|
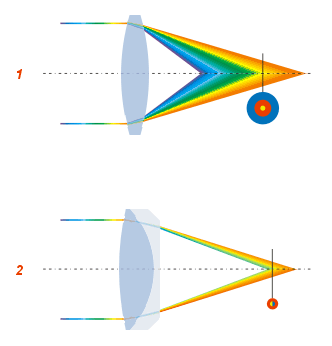
Coma Aberration
In optics (especially telescopes), the coma (), or comatic aberration, in an optical system refers to aberration inherent to certain optical designs or due to imperfection in the lens or other components that results in off-axis point sources such as stars appearing distorted, appearing to have a tail ( coma) like a comet. Specifically, coma is defined as a variation in magnification over the entrance pupil. In refractive or diffractive optical systems, especially those imaging a wide spectral range, coma can be a function of wavelength, in which case it is a form of chromatic aberration. Overview Coma is an inherent property of telescopes using parabolic mirrors. Unlike a spherical mirror, a bundle of parallel rays parallel to the optical axis will be perfectly focused to a point (the mirror is free of spherical aberration), no matter where they strike the mirror. However, this is only true if the rays are parallel to the axis of the parabola. When the incoming rays strike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens Coma
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Telescope
Schmidt may refer to: * Schmidt (surname), including list of people with the surname * Schmidt (singer) (born 1990), German pop and jazz singer * Schmidt (lunar crater), a small lunar impact crater * Schmidt (Martian crater), a crater on Mars * Schmidt (volcano), in Kamchatka * Schmidt Block, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Scott County, Iowa, USA * Schmidt Brewery, a St. Paul brewery * Schmidt camera, an astronomical telescope designed for photography * Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope, a version of the Schmidt camera * Schmidt Site, an archeological site in Michigan, USA, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 * Schmidt Spiele, a German games manufacturer * Schmidt Baking Company, makers of Schmidt's Blue Ribbon Bread * von Schmidt auf Altenstadt, a German baronial family in Kirchgattendorf, part of the municipality of Gattendorf * Schmidt Island, an island in the Novaya Zemlya archipelago in the Arctic Ocean * Schmidt Peninsula (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zernike Polynomials
In mathematics, the Zernike polynomials are a sequence of polynomials that are orthogonal on the unit disk. Named after optical physicist Frits Zernike, winner of the 1953 Nobel Prize in Physics and the inventor of phase-contrast microscopy, they play important roles in various optics branches such as beam optics and imaging. Definitions There are even and odd Zernike polynomials. The even Zernike polynomials are defined as :Z^_n(\rho,\varphi) = R^m_n(\rho)\,\cos(m\,\varphi) \! (even function over the azimuthal angle \varphi), and the odd Zernike polynomials are defined as :Z^_n(\rho,\varphi) = R^m_n(\rho)\,\sin(m\,\varphi), \! (odd function over the azimuthal angle \varphi) where ''m'' and ''n'' are nonnegative integers with ''n ≥ m ≥ 0'' (''m'' = 0 for even Zernike polynomials), ''\varphi'' is the azimuthal angle, ''ρ'' is the radial distance 0\le\rho\le 1, and R^m_n are the radial polynomials defined below. Zernike polynomials have the property of being l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Aberration
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which is not sharp. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration. Aberration can be an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baader Rowe Coma Corrector Comparison
Baader is a surname of German origin. People with the surname Baader * Andreas Baader (1943–1977), militant of the Red Army Faction (Rote Armee Fraktion), also known as the ''Baader Meinhoff Gang'' * Caspar Baader (born 1953), Swiss politician * Franz Xaver von Baader (1765–1841), German philosopher and theologian * Johannes Baader (1875–1955), architect, writer and artist associated with Dada * Joseph von Baader (1763–1835), German railway pioneer * Louis-Marie Baader (1828–1920), French painter * Ottilie Baader (1847–1925), German women's right activist and socialist See also * Baade (surname) * Bader * Badr (other) Badr (Arabic: بدر) as a given name below is an Arabic masculine and feminine name given to the "full moon on its fourteenth night" or the ecclesiastical full moon. Badr may refer to: .and it is also one of the oldest and rarest names in the Arab ... {{surname, Baader German-language surnames Occupational surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology (journal)
''Ophthalmology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier on behalf of the American Academy of Ophthalmology. It covers all aspects of ophthalmology. Editors The following persons are or have been editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ...: *Stephen McLeod (2017–present) * George B. Bartley (2012–2017) *Andrew P. Schachat (2003–2012) Family of Journals On June 6, 2016 The American Academy of Ophthalmology announced plans to launch ''Ophthalmology Retina'' as an extension of the journal ''Ophthalmology''. This new journal was planned in response to the growing volume of research within the retina subspecialty of ophthalmology, and will be a print and online publication. References External links * Ophthalmology journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratoconus
Keratoconus (KC) is a disorder of the eye that results in progressive thinning of the cornea. This may result in blurry vision, double vision, nearsightedness, irregular astigmatism, and light sensitivity leading to poor quality-of-life. Usually both eyes are affected. In more severe cases a scarring or a circle may be seen within the cornea. While the cause is unknown, it is believed to occur due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Patients with a parent, sibling, or child who has keratoconus have 15 to 67 times higher risk in developing corneal ectasia compared to patients with no affected relatives. Proposed environmental factors include rubbing the eyes and allergies. The underlying mechanism involves changes of the cornea to a cone shape. Diagnosis is most often by topography. Topography measures the curvature of the cornea and creates a colored "map" of the cornea. Keratoconus causes very distinctive changes in the appearance of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplanatic Lens
An aplanatic lens is a lens that is free of both spherical and coma aberrations. Aplanatic lenses can be made by combining two or three lens elements. A single-element aplanatic lens is an aspheric lens whose surfaces are surfaces of revolution A surface of revolution is a surface in Euclidean space created by rotating a curve (the generatrix) around an axis of rotation. Examples of surfaces of revolution generated by a straight line are cylindrical and conical surfaces depending on ... of a cartesian oval.. References Lenses {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane. For curves, the canonical example is that of a circle, which has a curvature equal to the reciprocal of its radius. Smaller circles bend more sharply, and hence have higher curvature. The curvature ''at a point'' of a differentiable curve is the curvature of its osculating circle, that is the circle that best approximates the curve near this point. The curvature of a straight line is zero. In contrast to the tangent, which is a vector quantity, the curvature at a point is typically a scalar quantity, that is, it is expressed by a single real number. For surfaces (and, more generally for higher-dimensional manifolds), that are embedded in a Euclidean space, the concept of curvature is more complex, as it depends on the choice of a direction on the surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barlow Lens
The Barlow lens, named after Peter Barlow, is a diverging lens which, used in series with other optics in an optical system, increases the effective focal length of an optical system as perceived by all components that are after it in the system. The practical result is that inserting a Barlow lens magnifies the image. A real barlow lens is not a single glass element, because that would generate chromatic aberration, and spherical aberration if the lens is not aspheric. More common configurations use three or more elements for achromatic correction or apochromatic correction and higher image quality. Telescope use In its astronomical use, a Barlow lens may be placed immediately before an eyepiece to effectively decrease the eyepiece's focal length by the amount of the Barlow's divergence. Since the magnification provided by a telescope and eyepiece is equal to the telescope's focal length divided by the eyepiece's focal length, this has the effect of increasing the magnificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtonian Reflector
The Newtonian telescope, also called the Newtonian reflector or just a Newtonian, is a type of reflecting telescope invented by the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton, using a concave primary mirror and a flat diagonal secondary mirror. Newton's first reflecting telescope was completed in 1668 and is the earliest known functional reflecting telescope. The Newtonian telescope's simple design has made it very popular with amateur telescope makers. Description [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma Corrector
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move. Comas can be derived by natural causes, or can be medically induced. Clinically, a coma can be defined as the inability consistently to follow a one-step command. It can also be defined as a score of ≤ 8 on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) lasting ≥ 6 hours. For a patient to maintain consciousness, the components of ''wakefulness'' and ''awareness'' must be maintained. Wakefulness describes the quantitative degree of consciousness, whereas awareness relates to the qualitative aspects of the functions mediated by the cortex, including cognitive abilities such as attention, sensory perception, explicit memory, language, the execution of tasks, temporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |