|
Deblurring
Deblurring is the process of removing blurring artifacts from images. Deblurring recovers a sharp image ''S'' from a blurred image ''B'', where ''S'' is convolved with ''K'' (the blur kernel) to generate ''B''. Mathematically, this can be represented as B=S*K (where * represents convolution). While this process is sometimes known as ''unblurring'', ''deblurring'' is the correct technical word. The blur K is typically modeled as point spread function and is convolved with a hypothetical sharp image ''S'' to get ''B'', where both the ''S'' (which is to be recovered) and the point spread function ''K'' are unknown. This is an example of an inverse problem. In almost all cases, there is insufficient information in the blurred image to uniquely determine a plausible original image, making it an ill-posed problem. In addition the blurred image contains additional noise which complicates the task of determining the original image. This is generally solved by the use of a regulariza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denoising
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. Noise rejection is the ability of a circuit to isolate an undesired signal component from the desired signal component, as with common-mode rejection ratio. All signal processing devices, both analog and digital, have traits that make them susceptible to noise. Noise can be random with an even frequency distribution (white noise), or frequency-dependent noise introduced by a device's mechanism or signal processing algorithms. In electronic systems, a major type of noise is ''hiss'' created by random electron motion due to thermal agitation. These agitated electrons rapidly add and subtract from the output signal and thus create detectable noise. In the case of photographic film and magnetic tape, noise (both visible and audible) is introduced due to the grain structure of the medium. In photogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deconvolution
In mathematics, deconvolution is the inverse of convolution. Both operations are used in signal processing and image processing. For example, it may be possible to recover the original signal after a filter (convolution) by using a deconvolution method with a certain degree of accuracy. Due to the measurement error of the recorded signal or image, it can be demonstrated that the worse the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), the worse the reversing of a filter will be; hence, inverting a filter is not always a good solution as the error amplifies. Deconvolution offers a solution to this problem. The foundations for deconvolution and time-series analysis were largely laid by Norbert Wiener of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in his book ''Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series'' (1949). The book was based on work Wiener had done during World War II but that had been classified at the time. Some of the early attempts to apply these theories were in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super-resolution
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that improve the resolution of an imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors is enhanced. In some radar and sonar imaging applications (e.g. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), high-resolution computed tomography), subspace decomposition-based methods (e.g. MUSIC) and compressed sensing-based algorithms (e.g., SAMV) are employed to achieve SR over standard periodogram algorithm. Super-resolution imaging techniques are used in general image processing and in super-resolution microscopy. Basic concepts Because some of the ideas surrounding super-resolution raise fundamental issues, there is need at the outset to examine the relevant physical and information-theoretical principles: * Diffraction limit: The detail of a physical object that an optical instrument can reproduce in an image has limits that are mandated by laws of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Restoration (motion Blur, Wiener Filtering)
Image restoration may refer to: * Conservation and restoration of photographs * Digital photograph restoration * Image restoration by artificial intelligence * Iterative reconstruction Iterative reconstruction refers to Iteration, iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D reconstruction, 3D images in certain Digital imaging, imaging techniques. For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from pro ... See also * Image restoration theory {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernel (image Processing)
In image processing, a kernel, convolution matrix, or mask is a small matrix used for blurring, sharpening, embossing, edge detection, and more. This is accomplished by doing a convolution between the kernel and an image An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di .... Or more simply, when each pixel in the output image is a function of the nearby pixels (including itself) in the input image, the kernel is that function. Details The general expression of a convolution is g_ = \omega * f_ = \sum_^a , where g(x,y) is the filtered image, f(x,y) is the original image, \omega is the filter kernel. Every element of the filter kernel is considered by -a \leq i \leq a and -b \leq j \leq b. Depending on the element values, a kernel can cause a wide range of effects: The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
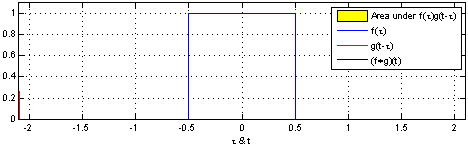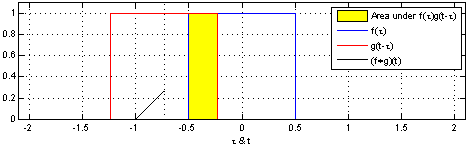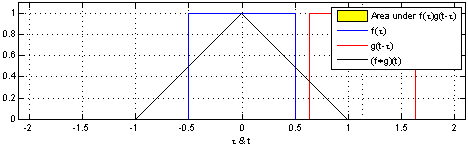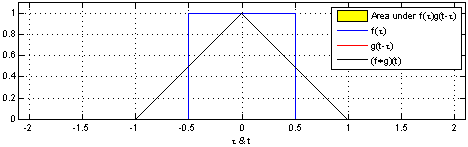
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the resulting function and to the process of computing it. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). Graphically, it expresses how the 'shape' of one function is modified by the other. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution f*g differs from cross-correlation f \star g only in that either f(x) or g(x) is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Spread Function
The point spread function (PSF) describes the response of a focused optical imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is the system's impulse response; the PSF is the impulse response or impulse response function (IRF) of a focused optical imaging system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the shapeless blob in an image that should represent a single point object. We can consider this as a spatial impulse response function. In functional terms, it is the spatial domain version (i.e., the inverse Fourier transform) of the Optical transfer function, optical transfer function (OTF) of an imaging system. It is a useful concept in Fourier optics, astronomy, astronomical imaging, medical imaging, electron microscope, electron microscopy and other imaging techniques such as dimension, 3D microscopy (like in confocal laser scanning microscopy) and fluorescence microscopy. The degree of spreading (blurring) in the image of a point ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolved
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the resulting function and to the process of computing it. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see commutativity). Graphically, it expresses how the 'shape' of one function is modified by the other. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution f*g differs from cross-correlation f \star g only in that either f(x) or g(x) is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus it is a cross-correlation of g(-x) and f(x), or f(-x) and g(x). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Problem
An inverse problem in science is the process of calculating from a set of observations the causal factors that produced them: for example, calculating an image in X-ray computed tomography, sound source reconstruction, source reconstruction in acoustics, or calculating the density of the Earth from measurements of its gravity field. It is called an inverse problem because it starts with the effects and then calculates the causes. It is the inverse of a forward problem, which starts with the causes and then calculates the effects. Inverse problems are some of the most important mathematical problems in science and mathematics because they tell us about parameters that we cannot directly observe. They can be found in system identification, optics, radar, acoustics, communication theory, signal processing, medical imaging, computer vision, geophysics, oceanography, astronomy, remote sensing, natural language processing, machine learning, nondestructive testing, slope stability analys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regularization (physics)
In physics, especially quantum field theory, regularization is a method of modifying observables which have singularities in order to make them finite by the introduction of a suitable parameter called the regulator. The regulator, also known as a "cutoff", models our lack of knowledge about physics at unobserved scales (e.g. scales of small size or large energy levels). It compensates for (and requires) the possibility of separation of scales that "new physics" may be discovered at those scales which the present theory is unable to model, while enabling the current theory to give accurate predictions as an "effective theory" within its intended scale of use. It is distinct from renormalization, another technique to control infinities without assuming new physics, by adjusting for self-interaction feedback. Regularization was for many decades controversial even amongst its inventors, as it combines physical and epistemological claims into the same equations. However, it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo Removal
Echo removal is the process of removing echo and reverberation artifacts from audio signals. The reverberation is typically modeled as the convolution of a (sometimes time-varying) impulse response with a hypothetical clean input signal, where both the clean input signal (which is to be recovered) and the impulse response are unknown. This is an example of an inverse problem. In almost all cases, there is insufficient information in the input signal to uniquely determine a plausible original image, making it an ill-posed problem. This is generally solved by the use of a regularization term to attempt to eliminate implausible solutions. This problem is analogous to deblurring in the image processing domain. See also * Echo suppression and cancellation * Digital room correction * Noise reduction Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |