|
Development Testing
Development testing is a software development process that involves synchronized application of a broad spectrum of defect prevention and detection strategies in order to reduce software development risks, time, and costs. Depending on the organization's expectations for software development, development testing might include static code analysis, data flow analysis, metrics analysis, peer code reviews, unit testing, code coverage analysis, traceability, and other software verification practices. Overview Development testing is performed by the software developer or engineer during the construction phase of the software development lifecycle. Rather than replace traditional QA focuses, it augments it. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, writing source code, code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing software requirements, requirements, software design, design, software testing, testing and software release life cycle, release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes management, organizational management, Software project management, project management, configuration management and other aspects. Software development involves many skills and job specializations including software programmer, programming, software test, testing, Technical writing, documentation, graphic design, user support, marketing, and fundraising. Software development involves many software tools, tools including: compiler, integrated develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
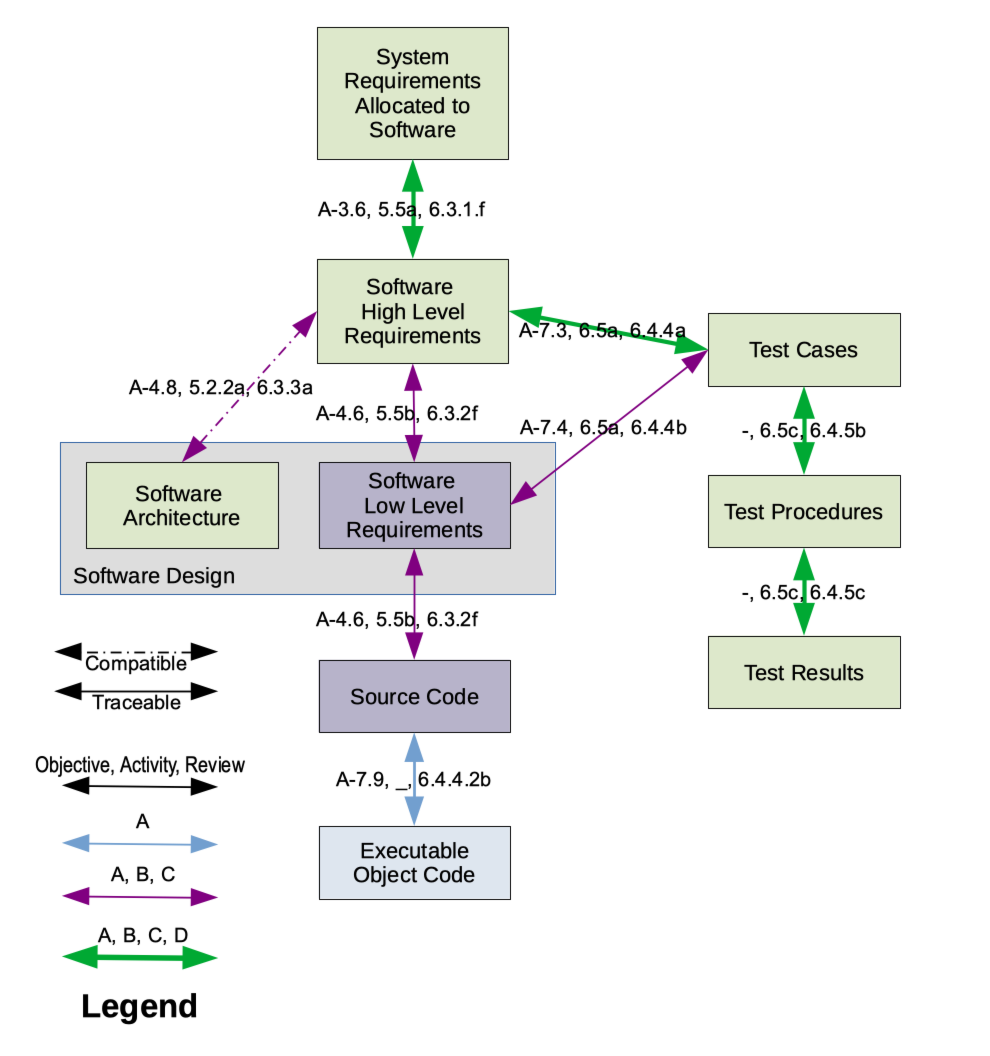
DO-178C
DO-178C, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is the primary document by which the certification authorities such as Federal Aviation Administration, FAA, European Aviation Safety Agency, EASA and Transport Canada approve all commercial software-based aerospace systems. The document is published by RTCA, Incorporated, in a joint effort with EUROCAE, EUROC and replaces DO-178B. The new document is called DO-178C/ED-12C and was completed in November 2011 and approved by the RTCA in December 2011. It became available for sale and use in January 2012. Except for Federal_Aviation_Regulations#Organization, FAR 33/Joint Aviation Requirements, JAR E, the Federal Aviation Regulations do not directly reference software airworthiness. On 19 Jul 2013, the FAA approved AC 20-115, AC 20-115C, designating DO-178C a recognized "acceptable means, but not the only means, for showing compliance with the applicable FAR airworthiness regulations for the software asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Regression Testing
Regression testing (rarely, ''non-regression testing'') is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a '' regression''. Changes that may require regression testing include bug fixes, software enhancements, configuration changes, and even substitution of electronic components ( hardware). As regression test suites tend to grow with each found defect, test automation is frequently involved. Sometimes a change impact analysis is performed to determine an appropriate subset of tests (''non-regression analysis''). Background As software is updated or changed, or reused on a modified target, emergence of new faults and/or re-emergence of old faults is quite common. Sometimes re-emergence occurs because a fix gets lost through poor revision control practices (or simple human error in revision control). Often, a fix for a problem will be " fragil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Functional Testing
In software development, functional testing is a form of software testing that verifies whether a system meets its functional requirements.ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2017, "Systems and software engineering — Vocabulary", International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Generally, functional testing is black-box, meaning the internal program structure is ignored (unlike for white-box testing).Kaner, Falk, Nguyen. ''Testing Computer Software''. Wiley Computer Publishing, 1999, p. 42. . Sometimes, functional testing is a quality assurance (QA) process.Prasad, Dr. K.V.K.K. (2008) ''ISTQB Certification Study Guide'', Wiley, , p. vi As a form of system testing, functional testing tests slices of functionality of the whole system. Despite similar naming, functional testing is not testing the code of a single function. The concept of incorporating testing earlier in the delivery cycle is not restricted to functional testing. Types Functional testing include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integration Testing
Integration testing is a form of software testing in which multiple software components, modules, or services are tested together to verify they work as expected when combined. The focus is on testing the interactions and data exchange between integrated parts, rather than testing components in isolation. Integration testing describes tests that are run at the integration-level to contrast testing at the unit or system level. Often, integration testing is conducted to evaluate the compliance of a component with functional requirements. In a structured development process, integration testing takes as its input modules that have been unit tested, groups them in larger aggregates, applies tests defined in an integration test plan, and delivers as output test results as a step leading to system testing. Approach Some different types of integration testing are big-bang, mixed (sandwich), risky-hardest, top-down, and bottom-up. Other Integration PatternsBinder, Robert V.: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computing), user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the Correctness (computer science), correctness of software for specific Scenario (computing), scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all software bug, bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an test oracle, oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, Design by Contract, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unit Testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior. Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration testing, integration or System testing, system level. History Unit testing, as a principle for testing separately smaller parts of large software systems, dates back to the early days of software engineering. In June 1956 at US Navy's Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers, H.D. Benington presented the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment, SAGE project. It featured a specification-based approach where the coding phase was followed by "parameter testing" to validate component subprograms against their specification, followed then by an "assembly testing" for parts put together. In 1964, a similar approach is described for the software of the Project Mercury, Mercury project, where individual units developed by dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flow Analysis
Data-flow analysis is a technique for gathering information about the possible set of values calculated at various points in a computer program. It forms the foundation for a wide variety of compiler optimizations and program verification techniques. A program's control-flow graph (CFG) is used to determine those parts of a program to which a particular value assigned to a variable might propagate. The information gathered is often used by compilers when optimizing a program. A canonical example of a data-flow analysis is reaching definitions. Other commonly used data-flow analyses include live variable analysis, available expressions, constant propagation, and very busy expressions, each serving a distinct purpose in compiler optimization passes. A simple way to perform data-flow analysis of programs is to set up data-flow equations for each node of the control-flow graph and solve them by repeatedly calculating the output from the input locally at each node until the whole sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Security Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are flaws or weaknesses in a system's design, implementation, or management that can be exploited by a malicious actor to compromise its security. Despite a system administrator's best efforts to achieve complete correctness, virtually all hardware and software contain bugs where the system does not behave as expected. If the bug could enable an attacker to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of system resources, it can be considered a vulnerability. Insecure software development practices as well as design factors such as complexity can increase the burden of vulnerabilities. Vulnerability management is a process that includes identifying systems and prioritizing which are most important, scanning for vulnerabilities, and taking action to secure the system. Vulnerability management typically is a combination of remediation, mitigation, and acceptance. Vulnerabilities can be scored for severity according to the Common Vulnerability Scori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
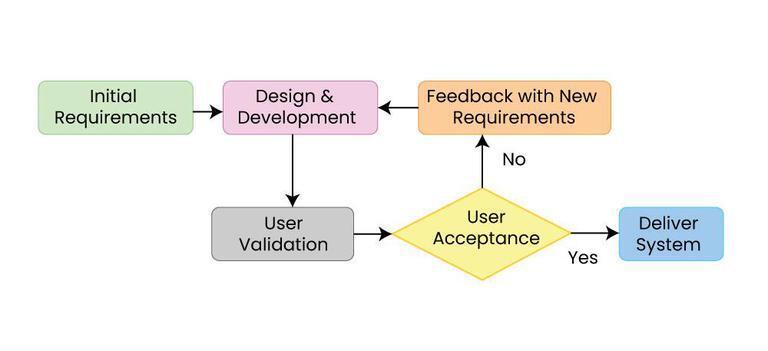
Software Validation
In software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation is the process of checking that a software engineer system meets specifications and requirements so that it fulfills its intended purpose. It may also be referred to as software quality control. It is normally the responsibility of software testers as part of the software development lifecycle. In simple terms, software verification is: "Assuming we should build X, does our software achieve its goals without any bugs or gaps?" On the other hand, software validation is: "Was X what we should have built? Does X meet the high-level requirements?" Definitions Verification and validation are not the same thing, although they are often confused. Boehm succinctly expressed the difference as * Verification: Are we building the product right? * Validation: Are we building the right product? "Building the product right" checks that the ''specifications'' are correctly implemented by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Root Cause Analysis
In science and engineering, root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving used for identifying the root causes of faults or problems. It is widely used in IT operations, manufacturing, telecommunications, industrial process control, accident analysis (e.g., in aviation, rail transport, or nuclear plants), medical diagnosis, the healthcare industry (e.g., for epidemiology), etc. Root cause analysis is a form of inductive inference (first create a theory, or ''root'', based on empirical evidence, or ''causes'') and deductive inference (test the theory, i.e., the underlying causal mechanisms, with empirical data). RCA can be decomposed into four steps: # Identify and describe the problem clearly # Establish a timeline from the normal situation until the problem occurrence # Distinguish between the root cause and other causal factors (e.g., via event correlation) # Establish a causal graph between the root cause and the problem. RCA generally serves as input to a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Computing * Data reliability (other), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage * Reliability (computer networking), a category used to describe protocols * Reliability (semiconductor), outline of semiconductor device reliability drivers Other uses in science, technology, and mathematics * Reliability (statistics), the overall consistency of a measure * Reliability engineering, concerned with the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified time ** Human reliability in engineered systems * Reliability theory, as a theoretical concept, to explain biological aging and species longevity Other uses * Reliabilism, in philosophy and epistemology * Unreliable narrator, whose credibility has been seriously compromised See also * * * * Reliant (other) Reliant may also refer to: * Reliant Energy, an energy c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |