|
Chloroquine Resistance
Chloroquine is a medication primarily used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to its effects. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the summer of 2020, and is not recommended for this purpose. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and low blood cell levels. Chloroquine is a member of the drug class 4-aminoquinoline. As an antimalarial, it works against the asexual form of the malaria parasite in the stage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
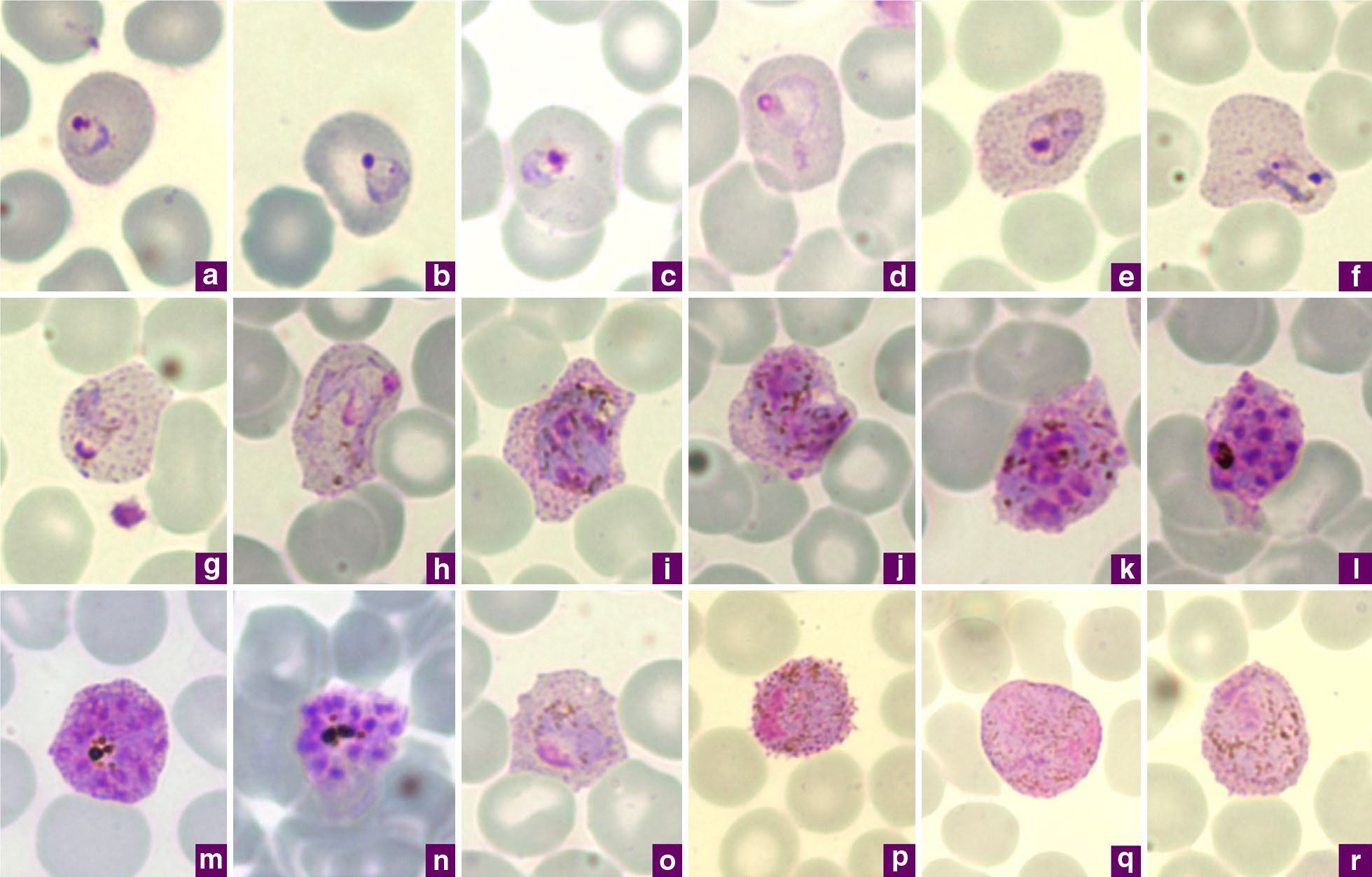
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female '' Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Disorder
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms can be diverse and transient, ranging from mild to severe, and generally include low grade fever and feeling tired. The cause is unknown. Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus run in families, and certain cases may be triggered by infections or other environmental factors. Some common diseases that are generally considered autoimmune include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, graves' disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, alopecia areata, addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis can be difficult to determine. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. Nonstero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitroimidazole
5-Nitroimidazole is an organic compound with the formula O2NC3H2N2H. The nitro group at position 5 on the imidazole ring is the most common positional isomer. The term nitroimidazole also refers to a class of antibiotics that share similar chemical structures. Synthesis Imidazole undergoes a nitration reaction with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to give 5-nitroimidazole: :C3H3N2H + HNO3 + H2SO4 → O2NC3H2N2H + H2O Nitroimidazole antibiotics From the chemistry perspective, nitroimidazole antibiotics can be classified according to the location of the nitro functional group. Structures with names 4- and 5-nitroimidazole are equivalent from the perspective of drugs since these tautomers readily interconvert. Drugs of the 5-nitro variety include metronidazole, tinidazole, nimorazole, dimetridazole, pretomanid, ornidazole, megazol, and azanidazole. Drugs based on 2-nitromidazoles include benznidazole. Nitroimidazole antibiotics have been used to combat anaerobic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It is effective for dracunculiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis, and amebiasis. It is an option for a first episode of mild-to-moderate ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis if vancomycin or fidaxomicin is unavailable. Metronidazole is available by mouth, as a cream, and by injection into a vein. Common side effects include nausea, a metallic taste, loss of appetite, and headaches. Occasionally seizures or allergies to the medication may occur. Some state that metronidazole should not be used in early pregnancy, while others state doses for trichomoniasis are safe. Metronidazole is generally considered compatible with breastfeeding. Metronidazole began to be commercially used in 1960 in France. It is on the World Health Organization's Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebic Liver Abscess
A amoebic liver abscess is a type of liver abscess caused by amebiasis. It is the involvement of liver tissue by trophozoites of the organism ''Entamoeba histolytica'' and of its abscess due to necrosis. Presentation Approximately 90% of patients with ''E histolytica'' are asymptomatic. The two most common manifestations of ''E histolytica'' include colitis (bloody stool with mucus, abdominal pain, and/or diarrhea), and discovery of a liver abscess on imaging. Liver abscess' commonly present as right upper quadrant abdominal pain and fever, with worsening features associated with abscess rupture. Symptoms * Pain right hypochondrium referred to the right shoulder * Pyrexia (100.4 F) * Profuse sweating and rigors * Loss of weight * Earthy complexion Signs * Pallor * Tenderness and rigidity in right hypochondrium * Palpable liver * Intercostal tenderness * Basal lung signs Diagnosis Diagnosis is primarily made by identifying stool ova and parasites on stool antigen testing in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It especially focuses its attention on infectious disease, food borne pathogens, environmental health, occupational safety and health, health promotion, injury prevention and educational activities designed to improve the health of United States citizens. The CDC also conducts research and provides information on non-infectious diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, and is a founding member of the International Association of National Public Health Institutes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atovaquone
Atovaquone, sold under the brand name Mepron, is an antimicrobial medication for the prevention and treatment of ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia (PCP). Atovaquone is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of naphthoquinones. Atovaquone is a hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, an analog of both ubiquinone and lawsone, with antipneumocystic activity. Medical uses Atovaquone is a medication used to treat or prevent: * For pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), it is used in mild cases, although it is not approved for treatment of severe cases. * For toxoplasmosis, the medication has antiparasitic and therapeutic effects. * For malaria, it is one of the two components (along with proguanil) in the drug Malarone. Malarone has fewer side effects and is more expensive than mefloquine. Resistance has been observed. * For babesia, it is often used in conjunction with oral azithromycin. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX, Bactrim) is generally considered first-line therapy for PCP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mefloquine
Mefloquine, sold under the brand name Lariam among others, is a medication used to prevent or treat malaria. When used for prevention it is typically started before potential exposure and continued for several weeks after potential exposure. It can be used to treat mild or moderate malaria but is not recommended for severe malaria. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, sleep disorders, and a rash. Serious side effects include potentially long-term mental health problems such as depression, hallucinations, and anxiety and neurological side effects such as poor balance, seizures, and ringing in the ears. It is therefore not recommended in people with a history of mental health problems or epilepsy. It appears to be safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Mefloquine was developed by the United States Army in the 1970s and came into use in the mid-1980s. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimalarial Drug
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease ("malaria burden") is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment (e.g., new combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Drug Administration
The administration of drugs to whole populations irrespective of disease status is referred to as mass drug administration (MDA). This article describes the administration of antimalarial drugs to whole populations an intervention which has been used as a malaria-control measure for more than 70 years. Recent proposals to eliminate or even to eradicate malaria have led to a renewed interest in mass drug administrations in areas with very high malaria endemicity. Drugs have been administered either directly as a full therapeutic course of treatment or indirectly through the fortification of salt. Mass drug administrations were generally unsuccessful in interrupting transmission but, in some cases, had a marked effect on parasite prevalence and on the incidence of clinical malaria. MDAs are likely to encourage the spread of drug-resistant parasites and so have only a limited role in malaria control. They may have a part to play in the management of epidemics and in the control of mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |