|
Château De Brest
The Château de Brest ( br, Kastell Brest) is a castle in Brest, Finistère, France. The oldest monument in the town, it is located at the mouth of the river Penfeld at the heart of the roadstead of Brest, one of the largest roadsteads in the world. From the Roman castellum to Vauban's citadel, the site has over 1700 years of history, holding right up to the present day its original role as a military fortress and a strategic location of the highest importance. It is thus the oldest castle in the world still in use, and was classified as a monument historique on 21 March 1923. The structure's heterogeneous architecture has been the result of continual adaptations to developments in siege warfare and armament on land and sea. The château stands on the opposite bank to the Tour Tanguy combining to defend the entrance to the Penfeld. An ideal geographic location The Roadstead of Brest, well-protected by a narrow "goulet" but sufficiently large to allow ships to turn or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landerneau
Landerneau (; br, Landerne, ) is a commune in the Finistère department of Brittany in north-western France. It lies at the mouth of the Elorn River which divides the Breton provinces of Cornouaille and Léon, east of Brest. The name is from Lan Terneo and can mean "(religious) enclosure of St Ténénan ()": allegedly a Welshman who also had in the Vale of Clwyd in North Wales and in Somerset, and who moved to Brittany in the 7th century. Lann means a religious sacred place. The town has been founded by Saint Arnoc, some times called Ternoc and confusion can occur with Saint Ténénan. Some sources point Saint Arnoc and Saint Ténénan as the same person. It was an important centre of the flax and linen industries in the 16th and 17th centuries. Landerneau is also the hometown of Édouard Leclerc, a businessman and entrepreneur who founded the French supermarket chain E.Leclerc in 1948. His first store applies a hard competition with other supermarket chains with local ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorica
Armorica or Aremorica (Gaulish: ; br, Arvorig, ) is the name given in ancient times to the part of Gaul between the Seine and the Loire that includes the Brittany Peninsula, extending inland to an indeterminate point and down the Atlantic Coast. Name The name ''Armorica'' is a Latinized form of the Gaulish toponym , which literally means 'place in front of the sea'. It is formed with the prefix ''are''- ('in front of') attached to -''mori''- ('sea') and the feminine suffix ''-(i)cā'', denoting the localization (or provenance). The inhabitants of the region were called ''Aremorici'' (sing. ''Aremoricos''), formed with the stem ''are-mori''- extended by the determinative suffix -''cos''. It is glossed by the Latin ''antemarini'' in Endlicher's Glossary. The Slavs use a similar formation, ''Po-mor-jane'' ('those in front of the sea'), to designate the inhabitants of Pomerania. The Latin adjective ''Armoricani'' was an administrative term designating in particular a sector of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus seized power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors. After deposing and killing the incumbent emperor Didius Julianus, Severus fought his rival claimants, the Roman generals Pescennius Niger and Clodius Albinus. Niger was defeated in 194 at the Battle of Issus in Cilicia. Later that year Severus waged a short punitive campaign beyond the eastern frontier, annexing the Kingdom of Osroene as a new province. Severus defeated Albinus three years later at the Battle of Lugdunum in Gaul. Following the consolidation of his rule over the western provinces, Severus waged another brief, more successful war in the east agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AV Antoninianus Posthumus
Av (also Menachem Av, ; from Akkadian ''ʾAbū'' "father") is the eleventh month of the civil year and the fifth month of the ecclesiastical year on the Hebrew calendar. The name comes from Araḫ Abu, "month of Abu", from the Babylonian calendar. The name ''Ab'' ( ar, آﺏ) also appears in the Arabic language for the month of August in the Levant (see Arabic names of calendar months).The name first appears in Second Temple literature, such as Megillat Taanit. It is one of several months which are not explicitly named in the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh). It is a month of 30 days. ''Av'' usually occurs in July–August on the Gregorian calendar. The Babylonian Talmud, Taanit 29a, states that "when we enter he month of''Av'', our joy is diminished". This is because the darkest events in Jewish history occurred during the first week and a half of this month, particularly the Nine Days which culminate in ''Tisha B'Av'', the 9th of ''Av''. However, there is a minor and largely unknown ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carhaix
Carhaix-Plouguer (; br, Karaez-Plougêr ), commonly known as just Carhaix (), is a commune in the French department of Finistère, region of Brittany, France.Commune de Carhaix-Plouguer (29024) INSEE The commune was created in 1957 by the merger of the former communes Carhaix and Plouguer. Geography 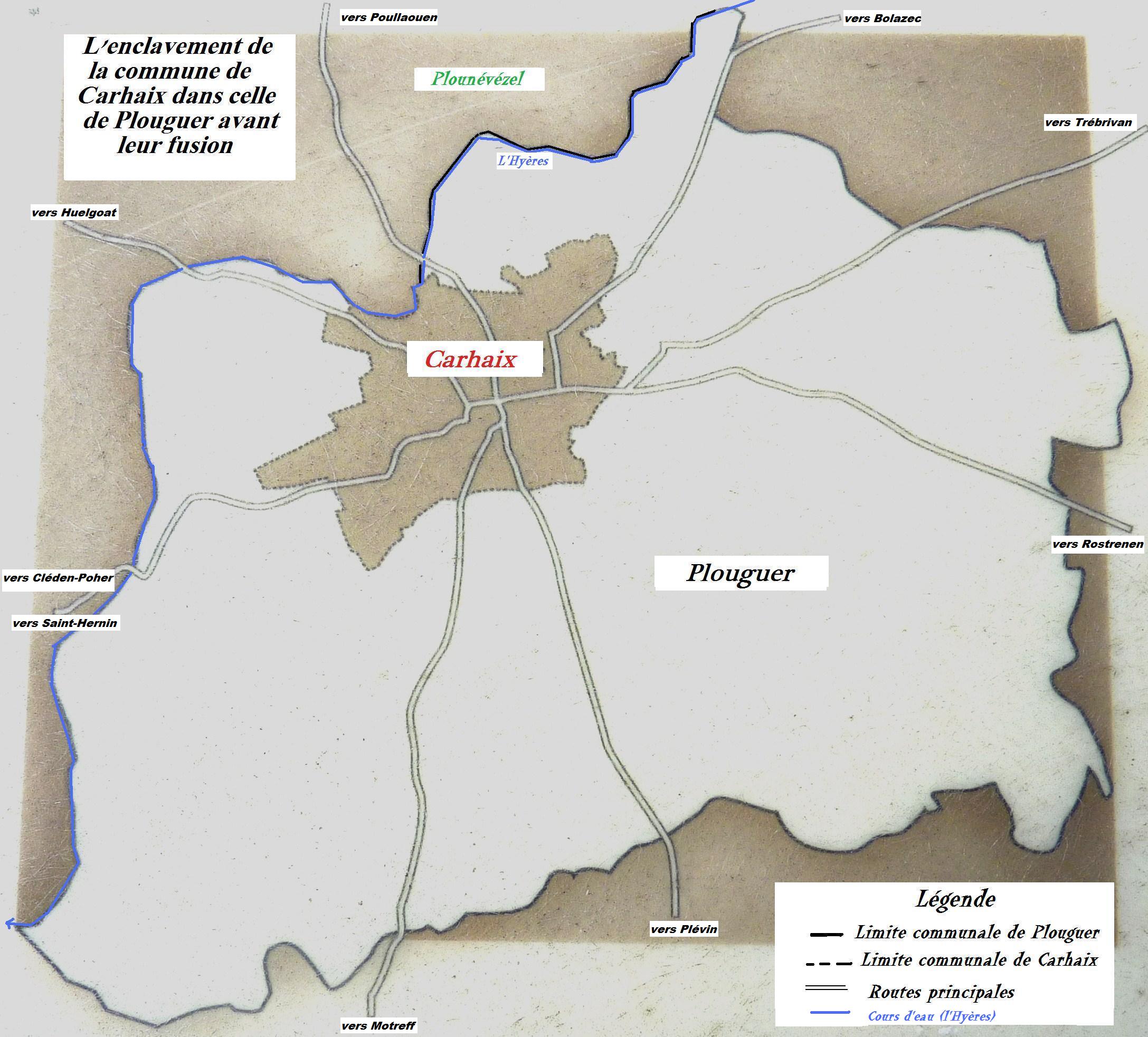 Carhaix is located in the Poher, an important territory of Brittany, sandwiched between the Arrée Mountains to ...
Carhaix is located in the Poher, an important territory of Brittany, sandwiched between the Arrée Mountains to ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veneti (Gaul)
The Venetī (, Gaulish: ''Uenetoi'') were a Gallic tribe dwelling in Armorica, in the northern part of the Brittany Peninsula, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. A seafaring people, the Veneti strongly influenced southwestern Brittonic culture through trading relations with Great Britain. After they were defeated by Junius Brutus Albinus in a naval battle in 56 BC, their maritime commerce eventually declined under the Roman Empire, but a prosperous agricultural life is indicated by archaeological evidence. Name They are mentioned as ''Venetos'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), Livy (late 1st c. BC) and Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Ouénetoi'' (Οὐένετοι) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD) and Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), ''Veneti'' on the ''Tabula Peutingeriana'' (5th c. AD), and as ''Benetis'' in the ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (5th c. AD). The ethnonym ''Venetī'' is a latinized form of Gaulish ''Uenetoi'', meaning 'the kinsmen' or 'the friendly ones', possibly also 'the merchants'. It d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osismii
The Osismii, Ossismii, or Ostimii (also Ossismi, Osismi) were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the western part of the Armorican Peninsula (modern Brittany) during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Etymology They are mentioned as ''Osismos'' and ''Osismi'' (var. ''ossismi'') by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''O̓sísmioi'' (Ὀσίσμιοι) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Ossismos'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''O̓sismíous'' (Ὀσισμίους; var. Ὀσίσμιοι, Ὀσισμαίους) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), and as ''Osismis'' in the ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (5th c. AD)., s.v. ''Osismii''. According to Strabo, the Massaliote explorer Pytheas, who travelled to northwestern Europe in the late 4th century BC, reported the variant ''Ōstimíous'' (Ὠστιμίους), which seems to be the earliest attested form of the name, documented before the Gaulish sound shift -''st''- > -''ss''- occurred. The Gaulish ethnonym ''Ostim(i)i'' (sing. ''Ostim(i)os'') literally means 'the ultimate', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





