|
DBASE Mac
dBASE Mac was a database management system for the Apple Macintosh, released by Ashton-Tate in 1987. Although the GUI was lauded in the press, the application was so slow that it became something of a joke in the industry. Sales were dismal, and Ashton-Tate eventually decided to give up on dBASE Mac and instead port dBASE IV to the Mac, complete with a DOS-like interface. The product was then sold to a series of third-party developers, but they had little success and it disappeared from the market in the mid-1990s. History Genesis dBASE Mac started life at a third-party developer, DigiCorp, a small two-person company in Salt Lake City. They had attempted to market it through other companies in 1984 as ''Hayden: Base'' via Hayden Software, a Mac publisher, ''TheBase'' and then ''°Base'' (''Dot-Base'', referring to a part of its internal syntax), but the product was not really ready and the deals fell through. Just before Christmas 1984, Ashton-Tate started negotiations with the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Ashton-Tate
Ashton-Tate Corporation was a US-based software company best known for developing the popular dBASE database application and later acquiring Framework from the Forefront Corporation and MultiMate from Multimate International. It grew from a small garage-based company to become a multinational corporation. Once one of the "Big Three" software companies, which included Microsoft and Lotus, the company stumbled in the late 1980s and was sold to Borland in September 1991. History The history of Ashton-Tate and dBASE are intertwined and as such, must be discussed in parallel. Early history: dBASE II (1981–1983) In 1978, Martin Marietta programmer Wayne Ratliff wrote Vulcan, a database application, to help him make picks for football pools. Written in Intel 8080 assembly language, it ran on the CP/M operating system and was modeled on JPLDIS, a Univac 1108 program used at JPL and written by fellow programmer Jeb Long. Ashton-Tate was launched as a result of Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
4th Dimension (Software)
4D (4th Dimension, or Silver Surfer, as it was known during early development) is a relational database management system and integrated development environment developed by Laurent Ribardière. 4D was created in 1984 and had a slightly delayed public release for Macintosh in 1987 with its own programming language. The 4D product line has since expanded to an SQL back-end, integrated compiler, integration of PHP, and several productivity plug-ins and interfaces. Some of the plug-ins created by 4D include 4D Write (a word processor), 4D View (somewhat like a spreadsheet, but with extra functionality) and 4D Internet Commands (which allowed for the addition of Internet-related functionality to a database). There are also over 100 third-party plugins, free and commercial. 4D can also be used as a web server, to run compiled database applications. Today, 4D is published by the French company 4D SAS and has a sales, distribution and support presence in most major markets, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
FullWrite Professional
FullWrite Professional was a word processor application for the Apple Macintosh, released in late 1988 by Ashton-Tate. The program was notable for its combination of a true WYSIWYG interface, powerful long-document processing features, and a well regarded outliner. It was also noted for its high resource demands, bugs, and its very late release. Despite these problems, FullWrite developed a faithful following and some amount of commercial success. Douglas Adams used FullWrite as his primary word processor for some time. Douglas Hofstadter published several of his books directly from FullWrite, notably ''Le Ton beau de Marot''. The product changed hands in the aftermath of Ashton-Tate's early 1990s business failure, and most of its problems were addressed in a major upgrade in 1995. By this point Microsoft Word dominated the Mac word processor market and the improved FullWrite never became particularly widely used. Since 1998, the product has been available as freeware for the clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Borland
Borland Software Corporation was a computing technology company founded in 1983 by Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, Mogens Glad, and Philippe Kahn. Its main business was developing and selling software development and software deployment products. Borland was first headquartered in Scotts Valley, California, then in Cupertino, California, and then in Austin, Texas. In 2009, the company became a full subsidiary of the British firm Micro Focus International plc. In 2023, Micro Focus (including Borland) was acquired by Canadian firm OpenText, which later absorbed Borland's portfolio into its application delivery management division. History The 1980s: Foundations Borland Ltd. was founded in August 1981 by three Danes, Danish citizens Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, and Mogens Glad to develop products like Word Index for the CP/M operating system using an off-the-shelf company. However, the response to the company's products at the CP/M-82 show in San Francisco showed that a U.S. company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Killer App
A killer application (often shortened to killer app) is any software that is so necessary or desirable that it proves the core value of some larger technology, such as its host computer hardware, video game console, software platform, or operating system. Consumers would buy the host platform just to access that application, possibly substantially increasing sales of its host platform. Usage The earliest recorded use of the term "killer app" in print is in the May 24, 1988 issue of '' PC Week'': "Everybody has only one killer application. The secretary has a word processor. The manager has a spreadsheet." The definition of "killer app" came up during the deposition of Bill Gates in the '' United States v. Microsoft Corp.'' antitrust case. He had written an email in which he described Internet Explorer as a killer app. In the questioning, he said that the term meant "a popular application," and did not connote an application that would fuel sales of a larger product or one that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
PowerMac
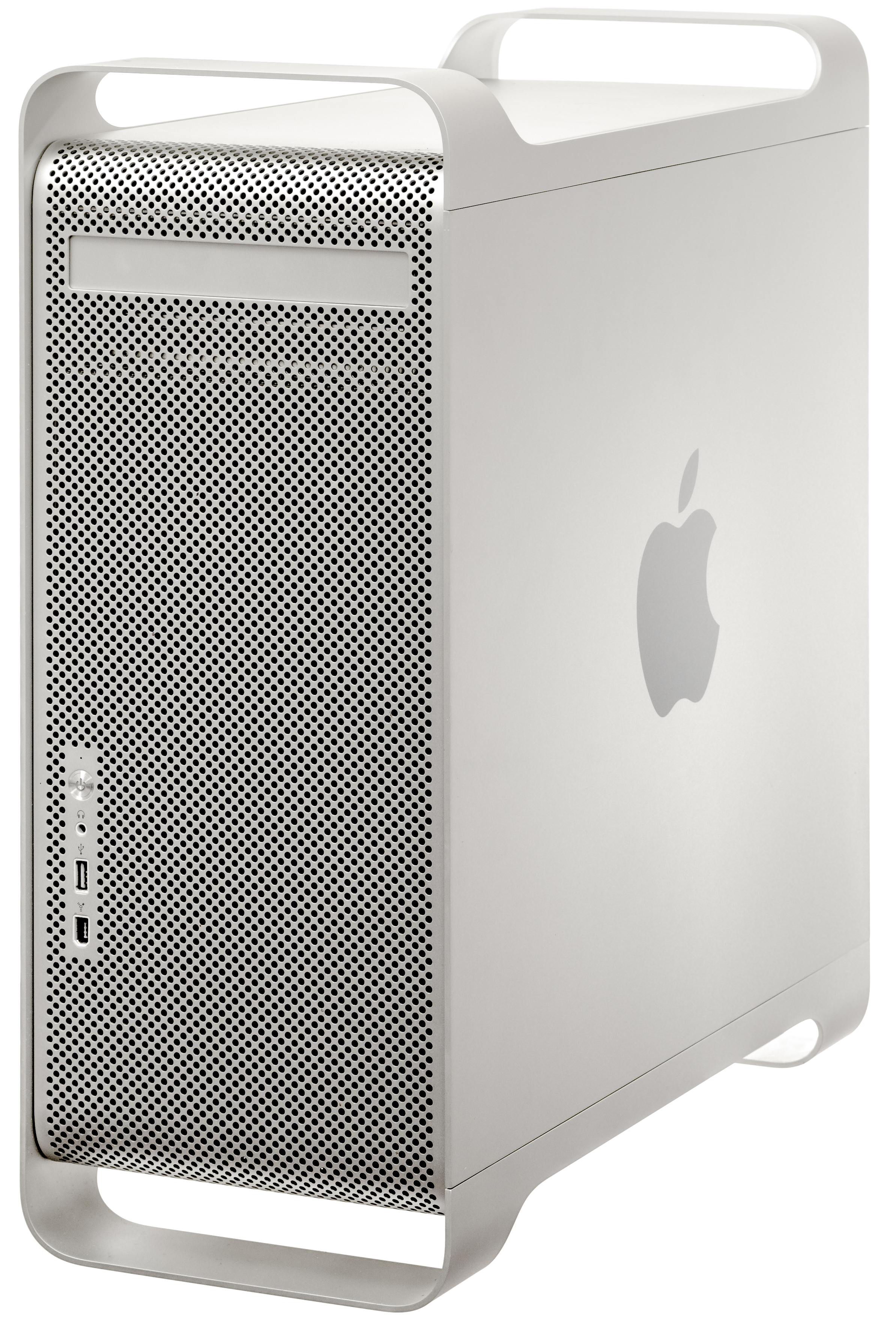
The Power Macintosh, later Power Mac, is a family of personal computers designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer, Inc as the core of the Macintosh brand from March 1994 until August 2006. Described by ''Macworld'' as "the most important technical evolution of the Macintosh since the Mac II debuted in 1987", it is the first computer with the PowerPC CPU architecture, the flagship product of the AIM alliance. Existing software for the Motorola 68k processors of previous Macintoshes do not run on it natively, so a Mac 68k emulator is in System 7.1.2. It provides good compatibility, at about two-thirds of the speed of contemporary Macintosh Quadra machines. The Power Macintosh replaced the Quadra and was initially sold in the same enclosures. Over the next twelve years, it evolved through a succession of enclosure designs, a rename to "Power Mac", five major generations of PowerPC chips, and a great deal of press coverage, design accolades, and controversy about perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
HyperCard
HyperCard is a application software, software application and software development kit, development kit for Apple Macintosh and Apple IIGS computers. It is among the first successful hypermedia systems predating the World Wide Web. HyperCard combines a flat-file database with a graphical, flexible, user-modifiable interface. HyperCard includes a built-in programming language called HyperTalk for manipulating data and the user interface. This combination of features – a database with simple form layout, flexible support for graphics, and ease of programming – suits HyperCard for many different projects such as rapid application development of applications and databases, interactive applications with no database requirements, command and control systems, and many examples in the demoscene. HyperCard was originally released in 1987 for $49.95 and was included free with all new Macs sold afterwards. It was withdrawn from sale in March 2004, having received its final update in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (''IW'') is an American information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a Web-only publication. Its parent company is International Data Group, and its sister publications include '' Macworld'' and '' PC World''. ''InfoWorld'' is based in San Francisco, with contributors and supporting staff based across the U.S. Since its founding, ''InfoWorld''s readership has largely consisted of IT and business professionals. ''InfoWorld'' focuses on how-to, analysis, and editorial content from a mixture of experienced technology journalists and working technology practitioners. The site averages 4.6 million monthly page views and 1.1 million monthly unique visitors. History The magazine was founded by Jim Warren in 1978 as ''The Intelligent Machines Journal'' (IMJ). It was sold to IDG in late 1979. On 18 February 1980, the magazine name was changed to ''InfoWorld''. In 1986, the Robert X. Cringely colum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
MacWorld Boston
Macworld/iWorld (originally Macworld) was an information technology trade show with conference tracks dedicated to Apple's Mac platform. It was held annually in the United States during January. Originally ''Macworld Expo'' and then ''Macworld Conference & Exposition'', the gathering dates back to 1985. The conference was organized by International Data Group (IDG), co-publisher of ''Macworld'' magazine. On December 18, 2008, Apple announced that the 2009 Macworld Conference & Expo would be the last in which the company participates. On October 14, 2014, IDG suspended Macworld/iWorld indefinitely. History The first Macworld Expo occurred in 1985 in San Francisco. The conference itself was created by Peggy Kilburn, who helped to increase the size and profit of the event during her tenure (1985–1999). Among the speakers recruited by Kilburn were David Pogue, Steve Case, Bob LeVitus, as well as representatives from BMUG, LaserBoard, and other major user groups. Participation by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Guy Kawasaki
Guy Takeo Kawasaki (born August 30, 1954) is an American marketing specialist, author, and Silicon Valley venture capitalist. He was one of the Apple employees originally responsible for marketing their Macintosh computer line in 1984. He popularized the word ''evangelist'' in marketing the Macintosh as an " Apple evangelist" and the concepts of evangelism marketing and technology evangelism/ platform evangelism in general. From March 2015 until December 2016, Kawasaki sat on the board of trustees of the Wikimedia Foundation, the non-profit operating entity of Wikipedia. Kawasaki has also written fifteen books, including '' The Macintosh Way'' (1990), ''The Art of the Start'' (2004), and ''Wise Guy: Lessons from a Life'' (2019). Early life and education Guy Kawasaki was born in Honolulu, Hawaii to Duke Takeshi Kawasaki (d. 2015) and Aiko Kawasaki. His family lived in an area outside Honolulu called Kalihi Valley. His father, Duke, once served as a fireman, real estate bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Classic Mac OS
Mac OS (originally System Software; retronym: Classic Mac OS) is the series of operating systems developed for the Mac (computer), Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems. Apple released the Macintosh 128K, original Macintosh on January 24, 1984. The System 1, first version of the system software, which had no official name, was partially based on the Lisa OS, which Apple previously released for the Apple Lisa, Lisa computer in 1983. As part of an agreement allowing Xerox to buy Share (finance), shares in Apple at a favorable price, it also used concepts from the PARC (company), Xerox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |