|
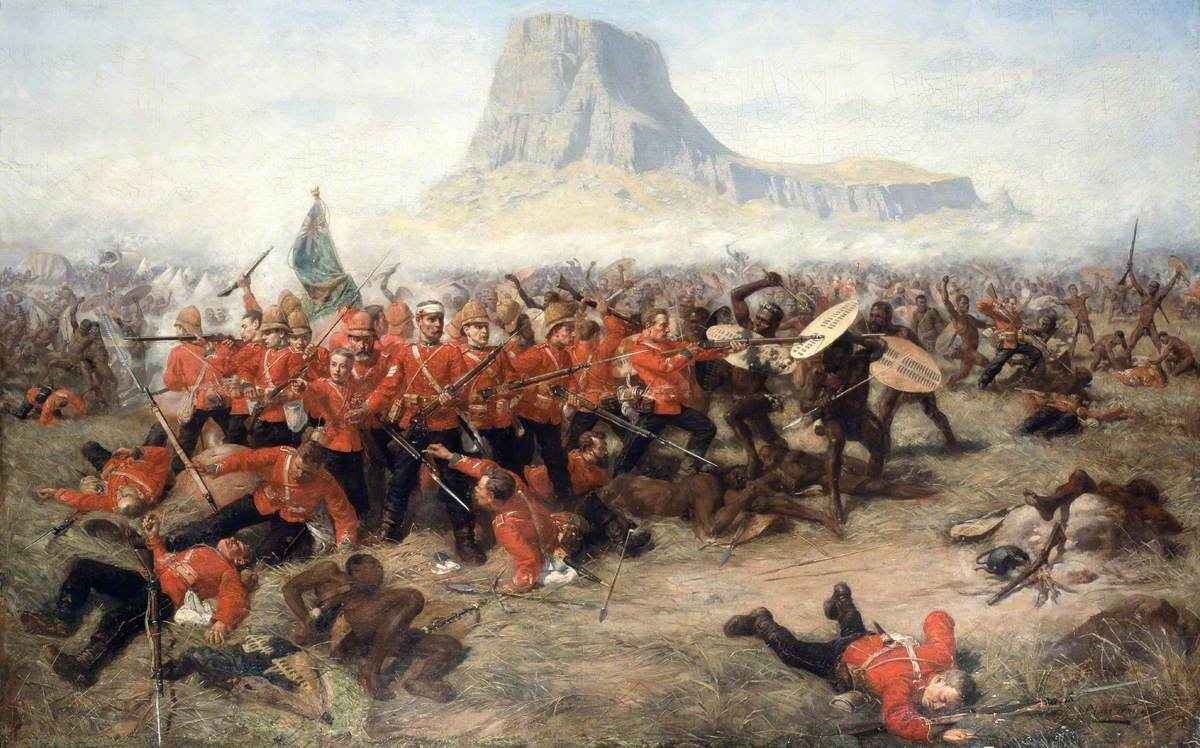
Colonial War
Colonial war (in some contexts referred to as small war) is a blanket term relating to the various conflicts that arose as the result of overseas territories being settled by foreign powers creating a colony. The term especially refers to wars fought during the nineteenth century between European armies in Africa and Asia. Description Classification Traditionally, wars could be divided into three categories: wars of conquest, wars of liberation, and wars between states. These classifications can likewise be distinguished among colonial wars. Still, the term "colonial war" typically refers to a war of conquest. Wars of conquest, in a colonial context, can be further broken down into two stages: a period of typically brief, regular warfare between an invading power and an indigenous force (which may be, in comparison to the invader, irregular in composition or organization) followed by a period of irregular warfare. Counter-insurgency operations may be undertaken in ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territories that are not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governed colonies controlled by colonial settlers. The term colony originates from the ancient Roman '' colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'. Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''metropolis'' ("mother- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, screening, and skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, horseman, trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as camels or elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18th century as ''dragoons'', a class of mounted infantry which in most armies later evolved into standard cavalry while retain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Algeria
French Algeria (french: Alger to 1839, then afterwards; unofficially , ar, الجزائر المستعمرة), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of French colonisation of Algeria. French rule in the region began in 1830 with the invasion of Algiers and lasted until the end of the Algerian War of Independence in 1962. While the administration of Algeria changed significantly over the 132 years of French rule, the Mediterranean coastal region of Algeria, housing the vast majority of its population, was an integral part of France from 1848 until its independence. As one of France's longest-held overseas territories, Algeria became a destination for hundreds of thousands of European immigrants known as ''colons'', and later as . However, the indigenous Muslim population remained the majority of the territory's population throughout its history. Many estimates indicates that the native Algerian population fell by one-third in the years between the French invasion a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total War
Total war is a type of warfare that includes any and all civilian-associated resources and infrastructure as legitimate military targets, mobilizes all of the resources of society to fight the war, and gives priority to warfare over non-combatant needs. The term has been defined as "A war that is unrestricted in terms of the weapons used, the territory or combatants involved, or the objectives pursued, especially one in which the laws of war are disregarded." In the mid-19th century, scholars identified total war as a separate class of warfare. In a total war, the differentiation between combatants and non-combatants diminishes due to the capacity of opposing sides to consider nearly every human, including non-combatants, as resources that are used in the war effort. Characteristics According to an analysis by Tiziano Peccia of Stig Förster's works, total war is characterized on four dimensions: # Total purposes (aim of continuous growth of the power of the parties invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Saïo
The siege of Saïo or battle of Saïo took place during the East African Campaign of World War II. Belgo-Congolese troops, British Commonwealth forces and local resistance fighters besieged the fort at the market town of Saïo in south-western Ethiopia in 1941. The siege lasted for several months, culminating in an Allied attack on the Italian garrison thereby forcing it to surrender. In the first months of 1941, British and Belgian colonial forces attacked Italian East Africa from the colony of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. By the end of March, they had seized the town of Gambela and begun containing retreating Italian forces, which were massing on a plateau in the mountain town of Saïo (presently Dembidolo) under the command of General Carlo De Simone and later General Pietro Gazzera. The British forces withdrew the following month and the Belgians advanced down the road to Saïo. The Italians repelled them and they were forced to hold their positions along a nearby brook. Almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Weller
George Anthony Weller (July 13, 1907 – December 19, 2002) was an American novelist, playwright, and journalist for ''The New York Times'' and ''Chicago Daily News''. He won a 1943 Pulitzer Prize as a ''Daily News'' war correspondent. Weller's reports from Nagasaki after its August 1945 nuclear bombing were censored by the U.S. military and not published in full until a book edited by his son in 2006. Life and career Weller was born in Boston in 1907 and graduated from the Roxbury Latin School in 1925. He was editorial chairman of ''The Harvard Crimson'' as a college student graduated from Harvard in 1929. During his senior year there, he wrote the book and co-wrote the lyrics for the 83rd annual Hasty Pudding Club musical comedy production, ''Fireman, Save My Child!'' He studied acting in Vienna, Austria as the only American member of Max Reinhardt's theater company. Weller was named to the Balkan reporting team of ''The New York Times'', and during the 1930s also publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-insurgency
Counterinsurgency (COIN) is "the totality of actions aimed at defeating irregular forces". The Oxford English Dictionary defines counterinsurgency as any "military or political action taken against the activities of guerrillas or revolutionaries" and can be considered war by a state against a non-state adversary. Insurgency and counterinsurgency campaigns have been waged since ancient history. However, modern thinking on counterinsurgency was developed during decolonization. Within the military sciences, counterinsurgency is one of the main operational approaches of irregular warfare. During insurgency and counterinsurgency, the distinction between civilians and combatants is often blurred. Counterinsurgency may involve attempting to win the hearts and minds of populations supporting the insurgency. Alternatively, it may be waged in an attempt to intimidate or eliminate civilian populations suspected of loyalty to the insurgency through indiscriminate violence. Models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
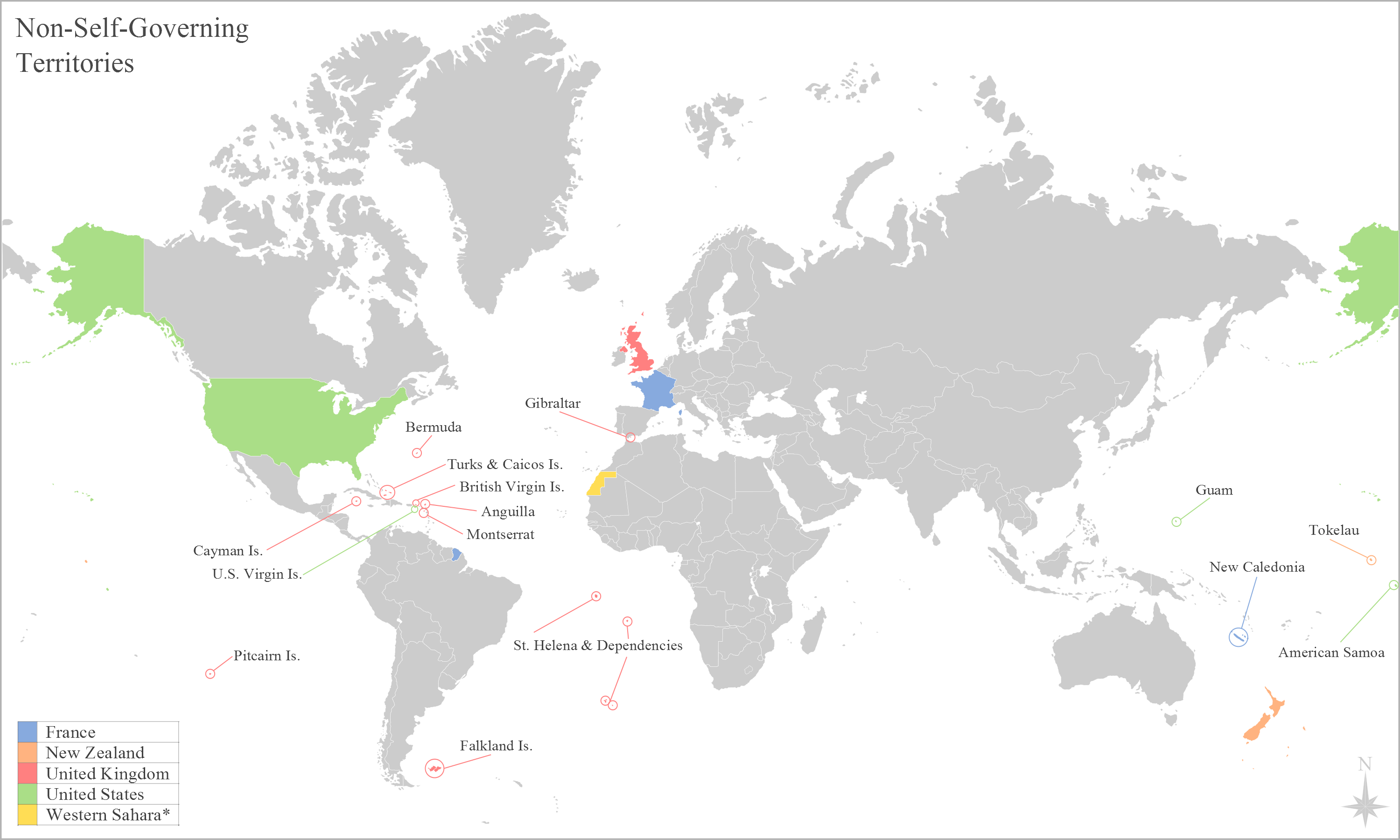
Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial dependency, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. The conflict began on 2 April, when Argentina invaded and occupied the Falkland Islands, followed by the invasion of South Georgia the next day. On 5 April, the British government dispatched a naval task force to engage the Argentine Navy and Air Force before making an amphibious assault on the islands. The conflict lasted 74 days and ended with an Argentine surrender on 14 June, returning the islands to British control. In total, 649 Argentine military personnel, 255 British military personnel, and three Falkland Islanders were killed during the hostilities. The conflict was a major episode in the protracted dispute over the territories' sovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Colonial War
The Portuguese Colonial War ( pt, Guerra Colonial Portuguesa), also known in Portugal as the Overseas War () or in the former colonies as the War of Liberation (), and also known as the Angolan, Guinea-Bissau and Mozambican War of Independence, was a 13-year-long conflict fought between Portugal's military and the emerging nationalist movements in Portugal's African colonies between 1961 and 1974. The Portuguese ultraconservative regime at the time, the , was overthrown by a military coup in 1974, and the change in government brought the conflict to an end. The war was a decisive ideological struggle in Lusophone Africa, surrounding nations, and mainland Portugal. The prevalent Portuguese and international historical approach considers the Portuguese Colonial War as was perceived at the time—a single conflict fought in the three separate Angolan, Guinea-Bissau and Mozambican theaters of operations, rather than a number of separate conflicts as the emergent African countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Wave Of European Colonization
The first European colonialism, European colonization wave began with Castilians, Castilian and Portuguese Empire, Portuguese conquests and explorations, and primarily involved the European colonization of the Americas, though it also included the establishment of European colonies in India and in Maritime Southeast Asia. During this period, European interests in Africa primarily focused on the establishment of trading posts there, particularly for the African slave trade. The wave ended with the British annexation of the Kingdom of Kandy in 1815 and the founding of the colony of Singapore in 1819. The time period in which much of the first wave of European colonization (and other exploratory ventures) occurred is often labeled the Age of Discovery. A New Imperialism, later major phase of European colonization, which started in the late 19th-century and primarily focused on Africa and Asia, is known as the period of New Imperialism. The Role of the Church Religious zeal playe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Troops
Colonial troops or colonial army refers to various military units recruited from, or used as garrison troops in, colonial territories. Colonial background Such colonies may lie overseas or in areas dominated by neighbouring land powers such as Imperial China or Tsarist Russia. Colonial troops have been used by Imperial powers whether ancient (such as Carthage and Rome), or modern (such as Great Britain, France, Netherlands, Denmark, the United States, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, and Portugal). Sometimes they have been recruited under local leaders, as auxiliaries; and at other times organised directly by the colonial power. Origins At the beginning of the modern colonial period such troops were predominantly Europeans from the home army of the country concerned, but locally raised "native" troops were soon recruited. The latter normally served in separate units, at first under their own leaders, later under European officers. The sepoys of the East India Company were an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |