|
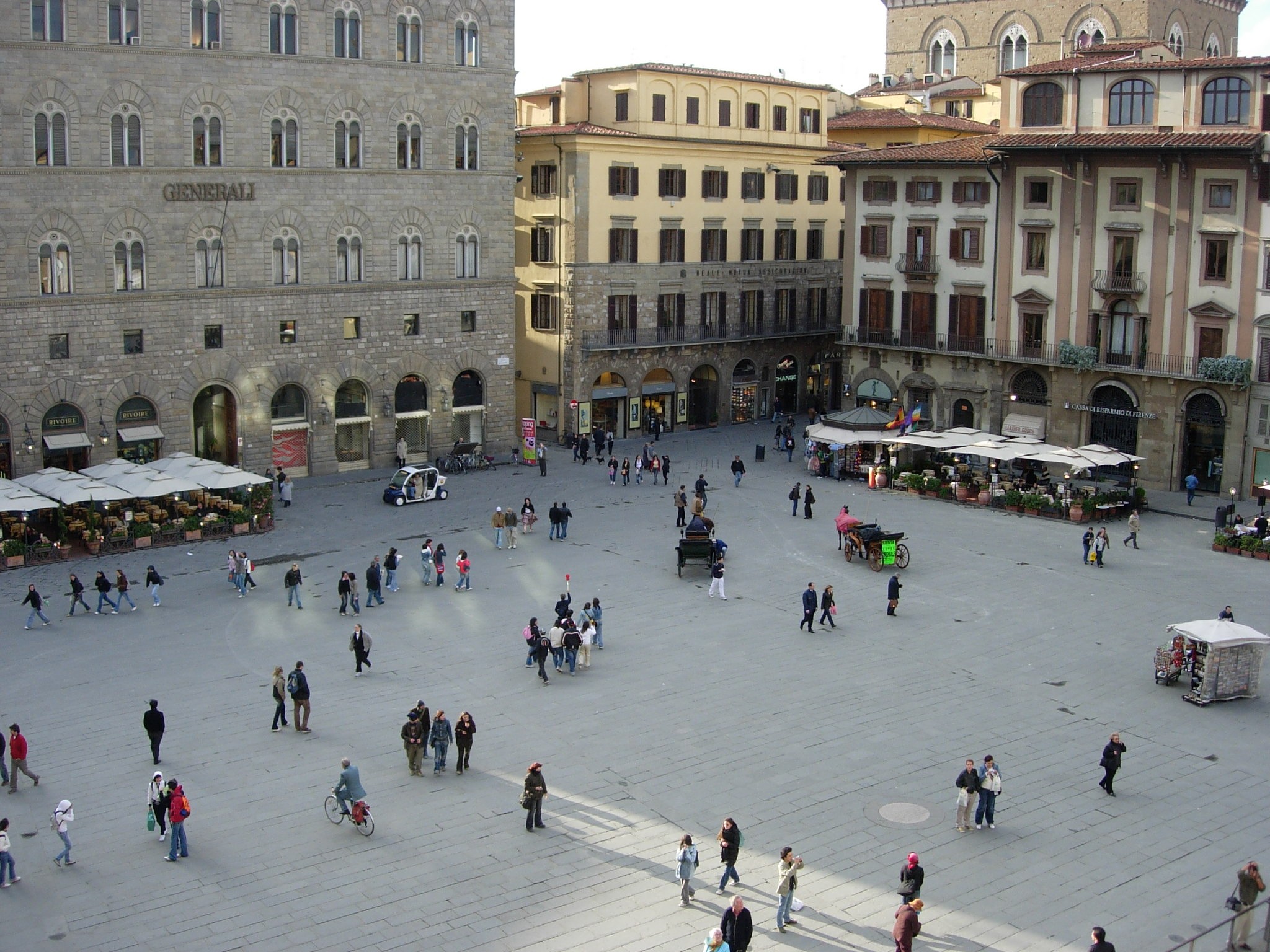
Civil Inattention
Civil inattention is the process whereby strangers who are in close proximity demonstrate that they are aware of one another, without imposing on each other – a recognition of the claims of others to a public space, and of their own personal boundaries. In practice Civil inattention is the term introduced by Erving Goffman to describe the care taken to maintain public order among strangers and thus to make anonymised life in cities possible. Rather than either ignoring or staring at others, civil inattention involves the unobtrusive and peaceful scanning of others so as to allow for neutral interaction. Through brief eye contact with an approaching stranger, a person both acknowledges their presence and forecloses the possibility of more personal contact or of conversation. Civil inattention is thus a means of making privacy possible within a crowd through culturally accepted forms of self-distancing. Seemingly (though not in reality) effortless, such civility is a way of shiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Boundaries
Personal boundaries or the act of'' setting boundaries'' is a life skill that has been popularized by self help authors and support groups since the mid 1980s. It is the practice of openly communicating and asserting personal values as way to preserve and protect against having them compromised or violated. The term "boundary" is a metaphor – with ''in-bounds'' meaning acceptable and ''out-of-bounds'' meaning unacceptable. Without values and boundaries our identities become diffused and often controlled by the definitions offered by others. The concept of ''boundaries'' has been widely adopted by the counseling profession.G. B. and J. S. Lundberg, ''I Don't Have to Make Everything All Better'' (2000) p. 13. ISBN 978-0-670-88485-8 Usage and application This life skill is particularly applicable in environments with controlling people or people not taking responsibility for their own life. Co-Dependents Anonymous recommends setting limits on what members will do to and for p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face (sociological Concept)
Face is a class of behaviors and customs practiced mainly in Asian cultures, associated with the morality, honor, and authority of an individual (or group of individuals), and its image in social groups. Face refers to a sociological concept in general linked to the dignity and prestige that a person has in terms of their social relationships. This idea with different nuances is observed in many societies and cultures such as Chinese, Arabic, Indonesian, Korean, Malaysian, Laotian, Indian, Japanese, Vietnamese, Filipino, Thai, Russian and other Slavic cultures. Face has more meanings within the context of Chinese culture. Definitions Although Chinese writer Lin Yutang claimed "face cannot be translated or defined", these definitions have been created: * Face is an image of self delineated in terms of approved social attributes. * Face is the respectability and/or deference which a person can claim for themself or from others. * Face is a quality that can be lost, maintain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Presentation Of Self In Everyday Life
''The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life'' is a 1956 sociological book by Erving Goffman, in which the author uses the imagery of theatre in order to portray the importance of human social interaction; this approach would become known as Goffman's dramaturgical analysis. Originally published in Scotland in 1956 and in the United States in 1959, it is Goffman’s first and most famous book, for which he received the American Sociological Association's MacIver award in 1961. In 1998, the International Sociological Association listed the work as the tenth most important sociological book of the 20th century. Background and summary ''The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life'' was the first book to treat face-to-face interaction as a subject of sociological study. Goffman treats it as a kind of report in which he frames out the theatrical performance that applies to these interactions. He believes that when an individual comes in contact with other people, that individual will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polity (publisher)
Polity is an academic publisher in the social sciences and humanities. It was established in 1984 and has offices in Cambridge (UK), Oxford (UK), New York (US) and Boston (US). It specializes in the areas of sociology, media, politics, and social theory Social theories are analytical frameworks, or paradigms, that are used to study and interpret social phenomena.Seidman, S., 2016. Contested knowledge: Social theory today. John Wiley & Sons. A tool used by social scientists, social theories rel .... Polity is committed to publishing textbooks and course books for students and scholars. Its list features some leading thinkers (Jürgen Habermas, Walter Benjamin, Ulrich Beck, Peter Sloterdijk and Anthony Giddens). References External links * Academic publishing companies Book publishing companies of the United Kingdom Publishing companies established in 1984 {{UK-publish-company-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
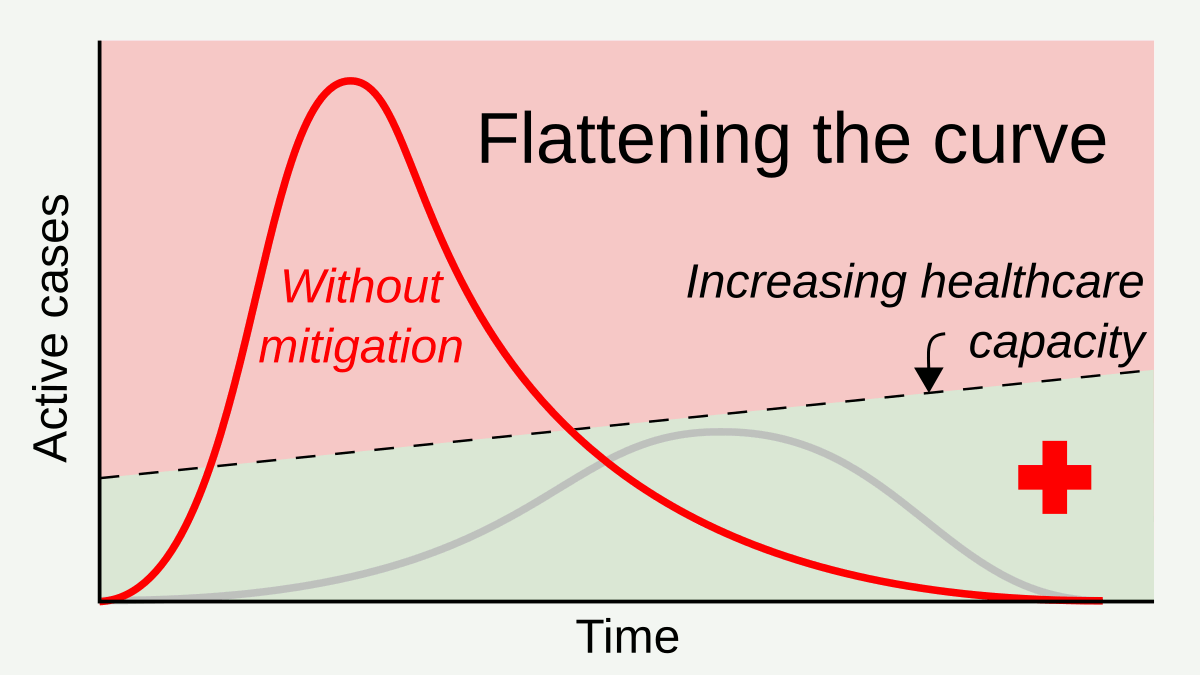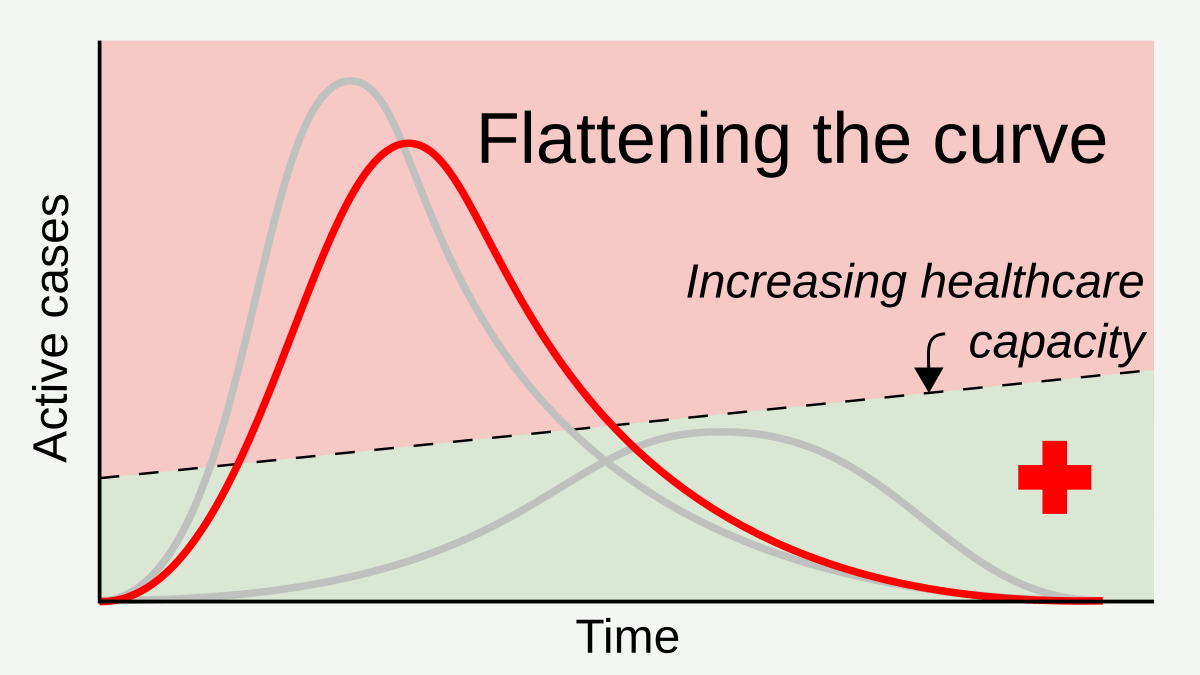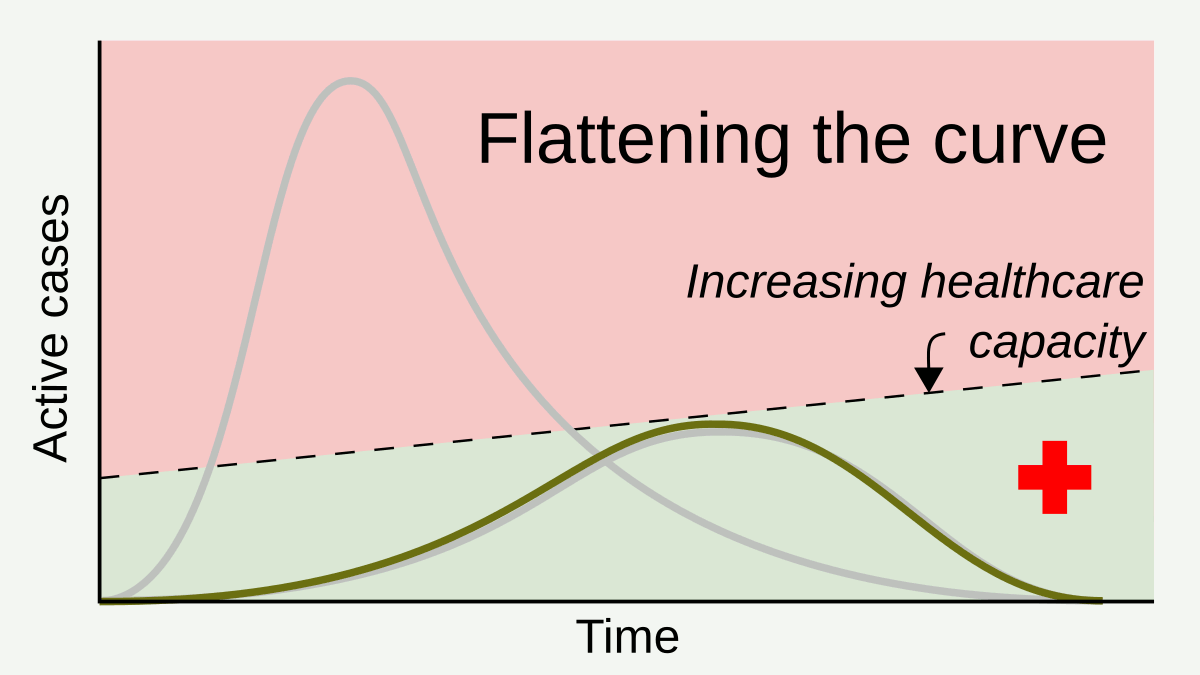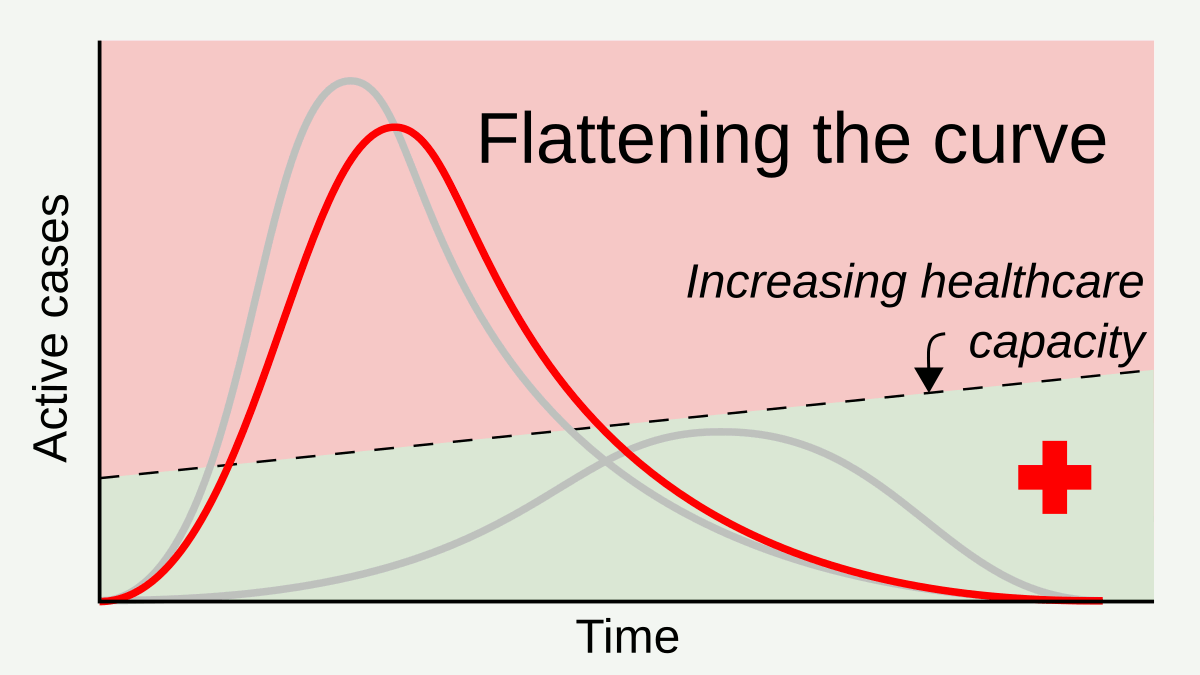
Social Distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious disease by maintaining a physical distance between people and reducing the number of times people come into close contact with each other. It usually involves keeping a certain distance from others (the distance specified differs from country to country and can change with time) and avoiding gathering together in large groups. By minimising the probability that a given uninfected person will come into physical contact with an infected person, the disease transmission can be suppressed, resulting in fewer deaths. The measures may be used in combination with others, such as good respiratory hygiene, face masks and hand washing. To slow down the spread of infectious diseases and avoid overburdening healthcare systems, particularly during a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Capital
Social capital is "the networks of relationships among people who live and work in a particular society, enabling that society to function effectively". It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships, a shared sense of identity, a shared understanding, shared norms, shared values, trust, cooperation, and reciprocity. Social capital is a measure of the value of resources, both tangible (e.g., public spaces, private property) and intangible (e.g., actors, human capital, people), and the impact that ideal creators have on the resources involved in each relationship, and on larger groups. Some have described it as a form of capital that produces public goods for a common purpose, although this does not align with how it has been measured. Social capital has been used to explain the improved performance of diverse groups, the growth of entrepreneurial firms, superior managerial performance, enhanced supply chain relations, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Space
A public space is a place that is open and accessible to the general public. Roads (including the pavement), public squares, parks, and beaches are typically considered public space. To a limited extent, government buildings which are open to the public, such as public libraries, are public spaces, although they tend to have restricted areas and greater limits upon use. Although not considered public space, privately owned buildings or property visible from sidewalks and public thoroughfares may affect the public visual landscape, for example, by outdoor advertising. Recently, the concept of shared space has been advanced to enhance the experience of pedestrians in public space jointly used by automobiles and other vehicles. Public space has also become something of a touchstone for critical theory in relation to philosophy, urban geography, visual art, cultural studies, social studies and urban design. The term 'public space' is also often misconstrued to mean other things ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proxemics
Proxemics is the study of human use of space and the effects that population density has on behaviour, communication, and social interaction. Proxemics is one among several subcategories in the study of nonverbal communication, including haptics (touch), kinesics (body movement), vocalics (paralanguage), and chronemics (structure of time). Edward T. Hall, the cultural anthropologist who coined the term in 1963, defined proxemics as "the interrelated observations and theories of humans use of space as a specialized elaboration of culture". In his foundational work on proxemics, ''The Hidden Dimension,'' Hall emphasized the impact of proxemic behavior (the use of space) on interpersonal communication. According to Hall, the study of proxemics is valuable in evaluating not only the way people interact with others in daily life, but also "the organization of space in heirhouses and buildings, and ultimately the layout of heirtowns". Proxemics remains a hidden component of interper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persona (psychology)
The persona, for Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, was the social face the individual presented to the world—"a kind of mask, designed on the one hand to make a definite impression upon others, and on the other to conceal the true nature of the individual." Jung's persona Identification According to Jung, the development of a viable social persona is a vital part of adapting to, and preparing for, adult life in the external social world. "A strong ego relates to the outside world through a flexible persona; identifications with a specific persona (doctor, scholar, artist, etc.) inhibits psychological development." For Jung, "the danger is that eoplebecome identical with their personas—the professor with his textbook, the tenor with his voice." The result could be "the shallow, brittle, conformist kind of personality which is 'all persona', with its excessive concern for 'what people think'"—an unreflecting state of mind "in which people are utterly unconscious of any distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideas Of Reference
Ideas of reference and delusions of reference describe the phenomenon of an individual experiencing innocuous events or mere coincidences and believing they have strong personal significance. It is "the notion that everything one perceives in the world relates to one's own destiny", usually in a negative and hostile manner. In psychiatry, delusions of reference form part of the diagnostic criteria for psychotic illnesses such as schizophrenia, delusional disorder, bipolar disorder (during the elevated stages of mania), narcissistic personality disorder, and schizotypal personality disorder, and even autism when under periods of intense stress. To a lesser extent, it can be a hallmark of paranoid personality disorder as well as body dysmorphic disorder. Such symptoms can also be caused by intoxication, such as from stimulants like methamphetamine. Psychoanalytic views In Sigmund Freud's view, "Delusions of being watched present this power in a regressive form, thus rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention (norm)
A convention is a set of agreed, stipulated, or generally accepted standards, norms, social norms, or criteria, often taking the form of a custom. In a social context, a convention may retain the character of an "unwritten law" of custom (for example, the manner in which people greet each other, such as by shaking each other's hands). Certain types of rules or customs may become law and sometimes they may be further codified to formalize or enforce the convention (for example, laws that define on which side of the road vehicles must be driven). In physical sciences, numerical values (such as constants, quantities, or scales of measurement) are called conventional if they do not represent a measured property of nature, but originate in a convention, for example an average of many measurements, agreed between the scientists working with these values. General A convention is a selection from among two or more alternatives, where the rule or alternative is agreed upon among parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |