|
Cystic Vein
When present the cystic vein drains the blood from the gall-bladder, and, accompanying the cystic duct, usually ends in the right branch of the portal vein The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approx .... It is usually not present, and the blood drains via small veins in the gall-bladder bed directly to the parenchyma of the liver. References External links * Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
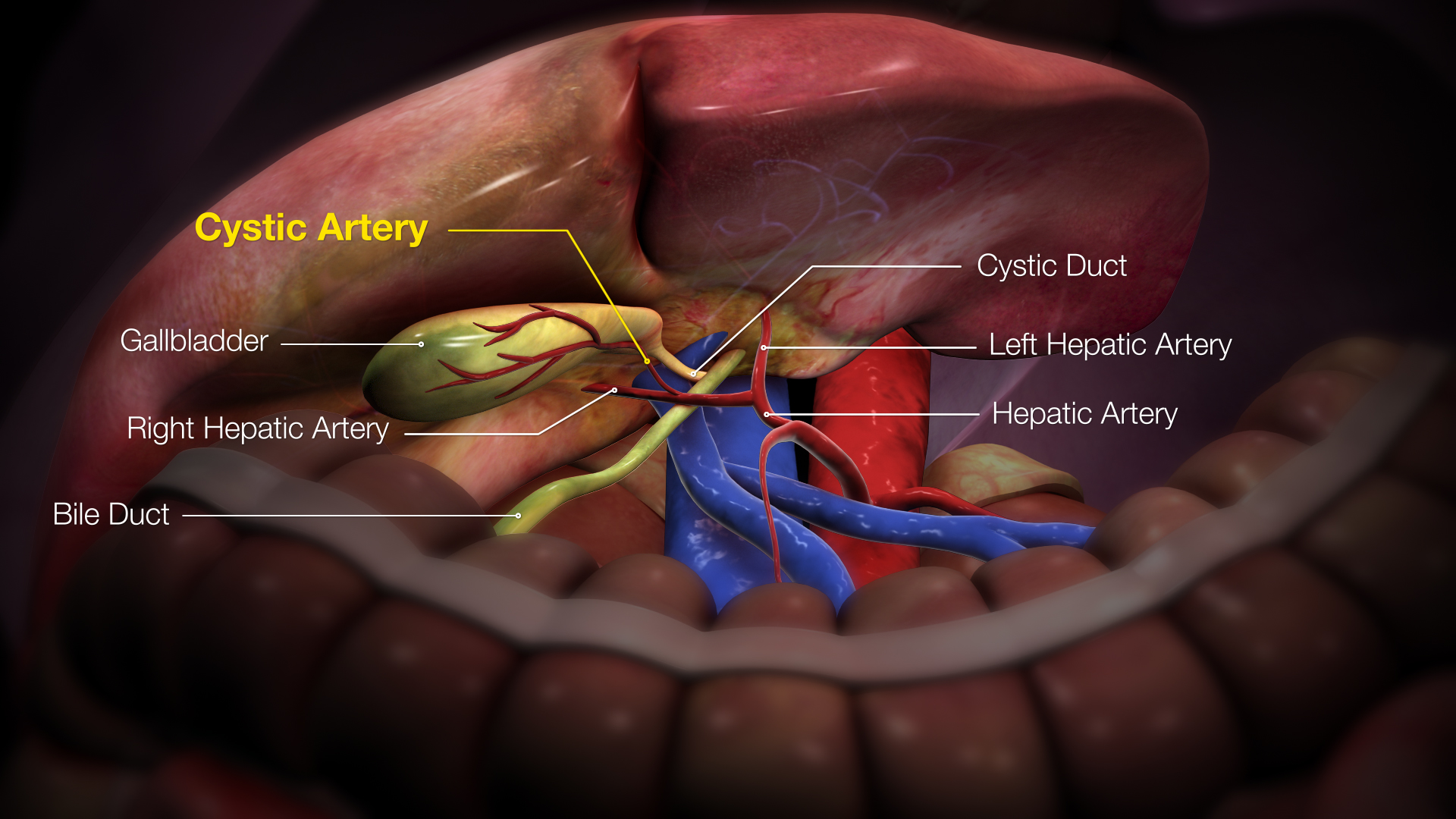
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Artery
The cystic artery (also known as bachelor artery) supplies oxygenated blood to the gallbladder and cystic duct. Most common arrangement In the classic arrangement, occurring with a frequency of approximately 70%, a singular cystic artery originates from the geniculate flexure of the right hepatic artery in the upper portion of the hepatobiliary triangle. A site of origin from a more proximal or distal portion of the right hepatic artery is also considered relatively normal. After separating from the right hepatic artery, the cystic artery travels superiorly to the cystic duct and produces 2 to 4 minor branches, known as ''Calot’s arteries'', that supply part of the cystic duct and cervix of the gallbladder before dividing into the major superficial and deep branches at the superior aspect of the gallbladder neck: * The ''superficial branch'' (or ''anterior branch'') passes subserously over the left aspect of the gallbladder. * The ''deep branch'' (or ''posterior branch'') runs b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gall-bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Duct
The cystic duct is the short duct that joins the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct. It usually lies next to the cystic artery. It is of variable length. It contains ' spiral valves of Heister', which do not provide much resistance to the flow of bile. Function Bile can flow in both directions between the gallbladder and the common bile duct and the hepatic duct. In this way, bile is stored in the gallbladder in between meal times. The hormone cholecystokinin, when stimulated by a fatty meal, promotes bile secretion by increased production of hepatic bile, contraction of the gall bladder, and relaxation of the Sphincter of Oddi. Clinical significance Gallstones can enter and obstruct the cystic duct, preventing the flow of bile. The increased pressure in the gallbladder leads to swelling and pain. This pain, known as biliary colic, is sometimes referred to as a gallbladder "attack" because of its sudden onset. During a cholecystectomy Cholecystectomy is the surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |