|
Close-up Lens
In photography, a close-up lens (sometimes referred to as ''close-up filter'' or a ''macro filter'') is a simple secondary lens used to enable macro photography without requiring a specialised primary lens. They work like reading glasses, allowing a primary lens to focus more closely. Bringing the focus closer allows the photographer more possibilities. Close-up lenses typically mount on the filter thread of the primary lens, and are often manufactured and sold by suppliers of photographic filters. Nonetheless, they are lenses and not photographic filter, filters. Some manufacturers refer to their close-up lenses as ''diopters'', after the unit of measurement of their optical power. Close-up lens do not affect exposure, unlike extension tubes, which also can be used for macro photography with a non-macro lens. Optical power Close-up lenses are often specified by their optical power in diopters, the reciprocal of the focal length in meters. For a close-up lens, the diopter valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens Filter Set
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plant) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diopters
A dioptre (British spelling) or diopter (American spelling) is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dioptre = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams. The main benefit of using optical power rather than focal length is that the thin lens formula has the object distance, image distance, and focal length all as reciprocals. Additionally, when relatively thin lenses are placed close together their powers approximately add. Thus, a thin 2.0-dioptre lens placed close t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extension Tube
An extension tube, sometimes also called a closeup tube or an extension ring, is used with interchangeable lenses to increase magnification. This is most often used in macro photography. Construction The tube contains no optical elements; its sole purpose is to move the lens farther from the image plane. The farther away the lens is, the closer the focus, the greater the magnification, and also the greater the loss of light (requiring a longer exposure time). Lenses classically focus closer than infinity by moving all optical elements farther from the film or sensor; an extension tube simply enables this movement. Because extension tubes do not have optics, they do not affect the optical quality of a lens. Because of their function, there are other effects: decrease of light; shallower depth of field; and loss of ability to focus at infinity. The longer the extension tube, the closer the lens can focus. Correspondingly, the amount of light and depth of field will be reduced. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Focus
Deep focus is a photographic and cinematographic technique using a large depth of field. Depth of field is the front-to-back range of focus in an image, or how much of it appears sharp and clear. In deep focus, the foreground, middle ground, and background are all in focus. Deep focus is normally achieved by choosing a small aperture. Since the aperture of a camera determines how much light enters through the lens, achieving deep focus requires a bright scene or long exposure. A wide-angle lens also makes a larger portion of the image appear sharp. It is also possible to achieve the illusion of deep focus with optical tricks (split-focus diopter) or by compositing two or more images together. The opposite of deep focus is shallow focus, in which the plane of the image that is in focus is very shallow. For example, the foreground might be in focus while the middle-ground and background are out-of-focus. When avoiding deep focus is used specifically for aesthetic effect—espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublet (lens)
In optics, a doublet is a type of lens made up of two simple lenses paired together. Such an arrangement allows more optical surfaces, thicknesses, and formulations, especially as the space between lenses may be considered an "element". With additional degrees of freedom, optical designers have more latitude to correct more optical aberrations more thoroughly. Types Doublets can come in many forms, though most commercial doublets are achromats, which are optimized to reduce chromatic aberration while also reducing spherical aberration and other optical aberrations. The lenses are made from glasses with different refractive indices and different amounts of dispersion. Often one element is made from crown glass and the other from flint glass. This combination produces a better image than a simple lens. Some Trilobites, which are now extinct, had natural doublet lenses in their eyes. Apochromats can also be made as doublets. Doublets can be air-spaced, cemented, or "oiled". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Aberration
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which is not sharp. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration. Aberration can be an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus Breathing
Breathing originally referred to any geometric change in field-of-view when changing focus distance. Even if the angle-of-view is constant distortion changes will cause visible breathing. It has been recently used by photographers for changes of focal length of a lens when changing the focus. Breathing is sometimes used for the suction and expulsion of air from within the lens as its internal volume changes. A lens with a constant focal length will exhibit narrowing of the angle of view at closer focus, and conversely, maintaining a constant angle of view requires precise reduction of focal length as focus is decreased, which some (often higher quality) lenses are designed to do. Lens breathing does not prevent one from racking focus A focus puller or first assistant camera (1st AC) is a member of a film crew's camera department whose primary responsibility is to maintain the camera lens's optical focus on whatever subject or action is being filmed. "Pulling focus" refers to ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioptre
A dioptre (British spelling) or diopter (American spelling) is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dioptre = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams. The main benefit of using optical power rather than focal length is that the thin lens formula has the object distance, image distance, and focal length all as reciprocals. Additionally, when relatively thin lenses are placed close together their powers approximately add. Thus, a thin 2.0-dioptre lens placed clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
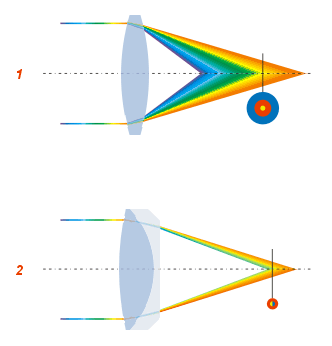
Achromatic Lens
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red and blue) into focus on the same plane. The most common type of achromat is the achromatic doublet, which is composed of two individual lenses made from glasses with different amounts of dispersion. Typically, one element is a negative (concave) element made out of flint glass such as F2, which has relatively high dispersion, and the other is a positive (convex) element made of crown glass such as BK7, which has lower dispersion. The lens elements are mounted next to each other, often cemented together, and shaped so that the chromatic aberration of one is counterbalanced by that of the other. In the most common type (shown), the positive power of the crown lens element is not quite equalled by the negative power of the flint lens element. Together they form a weak positive lens that will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power. In most photography and all telescopy, where the subject is essentially infinitely far away, longer focal length (lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length of the device: . High optical power corresponds to short focal length. The SI unit for optical power is the inverse metre (m−1), which is commonly called the dioptre. Converging lenses have positive optical power, while diverging lenses have negative power. When a lens is immersed in a refractive medium, its optical power and focal length change. For two or more thin lenses close together, the optical power of the combined lenses is approximately equal to the sum of the optical powers of each lens: . Similarly, the optical power of a single lens is roughly equal to the sum of the powers of each surface. These approximations are commonly used in optometry. An eye that has too much or too little refractive power to foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close-Up Lens Canon 500D 58 Mm
A close-up or closeup in filmmaking, television production, still photography, and the comic strip medium is a type of shot that tightly frames a person or object. Close-ups are one of the standard shots used regularly with medium and long shots (cinematic techniques). Close-ups display the most detail, but they do not include the broader scene. Moving toward or away from a close-up is a common type of zooming. A close up is taken from head to neck, giving the viewer a detailed view of the subject's face. History Most early filmmakers, such as Thomas Edison, Auguste and Louis Lumière and Georges Méliès, tended not to use close-ups and preferred to frame their subjects in long shots, similar to the stage. Film historians disagree as to the filmmaker who first used a close-up. One of the best claims is for George Albert Smith in Hove, who used medium close-ups in films as early as 1898 and by 1900 was incorporating extreme close-ups in films such as ''As Seen Through a Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).jpg)