|
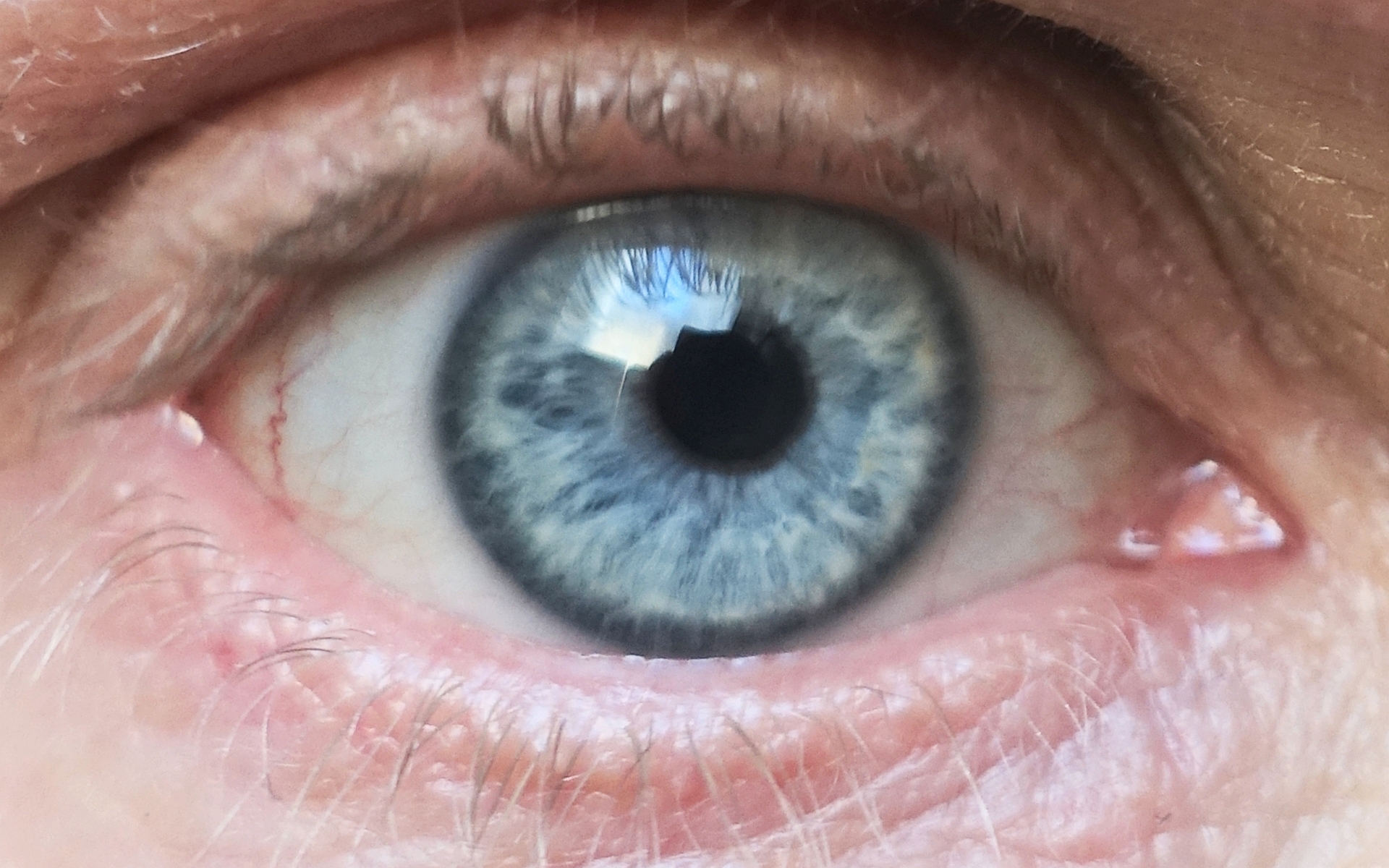
Corneal Limbus
The corneal limbus (''Latin'': corneal border) is the border between the cornea and the sclera (the white of the eye). It contains stem cells in its palisades of Vogt. It may be affected by cancer or by aniridia (a developmental problem), among other issues. Structure The corneal limbus is the border between the cornea and the sclera. It is highly vascularised. Its stratified squamous epithelium is continuous with the epithelium covering the cornea. The corneal limbus contains radially-oriented fibrovascular ridges known as the palisades of Vogt that contain stem cells. The palisades of Vogt are more common in the superior and inferior quadrants around the eye. Clinical significance Cancer The corneal limbus is a common site for the occurrence of corneal epithelial neoplasm. Aniridia Aniridia, a developmental anomaly of the iris, disrupts the normal barrier of the cornea to the conjunctival epithelial cells at the limbus. Glaucoma The corneal limbus may be cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris (anatomy)
In humans and most mammals and birds, the iris (plural: ''irides'' or ''irises'') is a thin, annular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. Eye color is defined by the iris. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm. Structure The iris consists of two layers: the front pigmented fibrovascular layer known as a stroma and, beneath the stroma, pigmented epithelial cells. The stroma is connected to a sphincter muscle ( sphincter pupillae), which contracts the pupil in a circular motion, and a set of dilator muscles ( dilator pupillae), which pull the iris radially to enlarge the pupil, pulling it in folds. The sphincter pupillae is the opposing muscle of the dilator pupillae. The pupil's diameter, and thus the inner border of the iris, changes size when constricting or dilating. The outer border of the iris does not change size. The constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbal Stem Cell
Limbal stem cells, also known as corneal epithelial stem cells, are stem cells located in the basal epithelial layer of the corneal limbus. They form the border between the cornea and the sclera. Characteristics of limbal stem cells include a slow turnover rate, high proliferative potential, clonogenicity, expression of stem cell markers, as well as the ability to regenerate the entire corneal epithelium. Limbal stem cell proliferation has the role of maintaining the cornea; for example, by replacing cells that are lost via tears. Additionally, these cells also prevent the conjunctival epithelial cells from migrating onto the surface of the cornea. Medical conditions and treatments Damage to the limbus can lead to limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD); this may be primary - related to an insufficient stromal microenvironment to support stem cell functions, such as aniridia, and other congenital conditions, or secondary – caused by external factors that destroy the limbal stem cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbal Ring
A limbal ring is a dark ring around the iris of the eye, where the sclera meets the cornea.Johnson and Johnson Vision Care Inc. Tinted contact lenses with combined limbal ring and iris patterns. US7246903B2. United States Patent and Trademark Office, July 24, 2007. http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&p=1&u=/netahtml/PTO/srchnum.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&d=PALL&s1=7246903.PN. It is a dark-colored manifestation of the corneal limbus resulting from optical properties of the region. The appearance and visibility of the limbal ring can be negatively affected by a variety of medical conditions concerning the peripheral cornea. It has been suggested that limbal ring thickness may correlate with health or youthfulness and may contribute to facial attractiveness. Some contact lenses are colored to simulate limbal rings. Youth, health, and attractiveness Both health and age are positively correlated with a prominent limbal ring. For instance, a darker limbal ring tends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbus Sign
The limbus sign is a ring of dystrophic calcification evident as a "milky precipitate" (i.e. abnormal white color) at the corneal limbus. The corneal limbus is the part of the eye where the cornea (front/center) meets the sclera (white part of the eye). Thought to be caused by increased calcium concentration in the blood, this sign however persists after calcium phosphate The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are whi ... concentration returns to normal. Compare the limbus sign (calcification) with arcus senilis (lipid).Edwards, Mark E. (2008)Geriatric physical diagnosis: a guide to observation and assessment.McFarland & Company. p. 96. Retrieved January 7, 2012. References {{med-sign-stub Eye Medical signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Incision
In surgery, a surgical incision is a cut made through the skin and soft tissue to facilitate an operation or procedure. Often, multiple incisions are possible for an operation. In general, a surgical incision is made as small and unobtrusive as possible to facilitate safe and timely operating conditions. Anatomy Surgical incisions are planned based on the expected extent of exposure needed for the specific operation planned. Within each region of the body, several incisions are common. Head and neck * Wilde's incision – This post-aural incision is used for a variant mastoiditis drainage, and was named after Sir William Wilde, an ENT surgeon in Dublin who first described it at the end of the nineteenth century. His son, Oscar Wilde's, death was stated by his doctors to be due to meningitis stemming from an ear infection. He had recently had an operation, believed by some to be a mastoidectomy. Chest * Median sternotomy – This is the primary incision used for cardiac p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabeculectomy
Trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure used in the treatment of glaucoma to relieve intraocular pressure by removing part of the eye's trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures. It is the most common glaucoma surgery performed and allows drainage of aqueous humor from within the eye to underneath the conjunctiva where it is absorbed. This outpatient procedure was most commonly performed under monitored anesthesia care using a retrobulbar block or peribulbar block or a combination of topical and subtenon ( Tenon's capsule) anesthesia. Due to the higher risks associated with bulbar blocks, topical analgesia with mild sedation is becoming more common. Rarely general anesthesia will be used, in patients with an inability to cooperate during surgery. Procedure An initial pocket is created under the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule and the wound bed is treated for several seconds to minutes with mitomycin C (MMC, 0.5–0.2 mg/ml) or 5-fluorouracil (5-FU, 50 mg/ml) soaked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irritation
Irritation, in biology and physiology, is a state of inflammation or painful reaction to allergy or cell-lining damage. A stimulus or agent which induces the state of irritation is an irritant. Irritants are typically thought of as chemical agents (for example phenol and capsaicin) but mechanical, thermal (heat), and radiative stimuli (for example ultraviolet light or ionising radiations) can also be irritants. Irritation also has non-clinical usages referring to bothersome physical or psychological pain or discomfort. Irritation can also be induced by some allergic response due to exposure of some allergens for example contact dermatitis, irritation of mucosal membranes and pruritus. Mucosal membrane is the most common site of irritation because it contains secretory glands that release mucous which attracts the allergens due to its sticky nature. Chronic irritation is a medical term signifying that afflictive health conditions have been present for a while. There are many dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Chamber Of Eyeball
The anterior chamber ( AC) is the aqueous humor-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Hyphema, anterior uveitis and glaucoma are three main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, blood fills the anterior chamber as a result of a hemorrhage, most commonly after a blunt eye injury. Anterior uveitis is an inflammatory process affecting the iris and ciliary body, with resulting inflammatory signs in the anterior chamber. In glaucoma, blockage of the trabecular meshwork prevents the normal outflow of aqueous humour, resulting in increased intraocular pressure, progressive damage to the optic nerve head, and eventually blindness. The depth of the anterior chamber of the eye varies between 1.5 and 4.0 mm, averaging 3.0 mm. It tends to become shallower at older age and in eyes with hypermetropia (far sightedness). As depth decreases below 2.5 mm, the risk for angle closure glaucoma increases. Clinical significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Humour
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber. Blood cannot normally enter the eyeball. Structure Composition * Amino acids: transported by ciliary muscles *98% water * Electrolytes ( pH = 7.4 -one source gives 7.1) **Sodium = 142.09 **Potassium = 2.2 - 4.0 **Calcium = 1.8 **Magnesium = 1.1 **Chloride = 131.6 **HCO3- = 20.15 **Phosphate = 0.62 ** Osm = 304 * Ascorbic acid * Glutathione * Immunoglobulins Function *Maintains the intraocular pressure and inflates the globe of the eye. It is this hydrostatic pressure that keeps the eyeball in a roughly spherical shape and keeps the walls of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |