|
Cladding (metalworking)
Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar metals. It is different from fusion welding or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling sheets together under high pressure. The United States Mint uses cladding to manufacture coins from different metals. This allows a cheaper metal to be used as a filler. For example, dimes and quarters struck since 1965 have cores made from pure copper, with a clad layer consisting of 75% copper and 25% nickel added during production. Laser cladding is an additive manufacturing approach for metal coatings or precise piece restorations by using high power multi-mode optical fiber laser. Roll bonding In roll bonding, two or more layers of different metals are thoroughly cleaned and passed through a pair of rollers under sufficient pressure to bond the layers. The pressure is high enough to deform the metals and reduce the combined thicknes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the ''metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials regarded as metals c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
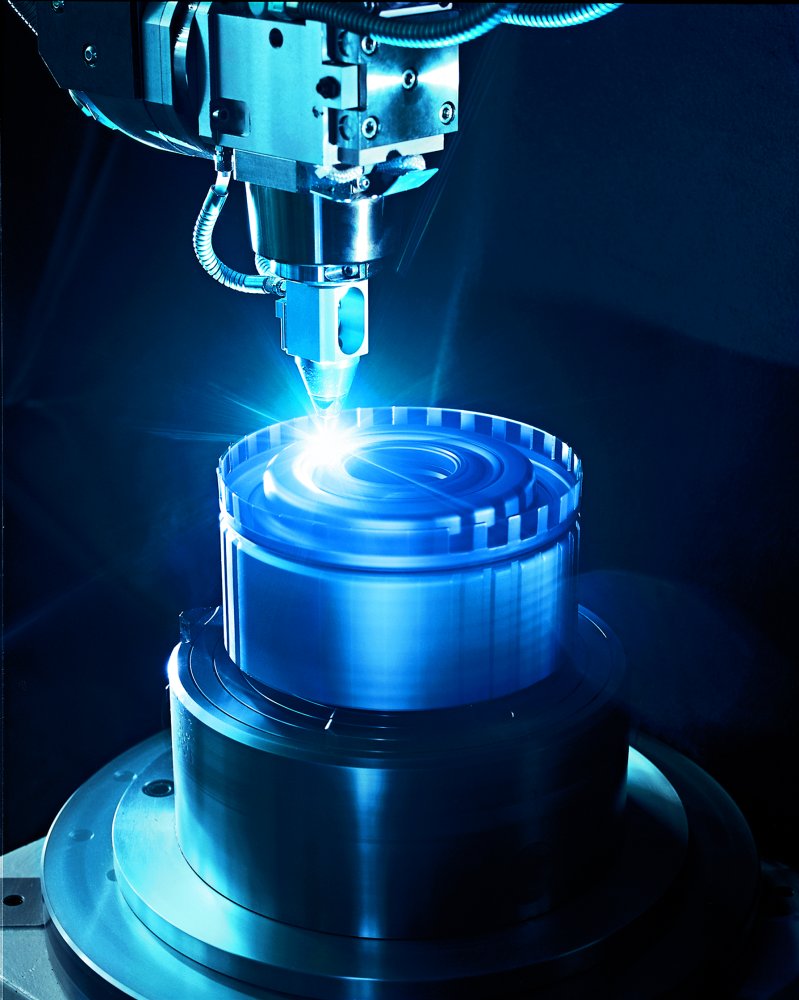
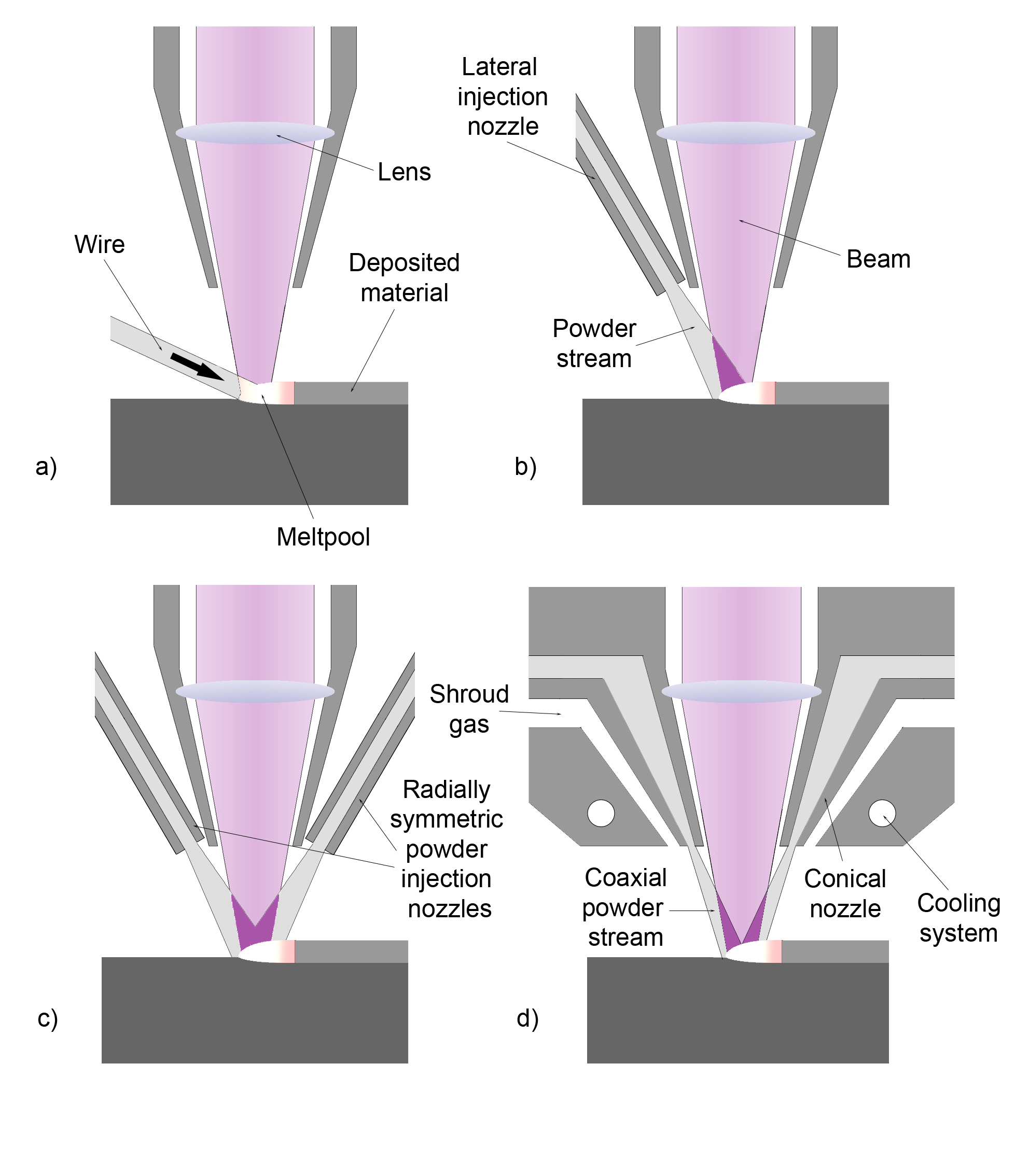
Laser Cladding System Setup
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Affected Zone
In fusion welding, the heat-affected zone (HAZ) is the area of base material, either a metal or a thermoplastic, which is not melted but has had its microstructure and properties altered by welding or heat intensive cutting operations. The heat from the welding process and subsequent re-cooling causes this change from the weld interface to the termination of the sensitizing temperature in the base metal. The extent and magnitude of property change depends primarily on the base material, the weld filler metal, and the amount and concentration of heat input by the welding process. The thermal diffusivity of the base material plays a large role—if the diffusivity is high, the material cooling rate is high and the HAZ is relatively small. Alternatively, a low diffusivity leads to slower cooling and a larger HAZ. The amount of heat input during the welding process also plays an important role as well, as processes like oxyfuel welding use high heat input and increase the size o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Welding Processes
This is a list of welding processes, separated into their respective categories. The associated ''N reference numbers'' (second column) are specified in ISO 4063 (in the European Union published as ''EN ISO 4063''). Numbers in parentheses are obsolete and were removed from the current (1998) version of ISO 4063. The AWS reference codes of the American Welding Society are commonly used in North America."Welding Inspection Handbook", 3rd edition, American Welding Society, , Miami, FL, pp. 10-11 (2000) Arc welding Oxyfuel gas welding Resistance welding Solid-state welding Other types of welding Notes and references *Cary, Howard B. and Scott C. Helzer (2005). Modern Welding Technology. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education. . *Lincoln Electric (1994). The Procedure Handbook of Arc Welding. Cleveland: Lincoln Electric. . See also * Welding * List of welding codes This page lists published welding codes, procedures, and specifications. American Society of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Net Shape
Near-net-shape is an industrial manufacturing technique. As the name implies, the initial production of the item is very close to the final, or ''net'', shape. This reduces the need for surface finishing. By minimizing the use of finishing methods like machining or grinding, near-net-shape production eliminates more than two-thirds of the production costs in some industries. Processes The following are various near-net-shape processes categorized by material. Ceramics * Gelcasting * Ceramic injection molding * Spray forming *Structural ceramic production Composites *Lanxide process Plastics *Injection moulding *Rapid prototyping Metals *Casting ** Permanent mold casting *Powder metallurgy *Linear friction welding *Friction welding *Metal injection molding *Rapid prototyping * Spray forming *Superplastic forming *Cold forming *Semi-solid metal casting Semi-solid metal casting (SSM) is a near net shape variant of die casting. The process is used today with non-ferrous metals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functionally Graded Material
In materials science Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) may be characterized by the variation in composition and structure gradually over volume, resulting in corresponding changes in the properties of the material. The materials can be designed for specific function and applications. Various approaches based on the bulk (particulate processing), preform processing, layer processing and melt processing are used to fabricate the functionally graded materials. History The concept of FGM was first considered in Japan in 1984 during a space plane project, where a combination of materials used would serve the purpose of a thermal barrier capable of withstanding a surface temperature of 2000 K and a temperature gradient of 1000 K across a 10 mm section. In recent years this concept has become more popular in Europe, particularly in Germany. A transregional collaborative research center (SFB Transregio) is funded since 2006 in order to exploit the potential of grading monomateri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Cladding Nozzle Configurations
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common; CAM may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and storage. Its primary purpose is to create a faster production process and components and tooling with more precise dimensions and material consistency, which in some cases, uses only the required amount of raw material (thus minimizing waste), while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. CAM is now a system used in schools and lower educational purposes. CAM is a subsequent computer-aided process after computer-aided design (CAD) and sometimes computer-aided engineering (CAE), as the model generated in CAD and verified in CAE can be input into CAM software, which then controls t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribological
Tribology is the science and engineering of interacting surfaces in relative motion. It includes the study and application of the principles of friction, lubrication and wear. Tribology is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, materials science, mathematics, biology and engineering. People who work in the field of tribology are referred to as ''tribologists''. The fundamental objects of study in tribology are tribosystems, which are physical systems of contacting surfaces. In lubricated tribosystems, contact stress can create tribofilms. Subfields of tribology include biotribology, nanotribology, space tribology and tribotronics. Etymology The word ''tribology'' derives from the Greek root τριβ- of the verb , ''tribo'', "I rub" in classic Greek, and the suffix ''-logy'' from , ''-logia'' "study of", "knowledge of". Peter Jost coined the word in 1966, in the eponymous report which highlighted the cost of friction, wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
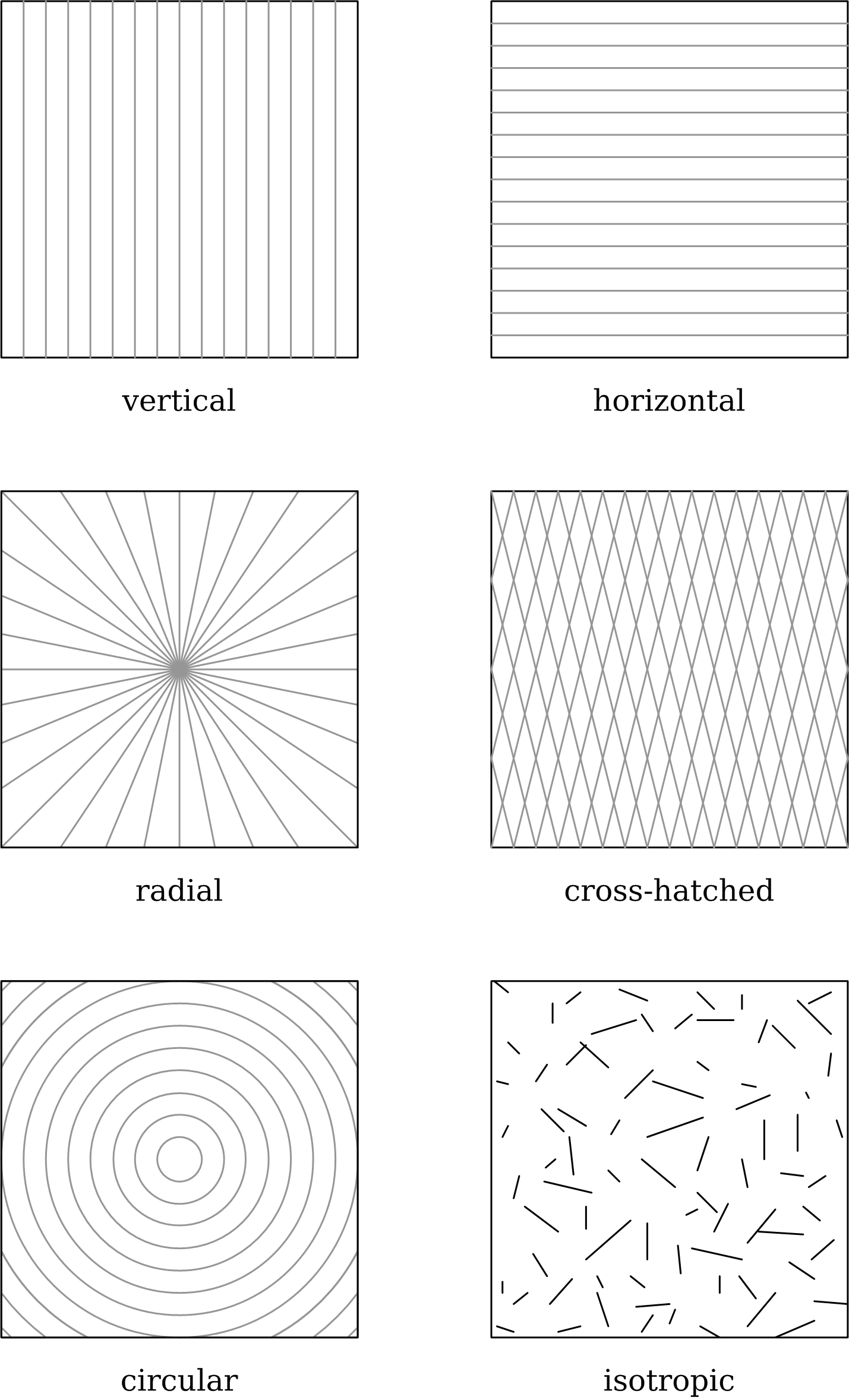
Surface Topography
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness.. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the perfectly flat ideal (a true plane). Surface texture is one of the important factors that control friction and transfer layer formation during sliding. Considerable efforts have been made to study the influence of surface texture on friction and wear during sliding conditions. Surface textures can be isotropic or anisotropic. Sometimes, stick-slip friction phenomena can be observed during sliding, depending on surface texture. Each manufacturing process (such as the many kinds of machining) produces a surface texture. The process is usually optimized to ensure that the resulting texture is usable. If necessary, an additional process will be added to modify the initial texture. The latter process may be grinding (abrasive cutting), polishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology. Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubricated systems are designed so that the applied load is partially or completely carried by hydrodynamic or hydrostatic pressure, which reduces solid body interactions (and consequently friction and wear). Depending on the degree of surface separation, different lubrication regimes can be distinguished. Adequate lubrication allows smooth, continuous operation of machine elements, reduces the rate of wear, and prevents excessive stresses or seizures at bearings. When lubrication breaks down, components can rub destructively against each other, causing heat, local welding, destructive damage and failure. Lubrication mechanisms Fluid-lubricated systems As the load increases on the contacting surfaces, distinct situations can be observed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Matrix Composite
In materials science, a metal matrix composite (MMC) is a composite material with fibers or particles dispersed in a metallic matrix, such as copper, aluminum, or steel. The secondary phase is typically a ceramic (such as alumina or silicon carbide) or another metal (such as steel). They are typically classified according to the type of reinforcement: short discontinuous fibers (whiskers), continuous fibers, or particulates. There is some overlap between MMCs and cermets, with the latter typically consisting of less than 20% metal by volume. When at least three materials are present, it is called a hybrid composite. MMCs can have much higher strength-to-weight ratios, stiffness, and ductility than traditional materials, so they are often used in demanding applications. MMCs typically have lower thermal and electrical conductivity and poor resistance to radiation, limiting their use in the very harshest environments. Composition MMCs are made by dispersing a reinforcing material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |