavy nucleus emits numerous nucleons as a result of being hit by a high-energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |