|
Critical Engine
The critical engine of a multi-engine fixed-wing aircraft is the engine that, in the event of failure, would most adversely affect the performance or handling abilities of an aircraft. On propeller aircraft, there is a difference in the remaining yawing moments after failure of the left or the right (outboard) engine when all propellers rotate in the same direction due to the P-factor. On turbojet and turbofan twin-engine aircraft, there usually is no difference between the yawing moments after failure of a left or right engine in no-wind condition. Description When one of the engines on a typical multi-engine aircraft becomes inoperative, a thrust imbalance exists between the operative and inoperative sides of the aircraft. This thrust imbalance causes several negative effects in addition to the loss of one engine's thrust. The tail-design engineer is responsible for determining the size of vertical stabilizer that will comply with the regulatory requirements for the control an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-wing Aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft (in which the wings form a rotor mounted on a spinning shaft or "mast"), and ornithopters (in which the wings flap in a manner similar to that of a bird). The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft and airplanes that use wing morphing are all examples of fixed-wing aircraft. Gliding fixed-wing aircraft, including free-flying gliders of various kinds and tethered kites, can use moving air to gain altitude. Powered fixed-wing aircraft (airplanes) that gain forward thrust from an engine include powered paragliders, powered hang gliders and some ground effect vehicles. Most fixed-wing aircraft are flown by a pilot on board the craf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of North Dakota
The University of North Dakota (also known as UND or North Dakota) is a public research university in Grand Forks, North Dakota. It was established by the Dakota Territorial Assembly in 1883, six years before the establishment of the state of North Dakota. The university has the only schools olawanmedicinein the state of North Dakota. The John D. Odegard School of Aerospace Sciences was the first in the country to offer a degree iunmanned aircraft systems operation Several national research institutions are on the university's campus including the Energy and Environmental Research Center, the School of Medicine and Health Sciences, and the USDA Human Nutrition Research Center. It is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". The National Science Foundation ranks UND #151 in the nation. History Founding UND was founded in 1883, six years before North Dakota became a state. UND was founded with a liberal arts foundation and expanded to include sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetrical Aircraft
Asymmetrical aircraft have left- and right-hand sides which are not exact mirror images of each other. Although most aircraft are symmetrical, there is no fundamental reason why they must be, and design goals can sometimes be best achieved with an asymmetrical aircraft. Types of asymmetry Asymmetry arises from a number of design decisions. Some are inherent in the type of aircraft, while others are consciously introduced. Engine torque On a powerful propeller-driven aircraft, the engine torque driving the propeller creates an equal and opposite torque on the engine itself. Because the engine is fixed to the airframe, this reactive torque is transmitted to the aircraft, causing a tendency to roll in the opposite direction to the propeller. On some early types, especially during the pioneer years, a single engine drove twin propellers and the drive was arranged to turn the propellers in opposite directions to cancel their torque. Examples include the Wright Flyer and the early desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutan Boomerang
__NOTOC__ The Rutan Model 202 Boomerang is an aircraft designed and built by Burt Rutan. The design was intended to be a multi-engine aircraft that in the event of failure of a single engine would not become dangerously difficult to control due to asymmetric thrust. The result is an asymmetrical aircraft with a very distinct appearance. Design and development The Boomerang was designed around the specifications of the Beechcraft Baron 58, one of the best known and most numerous twin-engine civilian aircraft. The use of the asymmetrical design allows the Boomerang to fly faster and farther than the Baron using smaller engines, and seating the same number of occupants. The Boomerang is powered by two engines, with the right engine producing 10 hp (8 kW) more power than the left one (the engines are in fact the same model, just rated differently). The wings are forward-swept.Schapiro, Steve.Burt Rutan's Favorite Ride, Air & Space/Smithsonian, September 2012. Retrieved: 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A400M - Yawing Moments After Engine Failure
A4 most often refers to: *A4 paper, a paper size defined by the ISO 216 standard, measuring 210 × 297 mm A4 and variants may also refer to: Science and mathematics * British NVC community A4 (''Hydrocharis morsus-ranae - Stratiotes aloides'' community), one type of Aquatic communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system * Combretastatin A-4, a stilbenoid chemical compound * ''A''4, the alternating group on four elements * A4, a type of stainless steel, as defined by ISO 3506, equivalent to SAE steel grade 316L * Subfamily A4, a rhodopsin-like receptors subfamily Medicine * ATC code A04 ''Antiemetics and antinauseants'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * Lipoxin A4, a lipoxin * Androstenedione, an androgen steroid hormone Transportation Aeronautics and astronautics * "A-4 Helldiver", the civil version of the Curtiss Falcon an attack aircraft manufactured by Curtiss Aircraft Company * Douglas A-4 Skyhawk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
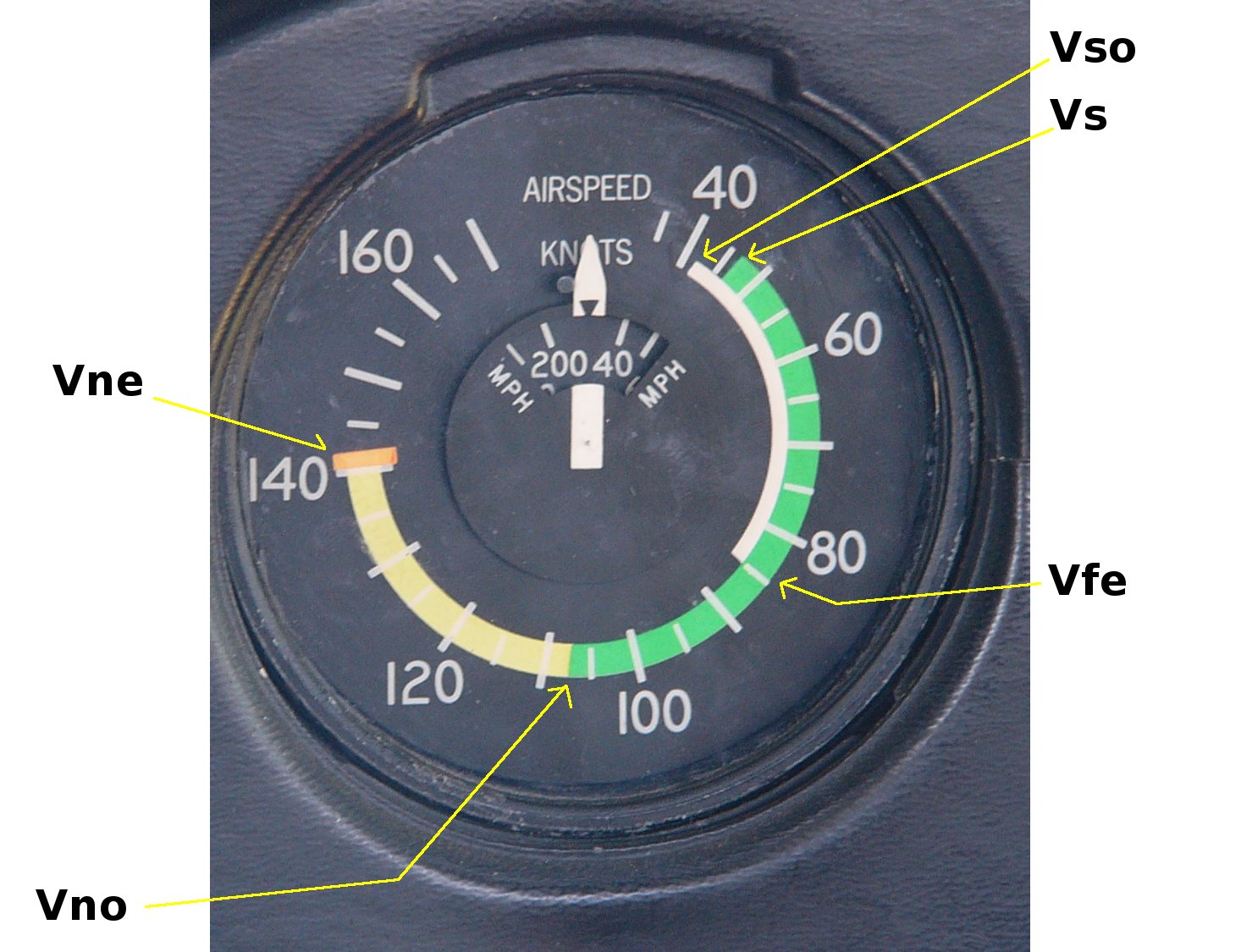
V Speeds
In aviation, V-speeds are standard terms used to define airspeeds important or useful to the operation of all aircraft. These speeds are derived from data obtained by aircraft designers and manufacturers during flight testing for aircraft type-certification. Using them is considered a best practice to maximize aviation safety, aircraft performance, or both. The actual speeds represented by these designators are specific to a particular model of aircraft. They are expressed by the aircraft's indicated airspeed (and not by, for example, the ground speed), so that pilots may use them directly, without having to apply correction factors, as aircraft instruments also show indicated airspeed. In general aviation aircraft, the most commonly used and most safety-critical airspeeds are displayed as color-coded arcs and lines located on the face of an aircraft's airspeed indicator. The lower ends of the white arc and the green arc are the stalling speed with wing flaps in landing con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
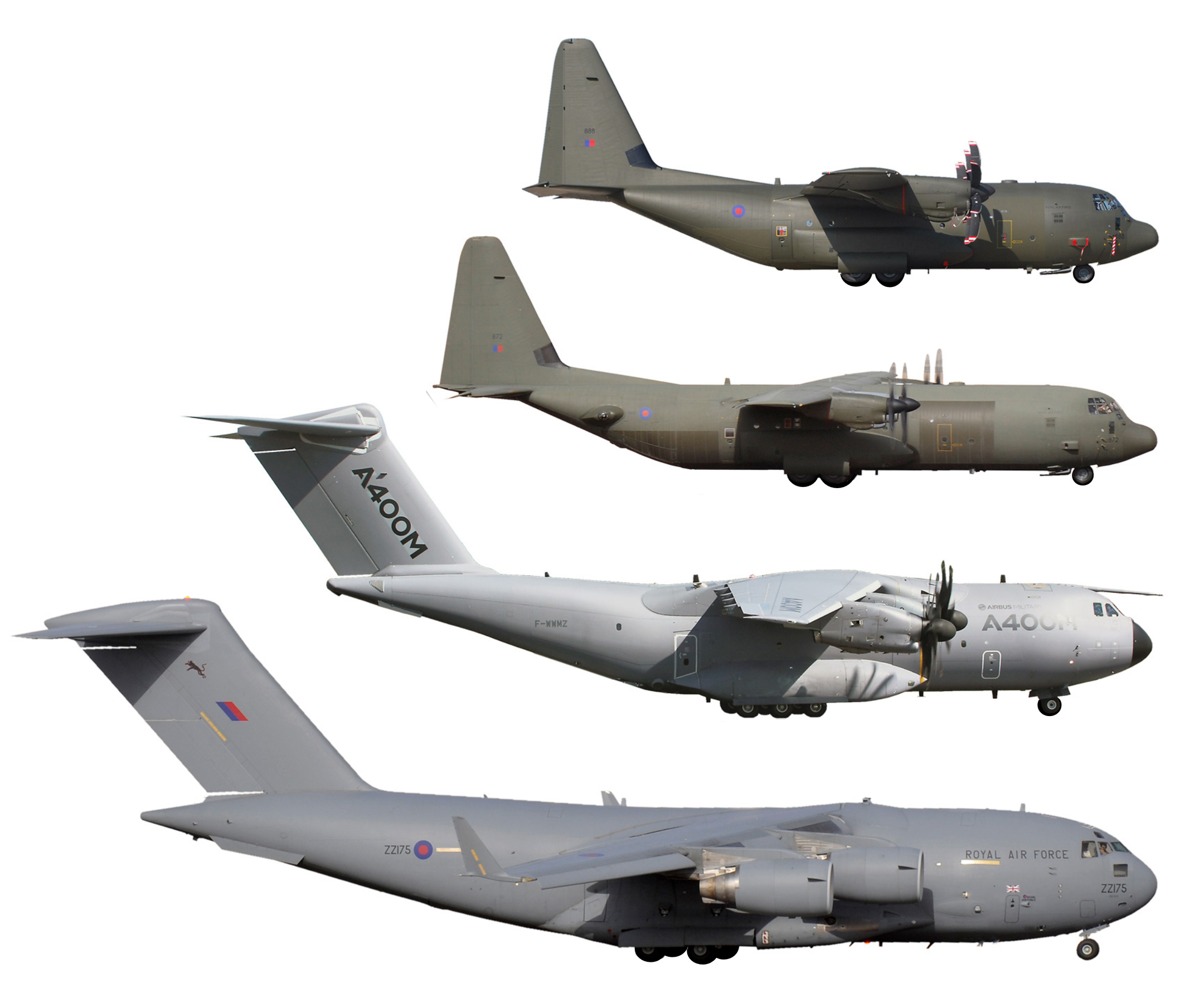
Airbus A400M
The Airbus A400M AtlasNamed after the Greek mythological figure. is a European four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft. It was designed by Airbus Military (now Airbus Defence and Space) as a tactical airlifter with strategic capabilities to replace older transport aircraft, such as the Transall C-160 and the Lockheed C-130 Hercules. The A400M is sized between the C-130 and the Boeing C-17 Globemaster III; it can carry heavier loads than the C-130 and is able to use rough landing strips. In addition to its transport capabilities, the A400M can perform aerial refueling and medical evacuation when fitted with appropriate equipment. The A400M's maiden flight, originally planned for 2008, took place on 11 December 2009 from Seville Airport, Spain. Between 2009 and 2010, the A400M faced cancellation as a result of development programme delays and cost overruns; however, the customer nations chose to maintain their support for the project. A total of 174 A400M aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Pilot
A test pilot is an aircraft pilot with additional training to fly and evaluate experimental, newly produced and modified aircraft with specific maneuvers, known as flight test techniques.Stinton, Darrol. ''Flying Qualities and Flight Testing of the Airplane.'' American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc., 1996, p. 265 History Test flying as a systematic activity started during the First World War, at the Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) in the United Kingdom. An "Experimental Flight" was formed at the Central Flying School. During the 1920s, test flying was further developed by the RAE in the UK, and by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) in the United States. In the 1950s, NACA was transformed into the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, or NASA. During these years, as work was done into aircraft stability and handling qualities, test flying evolved towards a more qualitative scientific profession. In the 1950s, test pilots we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Control Speed
The minimum control speed (VMC) of a multi-engine aircraft (specifically an airplane) is a V-speed that specifies the calibrated airspeed below which directional or lateral control of the aircraft can no longer be maintained, after the failure of one or more engines. The VMC only applies if at least one engine is still operative, and will depend on the stage of flight. Indeed, multiple VMCs have to be calculated for landing, air travel, and ground travel, and there are more still for aircraft with four or more engines. These are all included in the aircraft flight manual of all multi-engine aircraft. When design engineers are sizing an airplane's vertical tail and flight control surfaces, they have to take into account the effect this will have on the airplane's minimum control speeds. Minimum control speeds are typically established by flight tests as part of an aircraft certification process. They provide a guide to the pilot in the safe operation of the aircraft. Physical de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airworthiness
In aviation, airworthiness is the measure of an aircraft's suitability for safe flight. Initial airworthiness is demonstrated by a certificate of airworthiness issued by the civil aviation authority in the state in which the aircraft is registered, and continuing airworthiness is achieved by performing the required maintenance actions. Certification is based on standards applied by civil aviation authorities. Interoperability is served when national benchmarks adopt standards from international civil and military organizations such as International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), NATO and European Defence Agency (EDA). In the U.S., Title 14, Code of Federal Regulations, Subchapter F, Part 91.7 states: "a) No person may operate an aircraft unless it is in an airworthy condition. b) The pilot in command of a civil aircraft is responsible for determining whether that aircraft is in condition for safe flight. The pilot in command shall d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

.jpg)