|
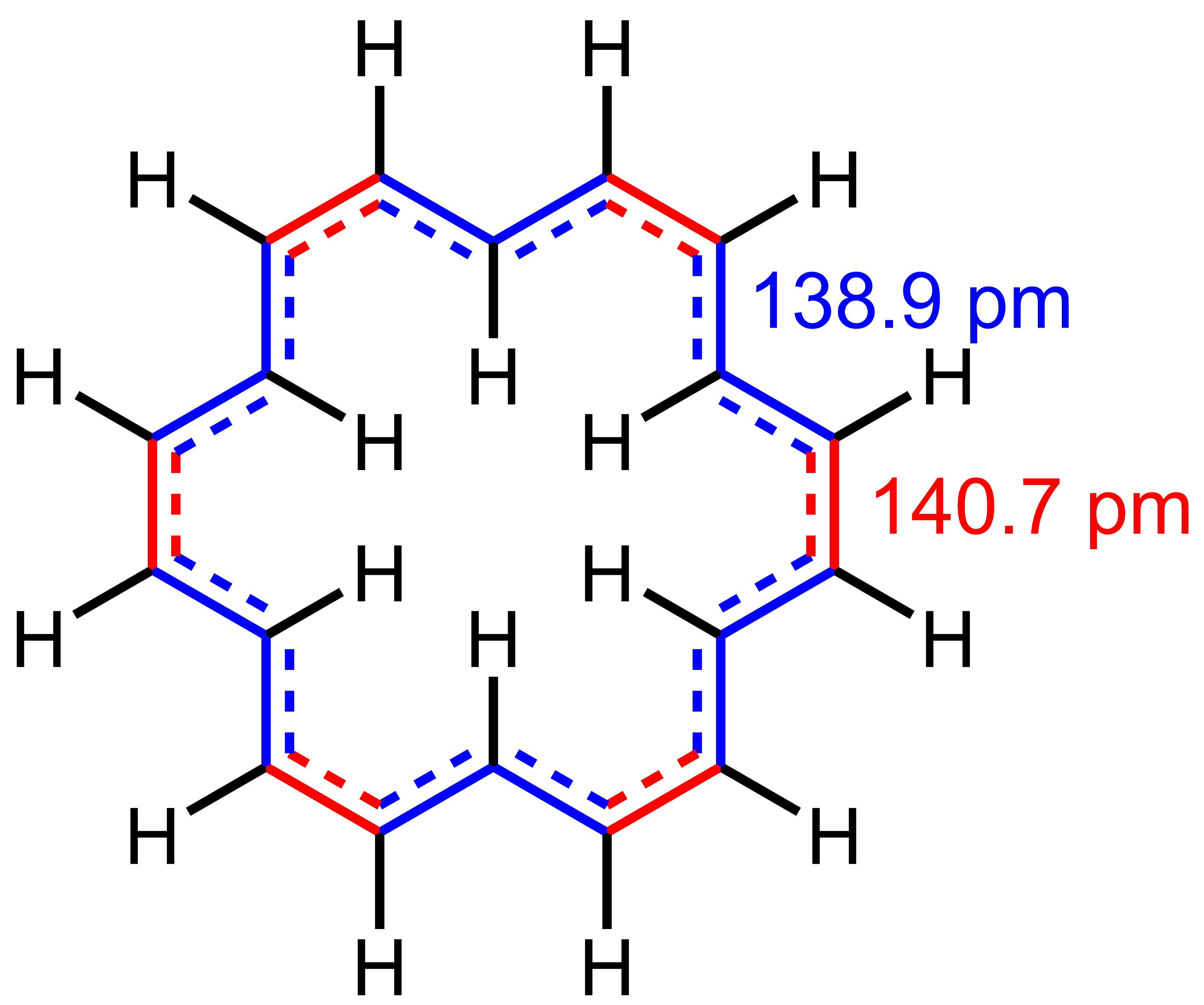
Cyclotetradecaheptaene
Cyclotetradecaheptaene, often referred to as 4nnulene, is a hydrocarbon with molecular formula C14H14, which played an important role in the development of criteria (Hückel's rule) for aromaticity, a stabilizing property of central importance in physical organic chemistry. It forms dark-red needle-like crystals. Structure and aromaticity Although the conjugated ring of 4 nnulene contains 4''n''+2 electrons, it only exhibits limited evidence for being aromatic. It does not fully conform to Hückel's rule because none of its ''cis''/''trans'' isomers can adopt a completely planar conformation due to crowding of the interior hydrogens. There is evidence that it has two isomeric forms of comparable stability (''trans'', ''cis'', ''trans'', ''cis'', ''trans'', ''trans'', ''cis''- with four interior hydrogens (shown in the infobox) and ''trans'', ''cis'', ''trans'', ''cis'', ''trans'', ''cis'', ''cis-'' with three interior hydrogens) which rapidly interconvert at room temperature b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromaticity
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulene
Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds (' mancude'). They have the general formula CnHn (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC naming conventions are that annulenes with 7 or more carbon atoms are named as 'n''nnulene, where ''n'' is the number of carbon atoms in their ring, though sometimes the smaller annulenes are referred to using the same notation, and benzene is sometimes referred to simply as annulene. The first three even annulenes are cyclobutadiene, benzene, and cyclooctatetraene ( nnulene). Some annulenes, namely cyclobutadiene, cyclodecapentaene ( 0nnulene), cyclododecahexaene ( 2nnulene) and cyclotetradecaheptaene ( 4nnulene), are unstable, with cyclobutadiene extremely so. In the related annulynes, one double bond is replaced by a triple bond. Aromaticity Annulenes may be ''aromatic'' (benzene, nnulene and 8nnulene), ''non-aromati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctadecanonaene
Cyclooctadecanonaene or 8nnulene is an organic compound with chemical formula . It belongs to the class of highly conjugated compounds known as annulenes and is aromatic. The usual isomer that 8nnulene refers to is the most stable one, containing six interior hydrogens and twelve exterior ones, with the nine formal double bonds in the ''cis'',''trans'',''trans'',''cis'',''trans'',''trans'',''cis'',''trans'',''trans'' configuration. It is reported to be a red-brown crystalline solid. Aromaticity Notably, 8nnulene is the first annulene after benzene ( nnulene) to be fully aromatic: its π-system contains 4''n'' + 2 electrons (''n'' = 4), and it is large enough to comfortably accommodate six hydrogen atoms in its interior, allowing it to adopt a planar shape, thus satisfying Hückel's rule. The discovery of aromatic stabilization for 8nnulene is historically significant for confirming earlier theoretical predictions based on molecular orbital theory, since simple versions of vale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major industrial chemical, it finds limited use in consumer items because of its toxicity. History Discovery The word "''benzene''" derives from "''gum benzoin''" ( ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or exemplified by the odors of gasoline and lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to the naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, and to their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hückel's Rule
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule predicts that a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties if it has 4''n'' + 2 π electrons, where ''n'' is a non-negative integer. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931. The succinct expression as the 4''n'' + 2 rule has been attributed to W. v. E. Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same time. In agreement with the Möbius–Hückel concept, a cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its π-electrons equals 4''n'' + 2, although clearcut examples are really only established for values of ''n'' = 0 up to about ''n'' = 6. Hückel's rule was originally based on calculations using the Hückel method, although it can also be justified by considering a particle in a ring system, by the LCAO method and by the Pariser–Parr–Pople method. Aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Organic Chemistry
Physical organic chemistry, a term coined by Louis Hammett in 1940, refers to a discipline of organic chemistry that focuses on the relationship between chemical structures and reactivity, in particular, applying experimental tools of physical chemistry to the study of organic molecules. Specific focal points of study include the rates of organic reactions, the relative chemical stabilities of the starting materials, reactive intermediates, transition states, and products of chemical reactions, and non-covalent aspects of solvation and molecular interactions that influence chemical reactivity. Such studies provide theoretical and practical frameworks to understand how changes in structure in solution or solid-state contexts impact reaction mechanism and rate for each organic reaction of interest. Application Physical organic chemists use theoretical and experimental approaches work to understand these foundational problems in organic chemistry, including classical and statist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclododecahexaene
Cyclododecahexaene or 2nnulene () is a member of the series of annulenes with some interest in organic chemistry with regard to the study of aromaticity. Cyclododecahexaene is non-aromatic due to the lack of planarity of the structure. On the other hand the dianion with 14 electrons is a Hückel aromat and more stable. According to in silico experiments the tri-trans isomer is expected to be the most stable, followed by the 1,7-ditrans and the all cis-isomers (+1 kcal/mol) and by the 1,5-ditrans isomer (+5 kcal/mol). The first 2nnulene with sym-tri-trans configuration was synthesized in 1970 from a tricyclic precursor by photolysis at low temperatures. On heating the compound rearranges to a bicyclic .4.0isomer. Reducing the compound at low temperatures allowed analysis of the dianion by proton NMR with the inner protons resonating at -4.5 ppm relative to TMS, evidence of an aromatic diamagnetic ring current. : In one study the 1,7-ditrans isomer is generated at low t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiaromaticity
Antiaromaticity is a chemical property of a cyclic molecule with a π electron system that has higher energy, i.e., it is less stable due to the presence of 4n delocalised (π or lone pair) electrons in it, as opposed to aromaticity. Unlike aromatic compounds, which follow Hückel's rule ( ''n''+2π electrons) and are highly stable, antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive. To avoid the instability of antiaromaticity, molecules may change shape, becoming non-planar and therefore breaking some of the π interactions. In contrast to the diamagnetic ring current present in aromatic compounds, antiaromatic compounds have a paramagnetic ring current, which can be observed by NMR spectroscopy. Examples of antiaromatic compounds are pentalene (A), biphenylene (B), cyclopentadienyl cation (C). The prototypical example of antiaromaticity, cyclobutadiene, is the subject of debate, with some scientists arguing that antiaromaticity is not a major factor contributin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

2.png)

